Original German Made M1891 Argentine Mauser Carbine by Ludwig Loewe serial A 0827 with Intact Crest – made in 1892 Original Items
$ 1.295,00 $ 323,75
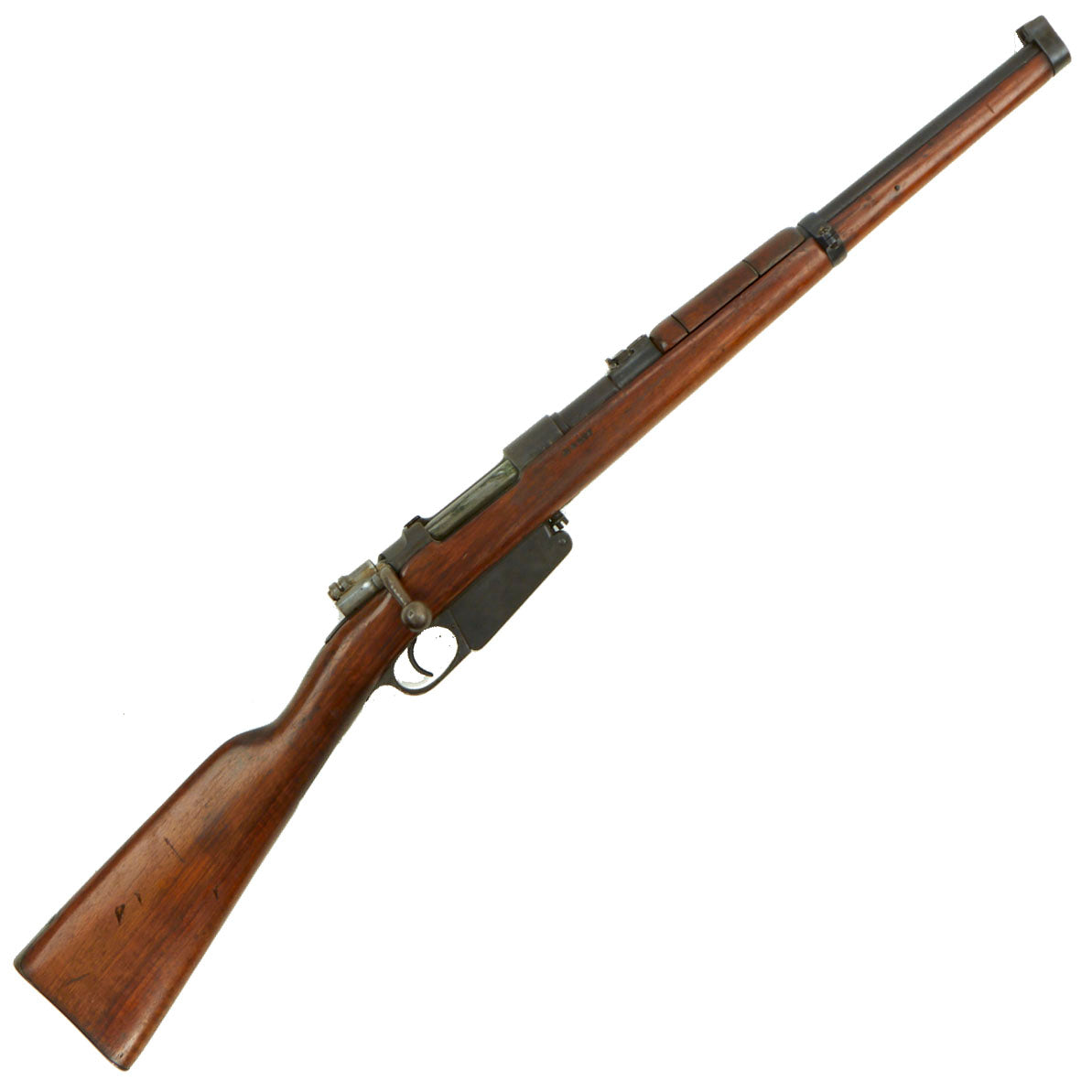
Original Item: Only one available. This is a very nice example of the Model 1891 Argentine Mauser carbine, one of many “export” models made for foreign governments, all based on the Mauser Model 1889.
