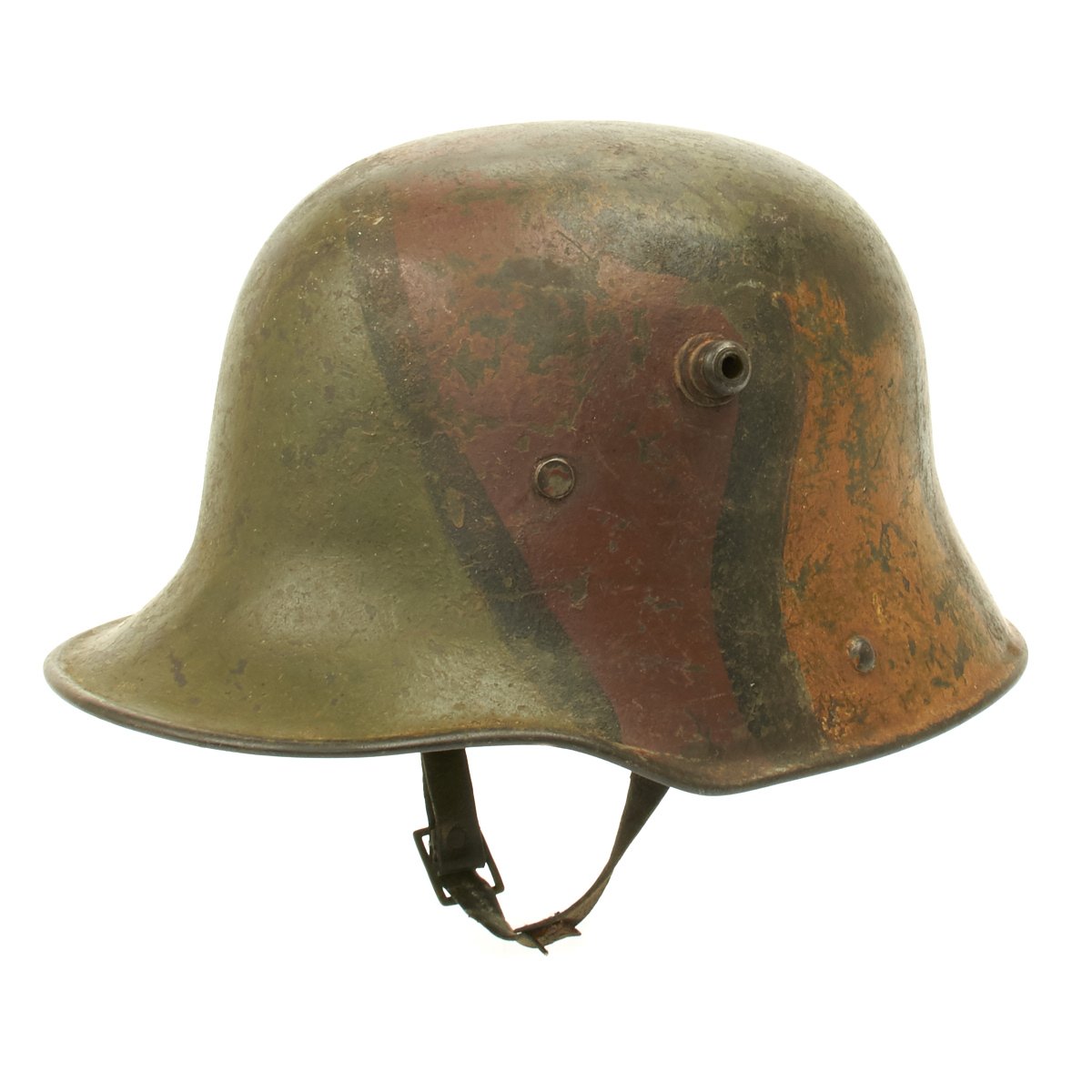
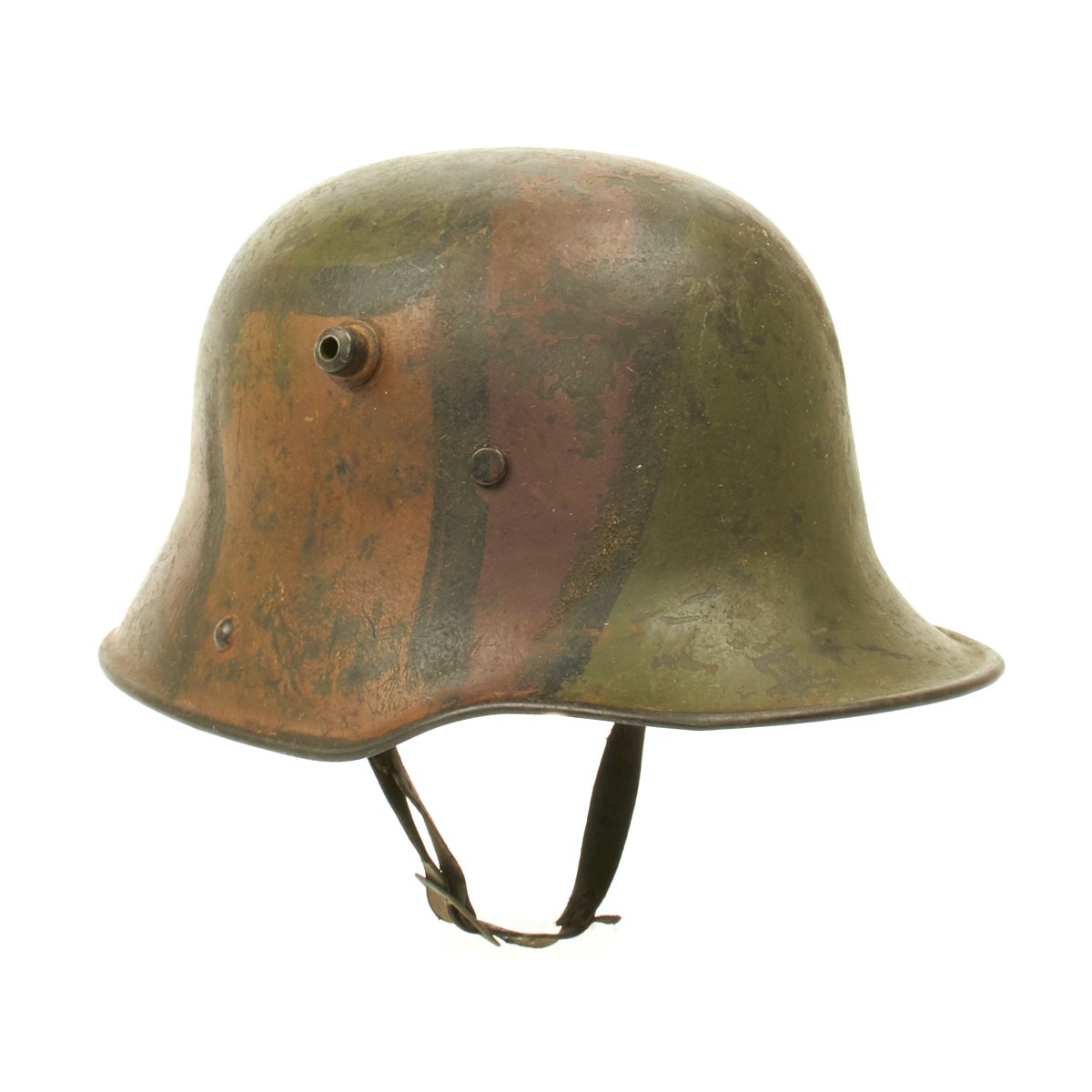
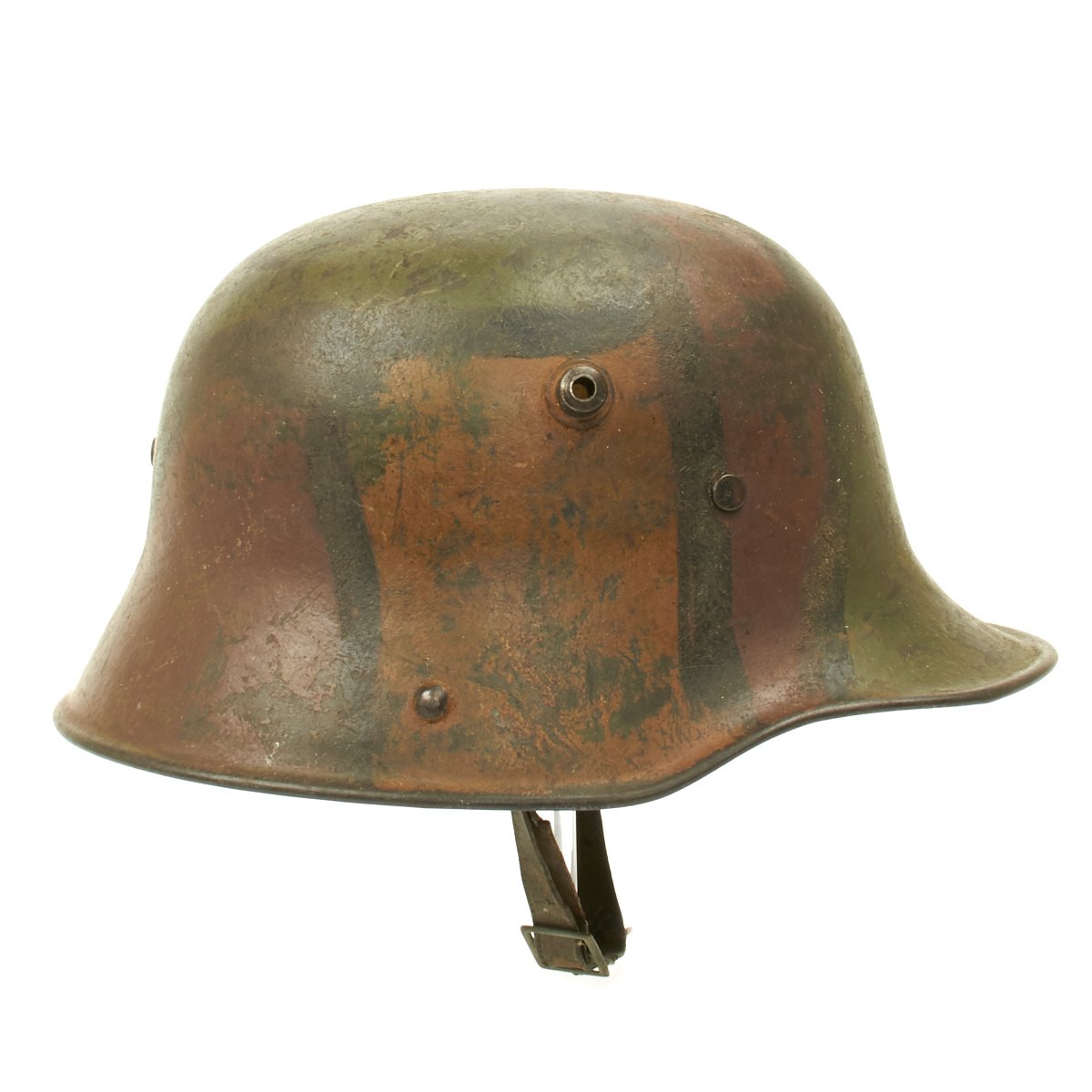
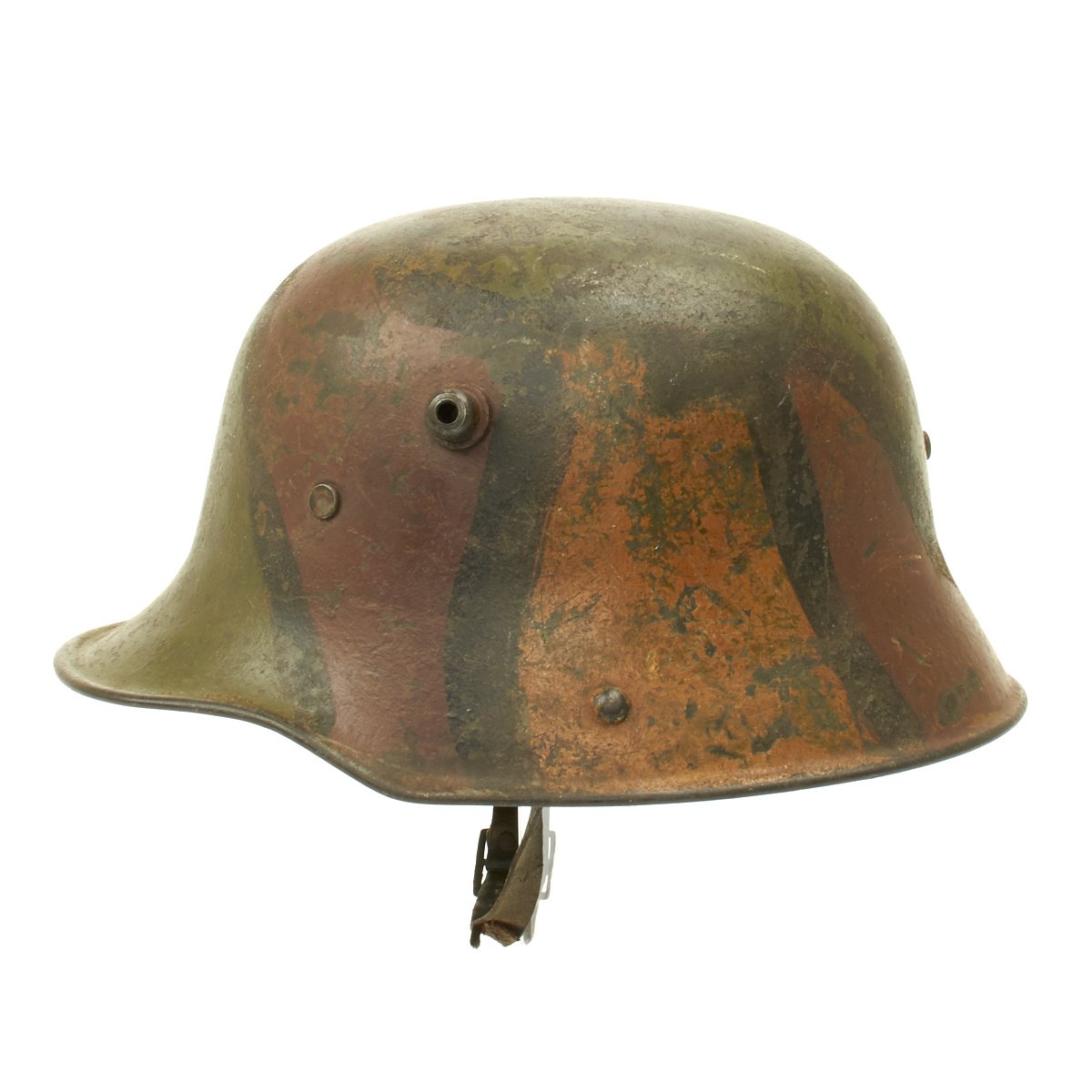
Original German WWI M17 Stahlhelm Helmet with Original Camouflage Paint and Liner with Chinstrap Original Items
$ 995,00 $ 248,75
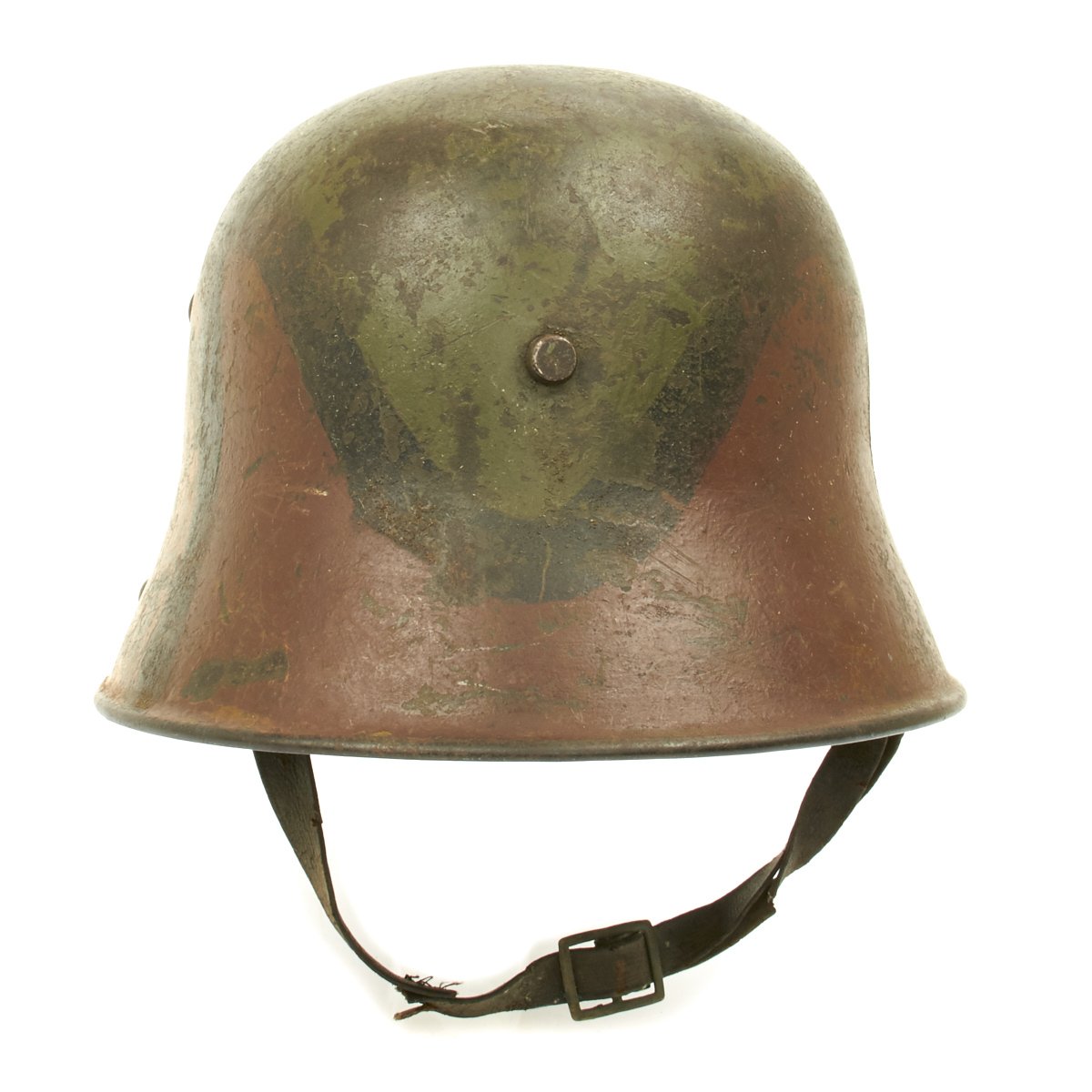
Original Item: Only One Available. This is an amazing example of a totally original WWI German M17 Helmet. The stamped, sheet steel construction, helmet retains about 80% of its original hand painted camouflage paint. The helmet has both the dome headed chinstrap retaining rivets, both of the extended ventilation side lugs and all three of the flat-headed liner retaining rivets.
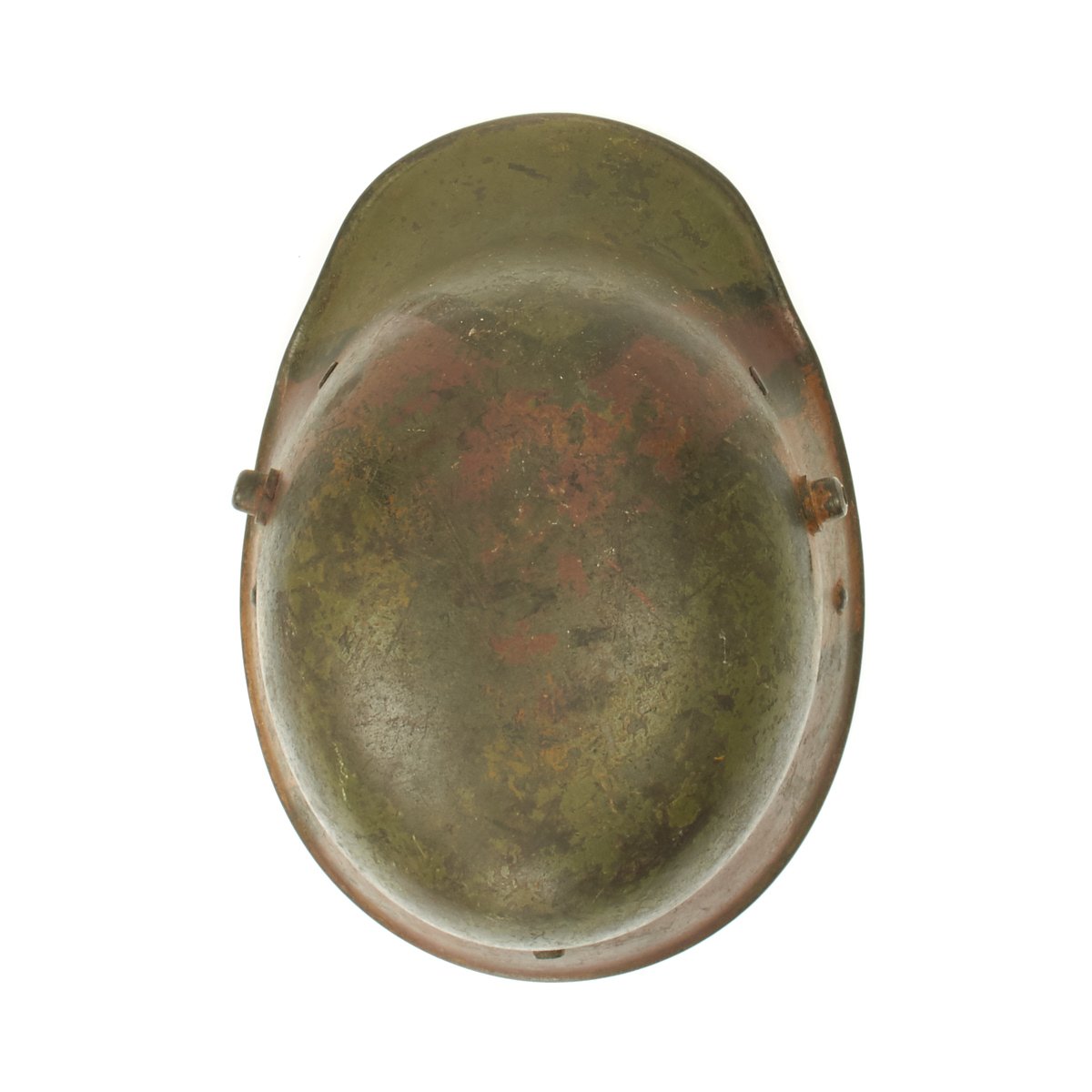
The interior of the helmet has the 1917 steel band pattern, three pad leather liner with leather retaining band still intact! All three leather pads are complete and retain their original horsehair stuffing! Pads soft and supple. All of the six-liner string adjustment tabs are intact. Original chinstrap is present, shows wear and damage and repairs but is still complete. Shell is stamped but it is difficult to read. Shell is size 64 (originally intended to accommodate head sizes of 56cm to 58cm or US 7 to US 7 ¼).
History of the M16/17
The Stahlhelm was introduced into regular service during the Verdun campaign in early 1916.
The M1916 design had side-mounted horn-like ventilator lugs which were intended to be support for an additional steel brow plate or Stirnpanzer, which only ever saw limited use by snipers and trench raiding parties, as it was too heavy for general use.
The shell came in different sizes, from 60 to 68, with some size 70s reported. The suspension, or liner, consisted of a headband with three segmented leather pouches, each holding padding materials, and leather or fabric cords could be adjusted to provide a comfortable fit. The one-piece leather chinstrap was attached to the shell by M1891 chinstrap lugs, the same kind used in the Pickelhaube helmet.
The M1916 design provided excellent protection: Reserve Lieutenant Walter Schulze of 8th Company Reserve Infantry Regiment 76 described his combat introduction to the helmet on the Somme, 29 July 1916:
“… suddenly, with a great clanging thud, I was hit on the forehead and knocked flying onto the floor of the trench… a shrapnel bullet had hit my helmet with great violence, without piercing it, but sufficiently hard to dent it. If I had, as had been usual up until a few days previously, been wearing a cap, then the Regiment would have had one more man killed.”
But the helmet was not without its flaws. The ventilator horns often let cold air in during the winter, requiring the wearer to block the vents with mud or fabric. The large, flared skirt tended to make it difficult for soldiers to hear, distorting surrounding sounds and creating an echo when the wearer spoke.
Originally painted Feldgrau (field grey), the Stahlhelm was often camouflaged by troops in the field using mud, foliage, cloth covers, and paint. Official issue cloth covers in white and grey appeared in late 1916 and early 1917. Camouflage paint was not formally introduced until July 1918, when German Army Order II, No 91 366, signed by General Erich Ludendorff on 7 July 1918, outlined official standards for helmet camouflage. The order stipulated that helmets should be painted in several colors, separated by a finger-wide black line. The colors should be relevant to the season, such as using green, brown and ocher in summer.
After the effectiveness of the M1916 design was validated during the 1916 campaigns, incremental improvements were subsequently made.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Angolan Rebel 1970s era 60mm Inert Display Mortar from Angolan Civil War Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Band of Brothers ORIGINAL GERMAN WWII Le. F.H. 18 10.5cm ARTILLERY PIECE Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Armoured Fighting Vehicles of the World: AFVs of World War One (Hardcover Book) New Made Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized