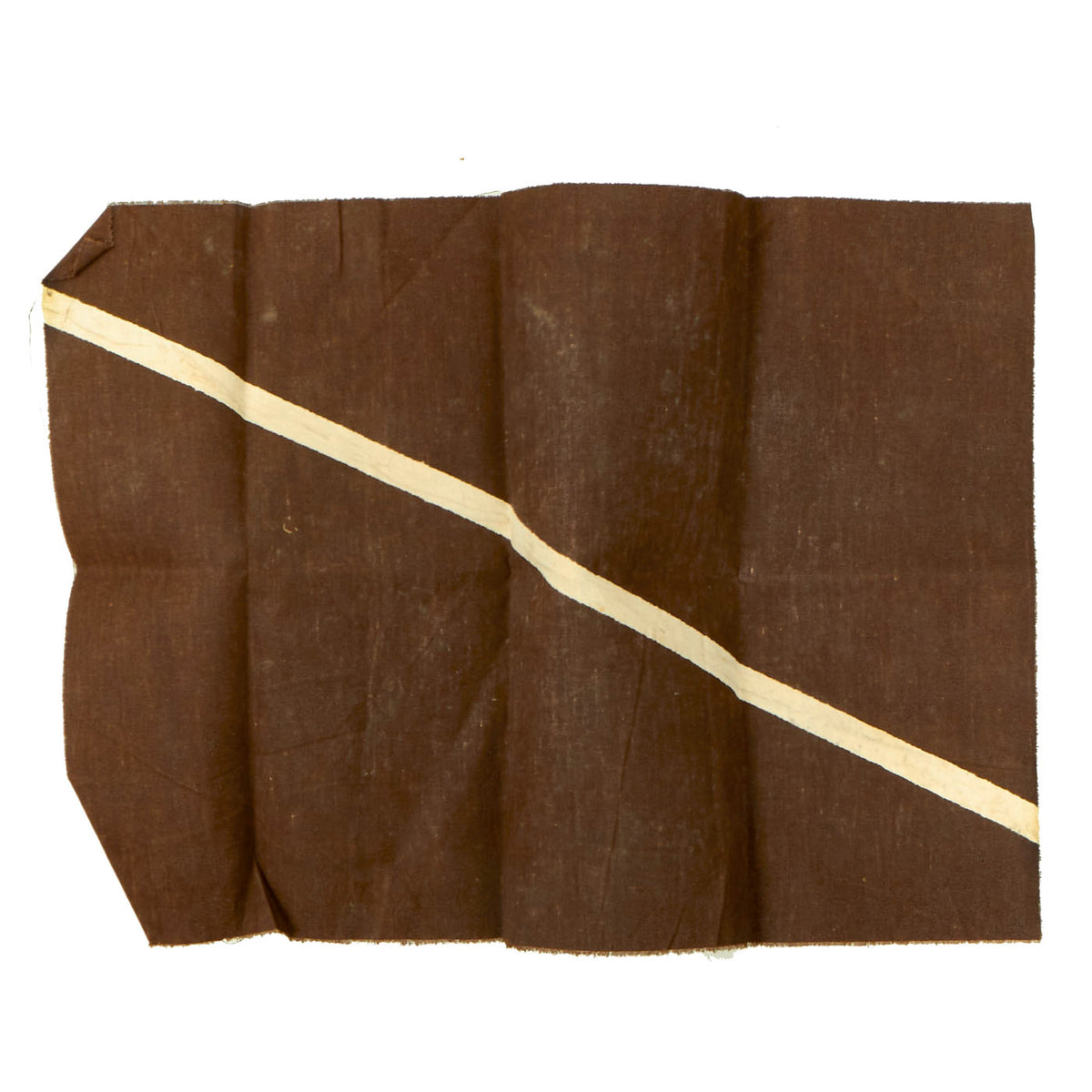
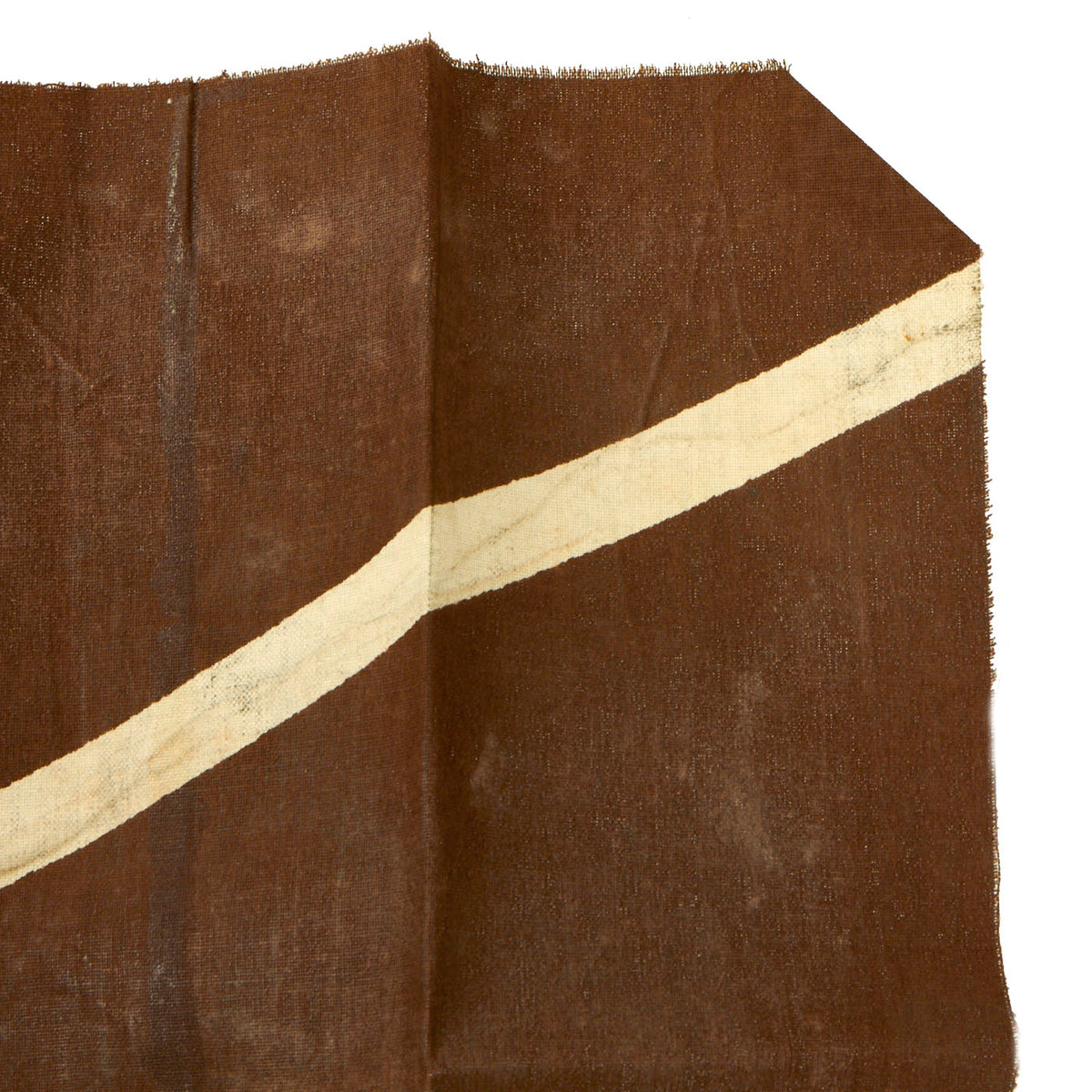
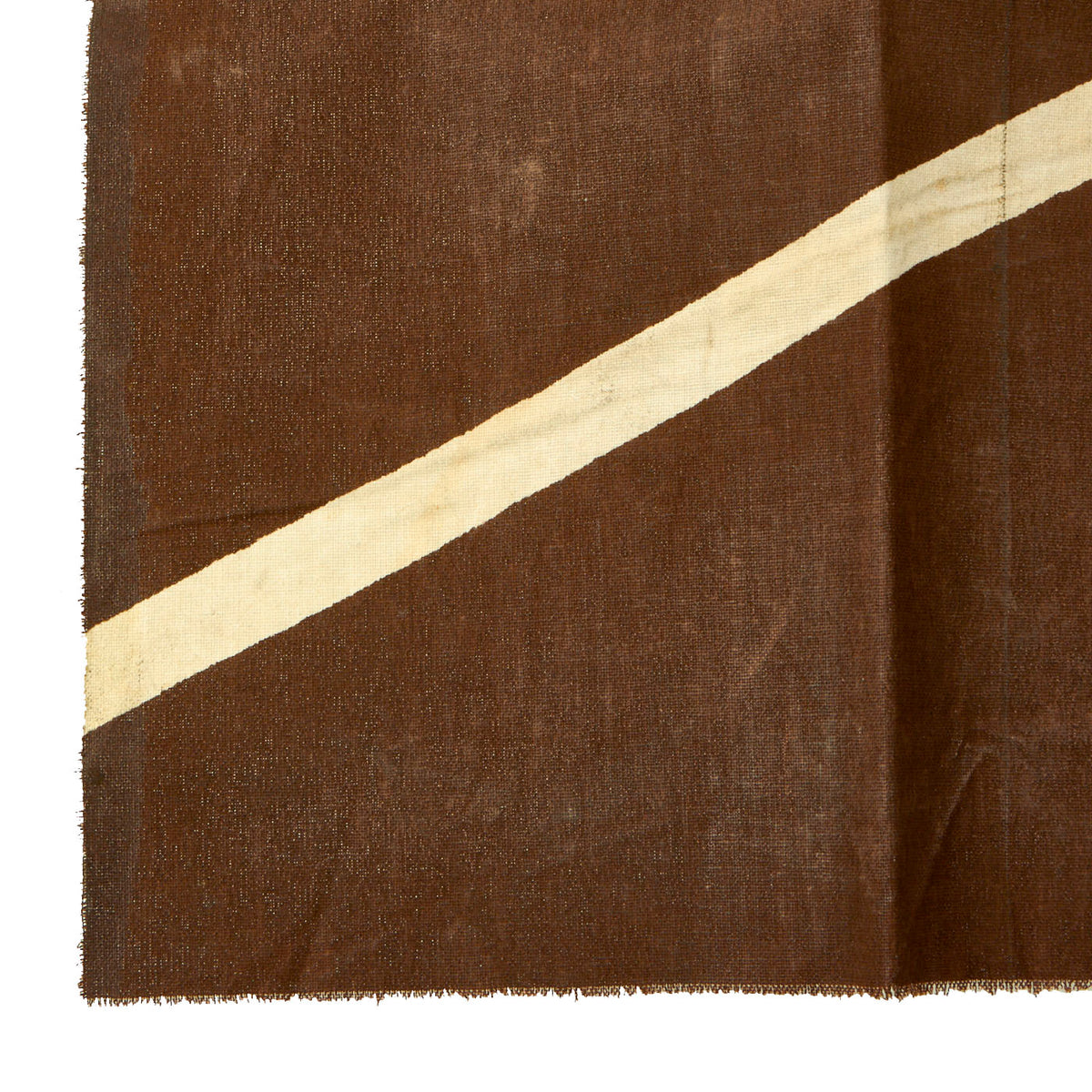
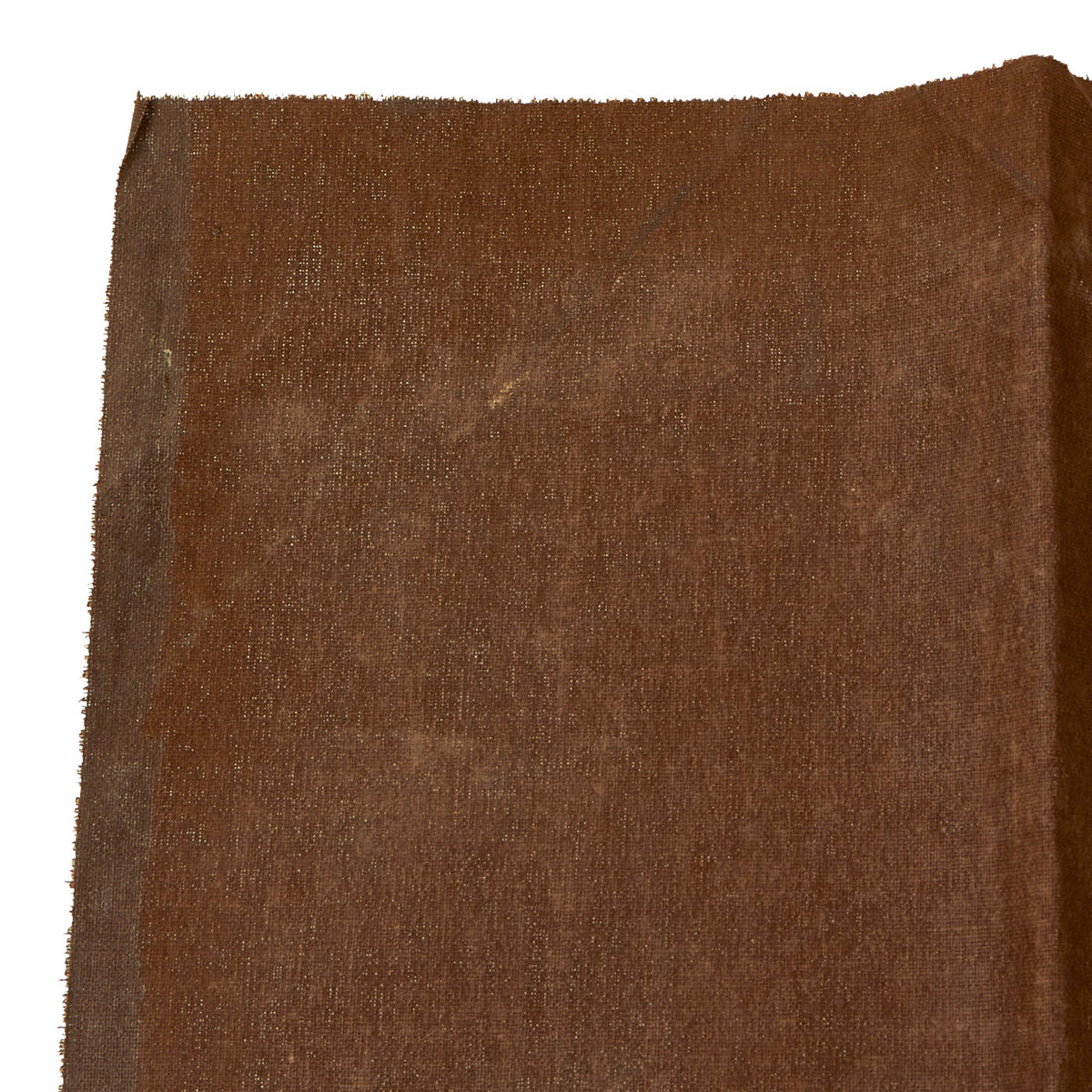
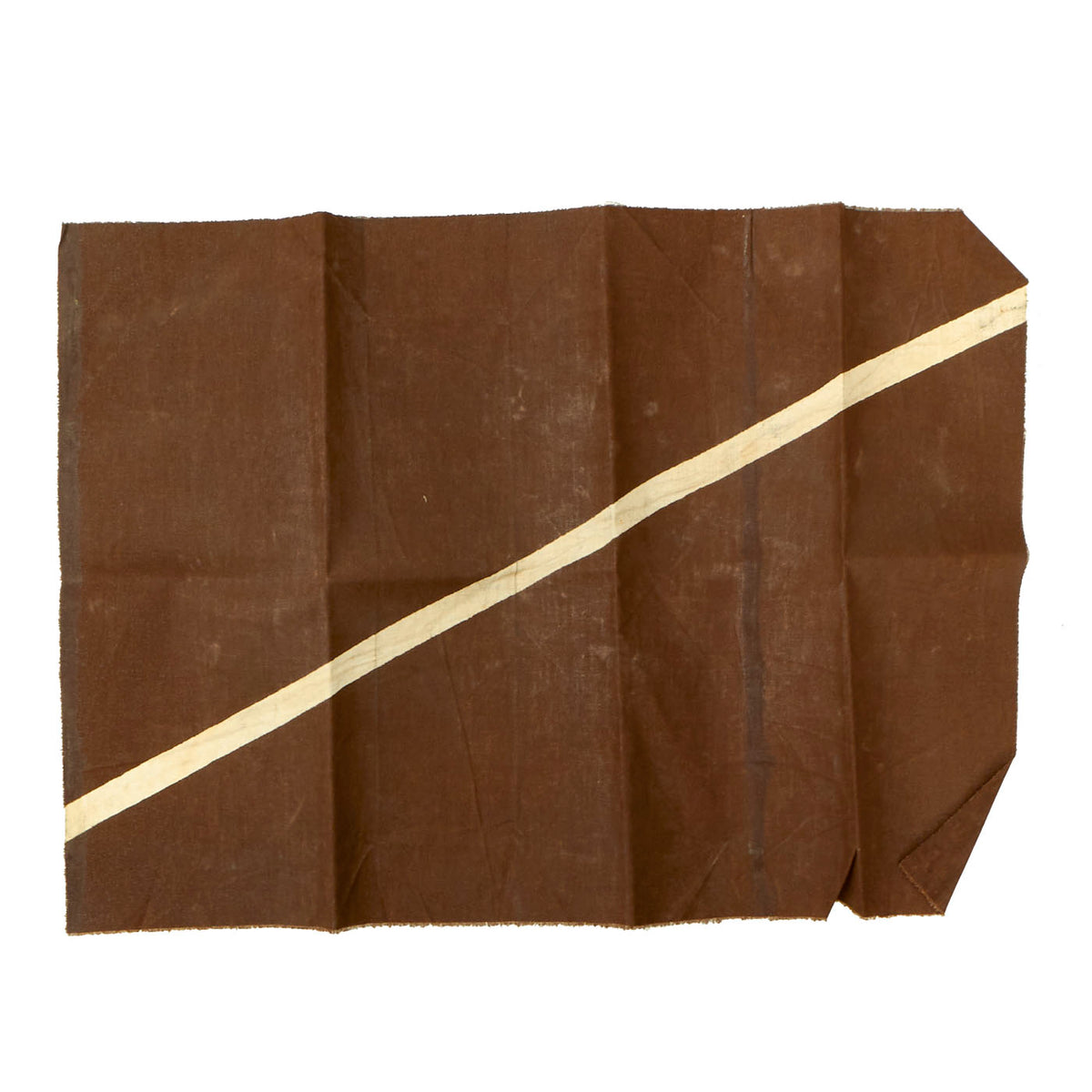
Original German WWI Imperial German Luftstreitkräfte Fokker D.VII Aircraft Canvas Piece – 18” x 13” Original Items
$ 595,00 $ 178,50
Original Item: Only One Available. The Fokker D.VII was a German World War I fighter aircraft designed by Reinhold Platz of the Fokker-Flugzeugwerke. Germany produced around 3,300 D.VII aircraft in the second half of 1918. In service with the Luftstreitkräfte, the D.VII quickly proved itself to be a formidable aircraft. The Armistice ending the war specifically required, as the fourth clause of the “Clauses Relating to the Western Front”, that Germany was required to surrender all D.VIIs to the Allies. Surviving aircraft saw much service with many countries in the years after World War I.
This piece of doped aircraft canvas is approximately 18” x 13” and is dark brown in color with a white vertical stripe. We are not certain on which Fokker D7 this section came from, but someone with access to period photos will be able to compare, making this a wonderful research project!
Comes more than ready for display.
Fokker’s chief designer, Reinhold Platz, had been working on a series of experimental V-series aircraft, starting in 1916. The aircraft were notable for the use of cantilever wings. Hugo Junkers and his aviation firm had originated the idea in 1915 with the first practical all-metal aircraft, the Junkers J 1 monoplane, nicknamed Blechesel (Sheet Metal Donkey or Tin Donkey). The wings were thick, with a rounded leading edge. The shape of the wings’ airfoil gave greater lift, with its relatively “blunt” leading edge (as seen in cross-section) giving it more docile stalling behavior than the thin wings commonly in use.
Late in 1917, Fokker built the experimental V 11 biplane, fitted with the standard Mercedes D.IIIa engine. In January 1918, Idflieg held a fighter competition at Adlershof. For the first time, front line pilots participated in the evaluation and selection of new fighters. Fokker submitted the V 11 along with several other prototypes. Manfred von Richthofen flew the V 11 and found it tricky, unpleasant and directionally unstable in a dive. Platz lengthened the rear fuselage by one structural bay and added a triangular fin in front of the rudder. Richthofen tested the modified V 11 and praised it as the best aircraft of the competition. It offered excellent performance from the outdated Mercedes engine, yet was safe and easy to fly. Richthofen’s recommendation virtually decided the competition, but he was not alone in recommending it. Fokker immediately received a provisional order for 400 production aircraft, which were named D.VII by Idflieg.
Fokker’s factory was not up to the task of meeting all D.VII production orders and Idflieg directed Albatross and AEG to build the D.VII under license, though AEG did not ultimately produce any aircraft. Because the Fokker factory did not use detailed plans as part of its production process, Fokker simply sent a D.VII airframe for Albatros to copy. Albatros paid Fokker a five percent royalty for every D.VII it built under license. Albatros Flugzeugwerke and its subsidiary, Ostdeutsche Albatros Werke (OAW), built the D.VII at factories in Johannisthal [Fokker D.VII (Alb)] and Schneidemühl [Fokker D.VII (OAW)] respectively. Aircraft markings included the type designation and factory suffix, immediately before the individual serial number.
Some parts were not interchangeable between aircraft produced at different factories, even between Albatros and OAW. Each manufacturer tended to differ in both nose paint styles and the patterning and layout of their engine compartment cooling louvers on the sides of the nose. OAW produced examples were delivered with distinctive mauve and green splotches on the cowling. All D.VIIs were produced with either the five-color Fünffarbiger or less often, the four-color Vierfarbiger lozenge camouflage covering, except for early Fokker-produced D.VIIs, which had a streaked green fuselage. Factory camouflage finishes were often overpainted with colorful paint schemes or insignia for the Jasta or for a pilot.
In September 1918, eight D.VIIs were delivered to Bulgaria. Late in 1918, the Austro-Hungarian company Magyar Általános Gépgyár (MÁG, Hungarian General Machine Company) commenced licensed production of the D.VII with Austro-Daimler engines. Production continued after the end of the war, with as many as 50 aircraft completed.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Armored Burgonet Helmet & Polearm from Scottish Castle Leith Hall Circa 1700 Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Angolan Rebel 1970s era 60mm Inert Display Mortar from Angolan Civil War Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Armoured Fighting Vehicles of the World: AFVs of World War One (Hardcover Book) New Made Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Australian WWII Owen MK1 Machine Carbine SMG Custom Fabricated Replica with Sling Original Items