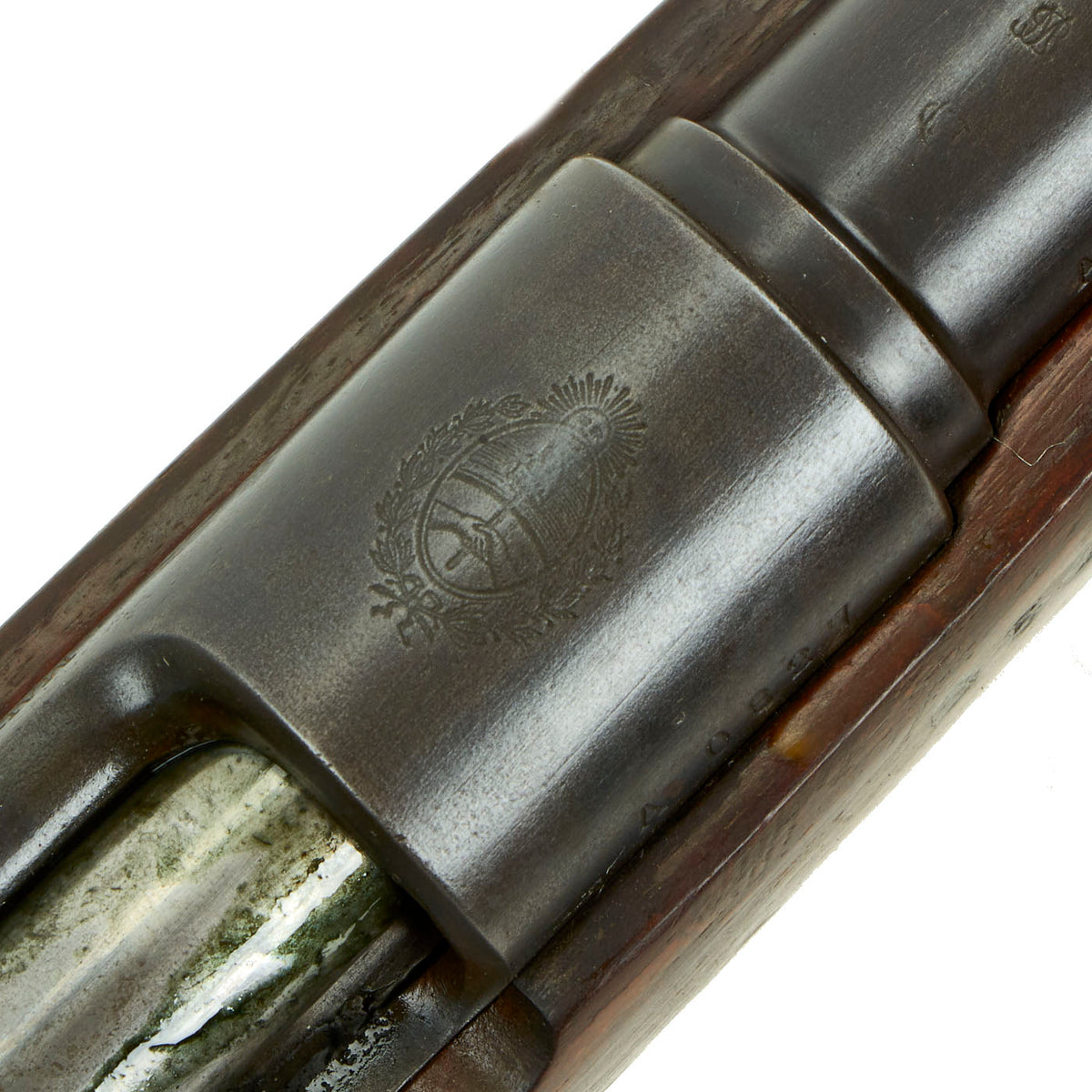
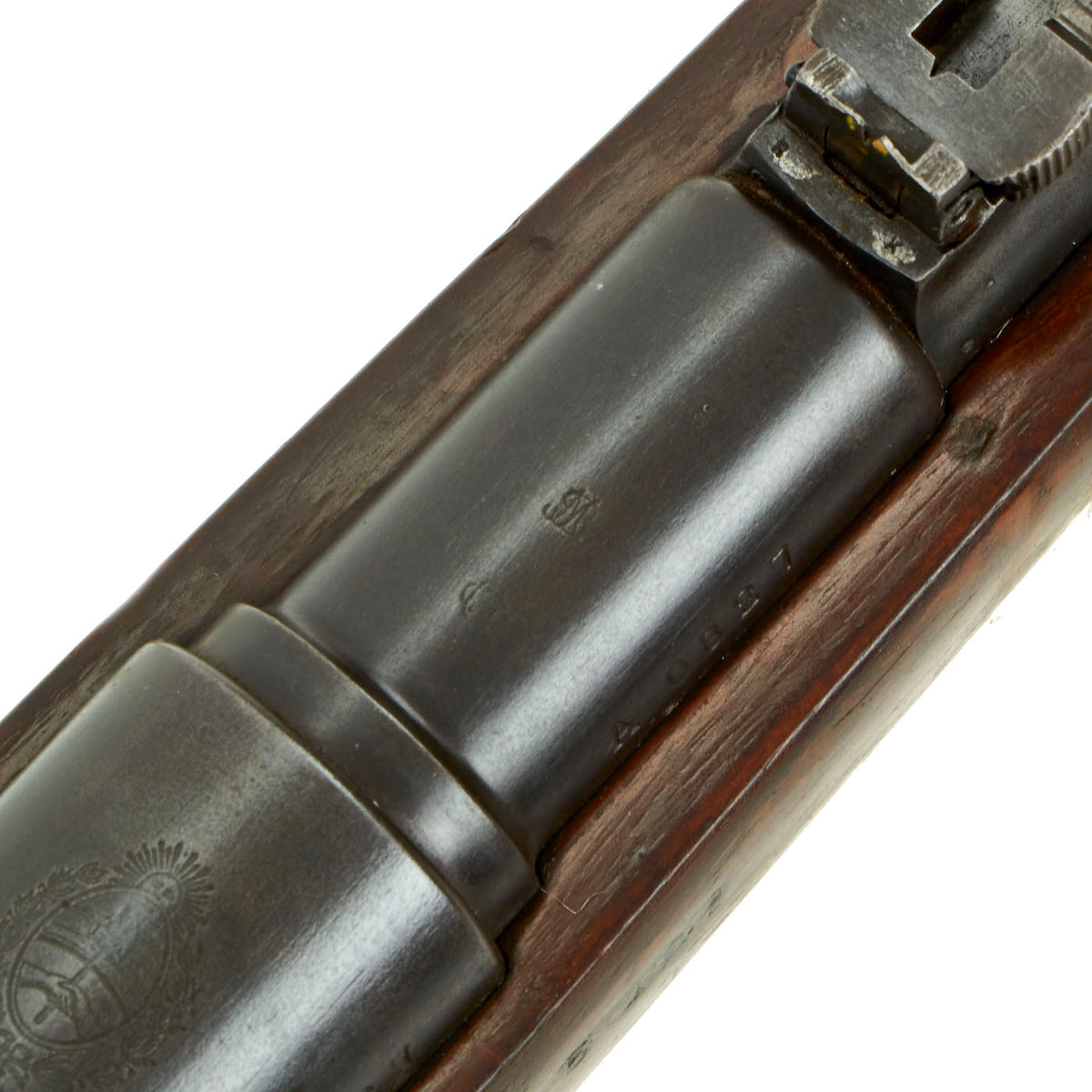
This example, like all of the Argentine Mausers made before 1896, was made by the renowned Company LUDWIG LOEWE of BERLIN, which from 1887 was actually part owner of Mauser Waffenfabrik. It has partial matching serial numbers, with A 0827 on the barrel and receiver, while the bolt and magazine have different numbers. The stock serial number is illegible. The serial numbers were issued sequentially with a single letter prefix. The Ludwig Loewe serial number records for the Argentine contract indicate that serial numbers A0000 to C4999 were produced in 1892, so this rifle was made probably made in the second quarter of that year. There were also surplus receivers made, which were then used later. In 1896 Ludwig Loewe founded Deutsche Waffen- und Munitionsfabriken, the famous D.W.M., and all rifle receivers made 1897 onward were marked as such.
The left side of the receiver is marked with the production information:
MAUSER MODELO ARGENTINO 1891.
MANUFACTURA LOEWE BERLIN.
Unlike almost all of the Argentine Mausers we have seen, this one never had the Argentine Crest removed from above the chamber. This shows a Sun wreathed panel with a sun on top, and a “Phrygian Cap” on a pole in the center, with two clasped hands below. The “Clasped Hands” markings is present on other components as well.
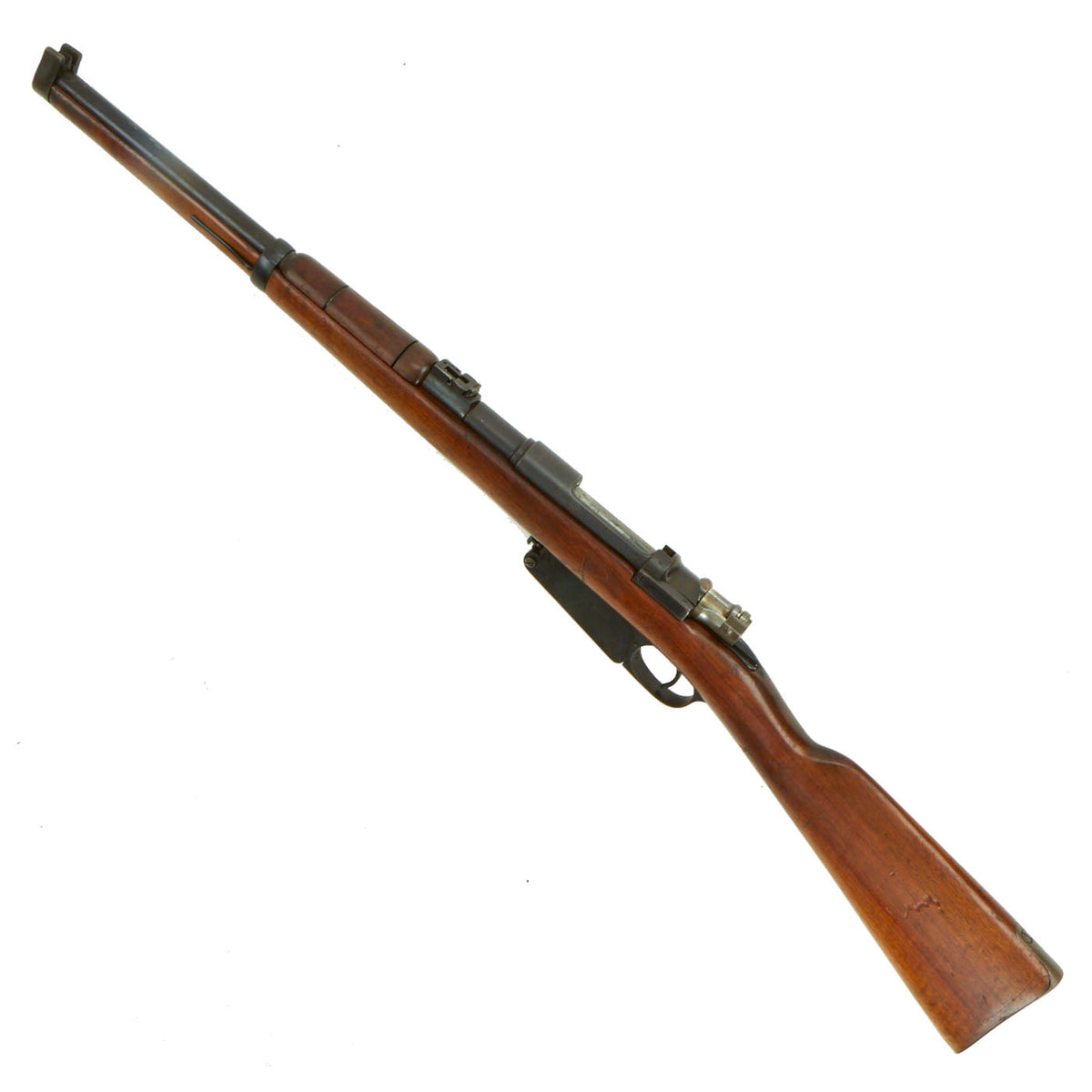
The metal finish is very good, with masses of the original blue finish on the metalwork and a nice finish on the walnut stock. The stock has some lovely curl to the grain in the butt stock area, and a great color, so it presents very nicely. This carbine definitely looks to have been arsenal reconditioned when the stock was replaced, which explains the lovely finish. The sling loop on the bottom of the wrist was either removed, or never present, with a metal plate where it would normally be.
The carbine cycles well, and has an intact firing pin, extractor, and ejector, with a strong dry fire. We checked the bore, and it does show clear rifling, however the lands are rounded and there is overall wear. This is definitely a carbine that saw some serious use during its service life, and possibly after.
Another Military Contract from the Victorian era that Mauser managed to snag from all its European competitors. In lovely condition and ready to display!
Specifications-
Year of Manufacture: 1892
Caliber: 7.65×53mm Mauser
Cartridge Type: Centerfire Cartridge
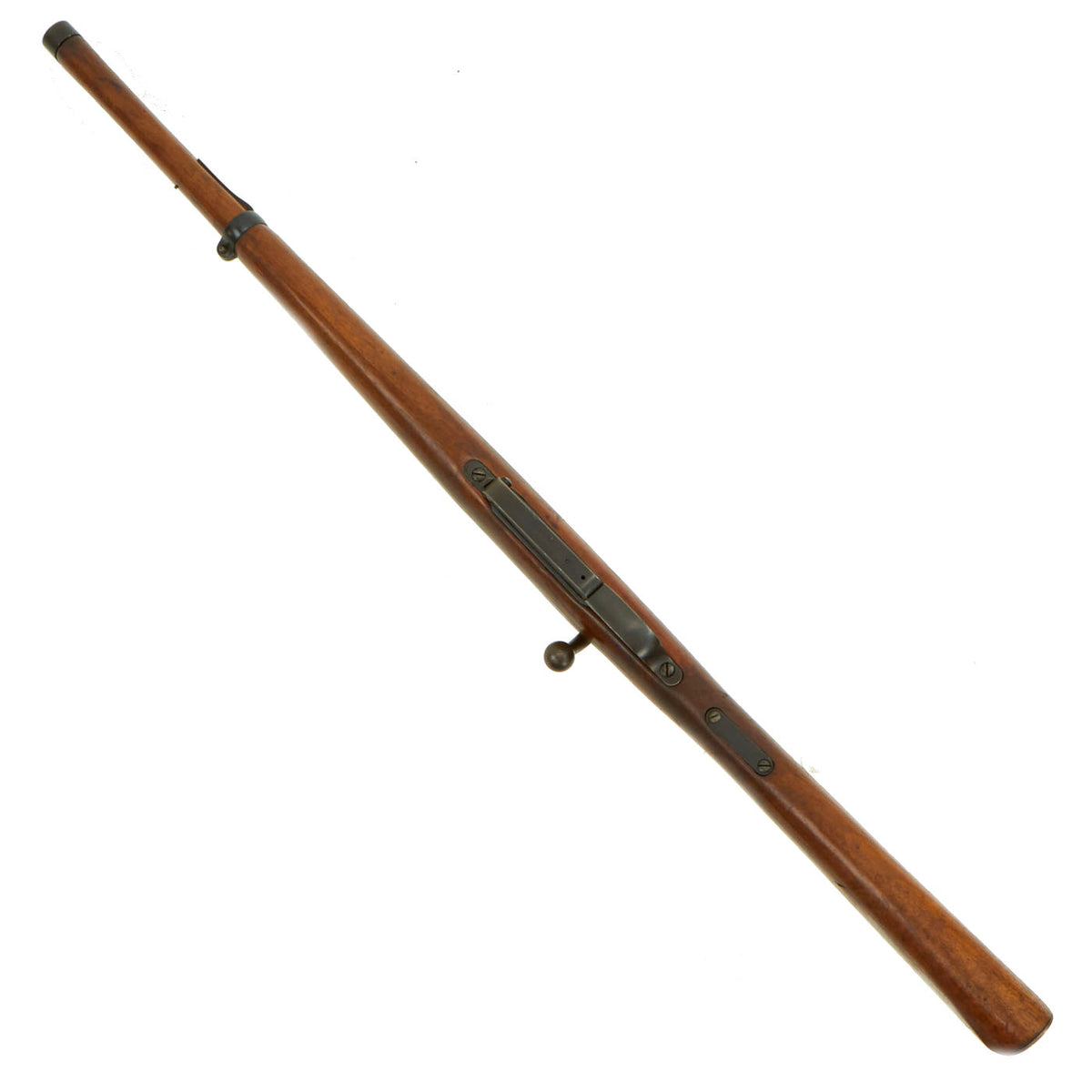
Barrel Length: 17 1/2 Inches
Overall Length: 37 Inches
Action type: Bolt-Action
Feed System: 5 round box magazine
More on the Model 1891 Argentine Mauser:
After the Mauser brothers finished work on the Model 71/84 for Germany in 1880, the design team set out to create a small caliber repeater that used smokeless powder. Because of setbacks brought on by Wilhelm Mauser’s death, they failed to have the design completed by 1882, and the German Rifle Test Commission (Gewehr-Prüfungskommission) was formed. The commission preferred to create their own design, which was what became the Gewehr 1888, often called the “Commission Rifle”.
In the meantime, Paul Mauser created two different variations of the same rifle, one with a stock strengthened with a barrel shroud and a traditional design following the layout of the 71 series, in hope he might be able to overturn the commission’s decision, or at least sell his design to the Kingdom of Bavaria, which adopted its own arms. The two rifles became known as the 89 Belgian (with a barrel shroud) and the 91 Argentine (with a 71 layout) Mausers, identical in their function and feed system. The main features were the ability to use stripper clips to feed the magazine (a revolution in rate of fire), and its rimless cartridge (7.65 Argentine Mauser), advanced for the time.
The Mauser Company then set about trying to sell this new design. Unfortunately they failed to convince the Commission to reverse its decision, and the attempt to win over Bavaria did not succeed either. However, Mauser already had supplied arms to numerous countries, and when they were looking to update their rifles, they came back to Mauser. At the time, Belgium was looking to bolster its domestic arms industry, and felt that manufacturing a Mauser Design would really help them in this goal. This resulted in the founding of Fabrique Nationale d’Armes de Guerre, owned in part by Ludwig Loewe, to manufacture the Model 1889 Belgian Mauser. This company would go on to become a major arms manufacturer, which exists today as FN Herstal.
At the same time, the Ottoman Empire had a contract for Model 1877 Turkish Mausers, which were based on the model 1871. The contract however had an “escape clause” that allowed them to change the contract in the event of a more advanced Mauser system being developed. This resulted in a new contract for the Model 1890 Turkish Mauser. While this was taking place, the Argentine Small Arms Commission contacted Mauser in 1886 to replace their own Model 71s. Since they wished to keep retraining of their armed forces to a minimum, they went for the Mauser 91, as the operating principles were identical. As with other early Mausers, most such arms were made by the Ludwig Loewe company, who in 1896 joined with other manufactures to form Deutsche Waffen und Munitionsfabriken.
One of the principal defining features of the Belgian/Turkish/Argentine Mauser was its thin sheet steel jacket surrounding the barrel—a rather unusual element not common to any other Mauser mark of note. The jacket was instituted as a feature intended to maintain the effectiveness of the barrel and the solid wooden body over time, otherwise lengthening its service life and long-term accuracy when exposed to excessive firing and battlefield abuse. In spite of this approach, the jacketed barrel proved susceptible to moisture build-up and, therefore, introduced the problem of rust forming on the barrel itself–unbeknown to the user. In addition, the jacket was not perforated in any such way as to relieve the barrel of any heat build-up and consequently proved prone to denting. As such, barrel quality was affected over time regardless of the protective measure. Furthermore, another design flaw of the jacket was its extra steel content. Not only was it expensive but it was also needed in huge quantities to provide for tens of thousands of soldiers. By many accounts, the barrel jacket was not appreciated by its operators who depended on a perfect rifle in conflict. Another defining characteristic, unlike most Mausers, was a spring-loaded cock on closing bolt action resembling that of the British Lee-Metford, which predates the Mauser 1889 by five years. This development allowed for faster firing and was well received.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Angolan Rebel 1970s era 60mm Inert Display Mortar from Angolan Civil War Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized