Original German WWII Luftwaffe Flight Branch Unit Marked Schirmmütze Visor Cap dated 1938 – Hangar Commander Original Items
$ 995,00 $ 248,75
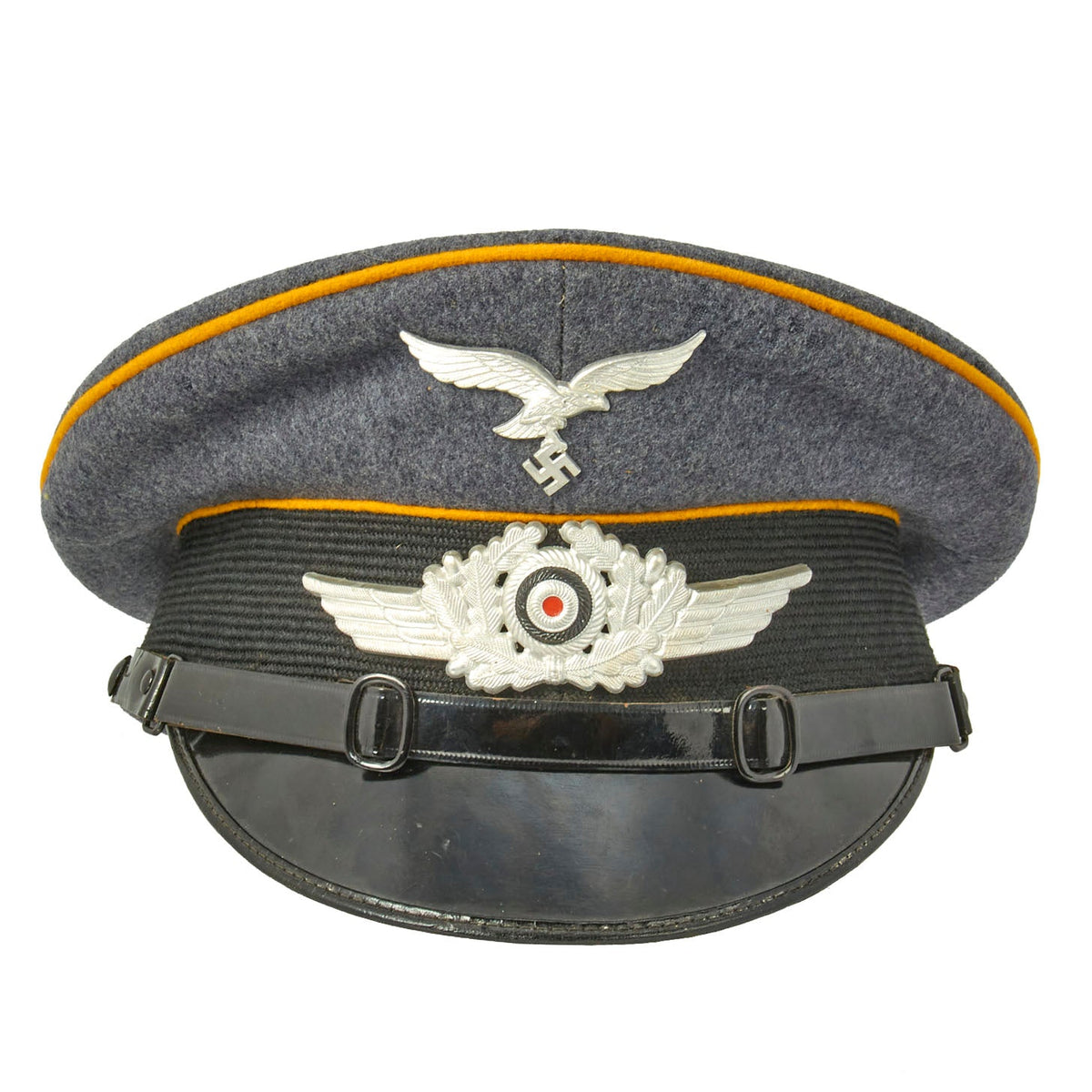
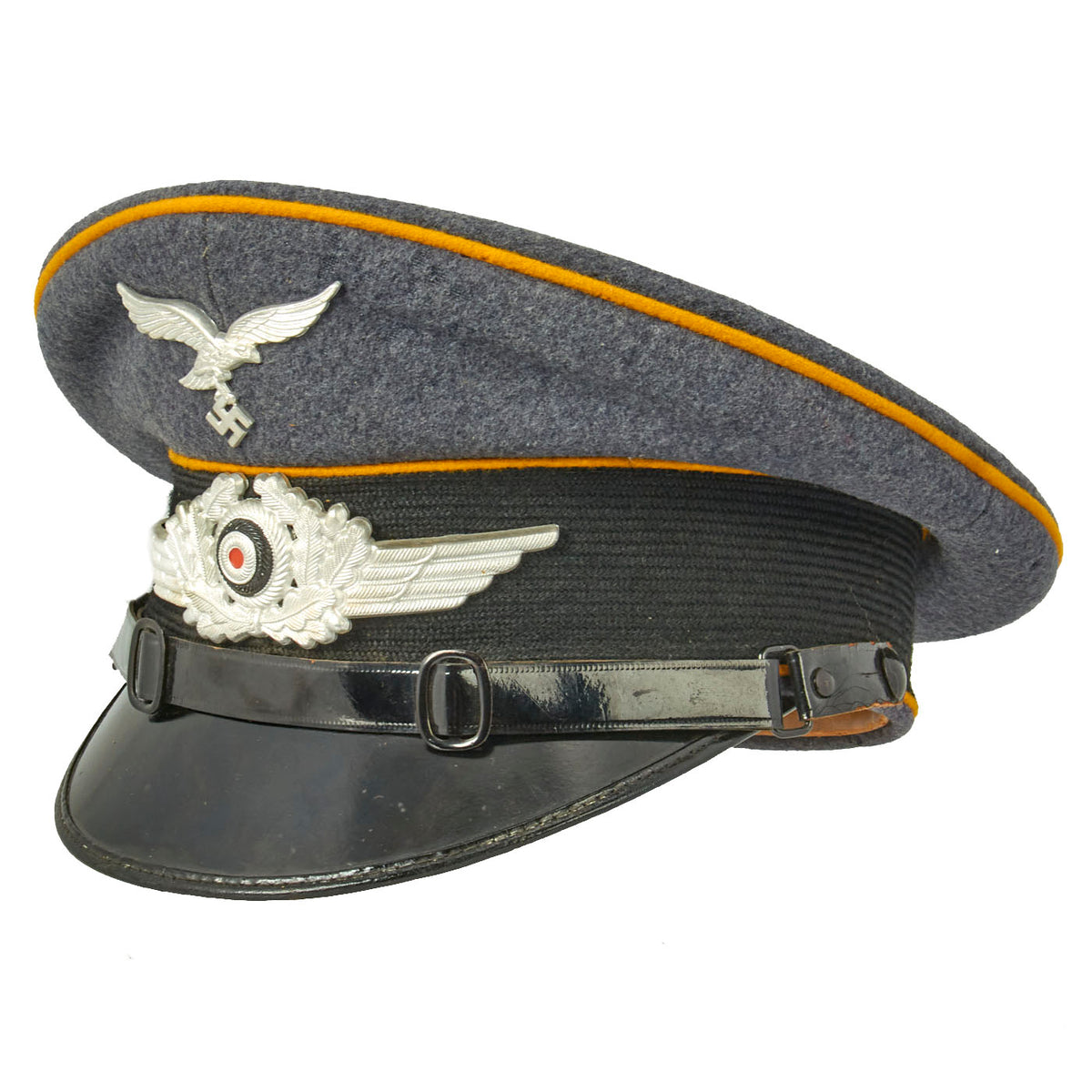
Original Item: One of a Kind. This is a fantastic condition Flight Branch Luftwaffe NCO Visor Cap. A wonderful honest example with a fantastic swept back shape. It has the saddle appearance, which we all love. Fabricated in Luftwaffe blue gray Fliegerblau (Flier’s Blue) wool, with a wide black ribbed rayon cap band and traditional high peak. There are three matching rows of goldgelb (Gold-Yellow) color piping flanking the band and on the crown, the Waffenfabe (Corps Color) for the Luftwafe flight branch. This included Aviator troops such as pilots and ground personnel as well as Fallschirmjäger (parachute troops).
This excellent wartime NCO Schirmmütze Visor Cap has a high quality manufactured visor. It also retains a perfect, high quality, aluminum pin Luftwaffe eagle with swas as well as centrally mounted aluminum oak leaves with cockade. Chinstrap and buttons are still present and in very good condition. The visor is a classic gloss pattern with very minor crazing.
The body with its lemon-yellow piping is in excellent shape. The size 57 liner has the champagne color rayon interior with the celluloid moisture shield. The tan sweatband is in excellent supple condition with minor tearing. Hat is maker marked CHRISTIAN HAUG and dated 1938. Inside the sweatband are ink stamped regimental markings. Fl. H. Kdt. Stdl. We believe the markings to be for a Hangar Commander, possibly for communications.
This is an excellent totally honest Luftwaffe NCO peaked visor cap offered with a beautiful saddle-form shape. Hard to find a better one!
Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe was the aerial-warfare branch of the German Wehrmacht before and during World War II. Germany’s military air arms during World War I, the Luftstreitkräfte of the Imperial Army and the Marine-Fliegerabteilung of the Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles which banned Germany from having any air force.
During the interwar period, the German armed forces secretly trained pilots – in violation of the Treaty – at Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the NSDAP (in power from 1933) and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the Luftwaffe’s existence was publicly acknowledged on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through the announcement of German rearmament and conscription on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a Luftwaffe detachment sent to aid Nationalist forces in the Spanish Civil War, provided the force with a valuable testing-ground for new tactics and aircraft. Partially as a result of this combat experience, the Luftwaffe had become one of the most sophisticated, technologically advanced, and battle-experienced air forces in the world when World War II broke out in 1939. By the summer of 1939, the Luftwaffe had twenty-eight Geschwader (wings). The Luftwaffe also operated Fallschirmjäger paratrooper units.
The Luftwaffe proved instrumental in the German victories across Poland and Western Europe in 1939 and 1940. During the Battle of Britain, however, despite inflicting severe damage to the RAF’s infrastructure and, during the subsequent Blitz, devastating many British cities, the German air force failed to batter the beleaguered British into submission. From 1942, Allied bombing campaigns gradually destroyed the Luftwaffe’s fighter arm. From late 1942, the Luftwaffe used its surplus ground support and other personnel to raise Luftwaffe Field Divisions. In addition to its service in the West, the Luftwaffe operated over the Soviet Union, North Africa and Southern Europe. Despite its belated use of advanced turbojet and rocket-propelled aircraft for the destruction of Allied bombers, the Luftwaffe was overwhelmed by the Allies’ superior numbers and improved tactics, and a lack of trained pilots and aviation fuel. In January 1945, during the closing stages of the Battle of the Bulge, the Luftwaffe made a last-ditch effort to win air superiority, and met with failure. With rapidly dwindling supplies of petroleum, oil, and lubricants after this campaign, and as part of the entire combined Wehrmacht military forces as a whole, the Luftwaffe ceased to be an effective fighting force.
After the defeat of Germany, the Luftwaffe was disbanded in 1946. During World War II, German pilots claimed roughly 70,000 aerial victories, while over 75,000 Luftwaffe aircraft were destroyed or significantly damaged. Of these, nearly 40,000 were lost entirely. The Luftwaffe had only two commanders-in-chief throughout its history: Hermann Göring and later Generalfeldmarschall Robert Ritter von Greim for the last two weeks of the war.
The German Schirmmütze Visor Cap:
The visor cap (Schirmmütze) was an important part of the headgear worn by German uniformed military, civil, paramilitary and political organizations during the Third Reich. This was the standard cloth headgear worn as a part of the service uniform. Visor caps were worn outdoors as well as indoors, and were often required to be worn by all personnel on duty. Visor caps were made in versions specific to each organization and were often further differentiated through the use of insignia, colored piping, or style of chin cord, to indicate rank, role or branch. The insignia used on these caps ranged from simple stamped metal emblems, to elaborate hand embroidery.
Visor caps were issued to enlisted soldiers and NCOs in the military and in some other organizations. Officers had to purchase their own hats, and lower ranks could choose to purchase caps that were of a higher quality than the rather basic, issued examples. The private purchase caps were generally made in very high quality, with fine materials. A wide variety of fabrics were used, from Trikot and doeskin, to heavy wool, or even lightweight white fabric for summer wear. In the military, issue of these caps was generally suspended shortly after the outbreak of the war, but they continued to be worn by some troops until the end of the war.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Band of Brothers ORIGINAL GERMAN WWII Le. F.H. 18 10.5cm ARTILLERY PIECE Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Armoured Fighting Vehicles of the World: AFVs of World War One (Hardcover Book) New Made Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Australian WWII Owen MK1 Machine Carbine SMG Custom Fabricated Replica with Sling Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized