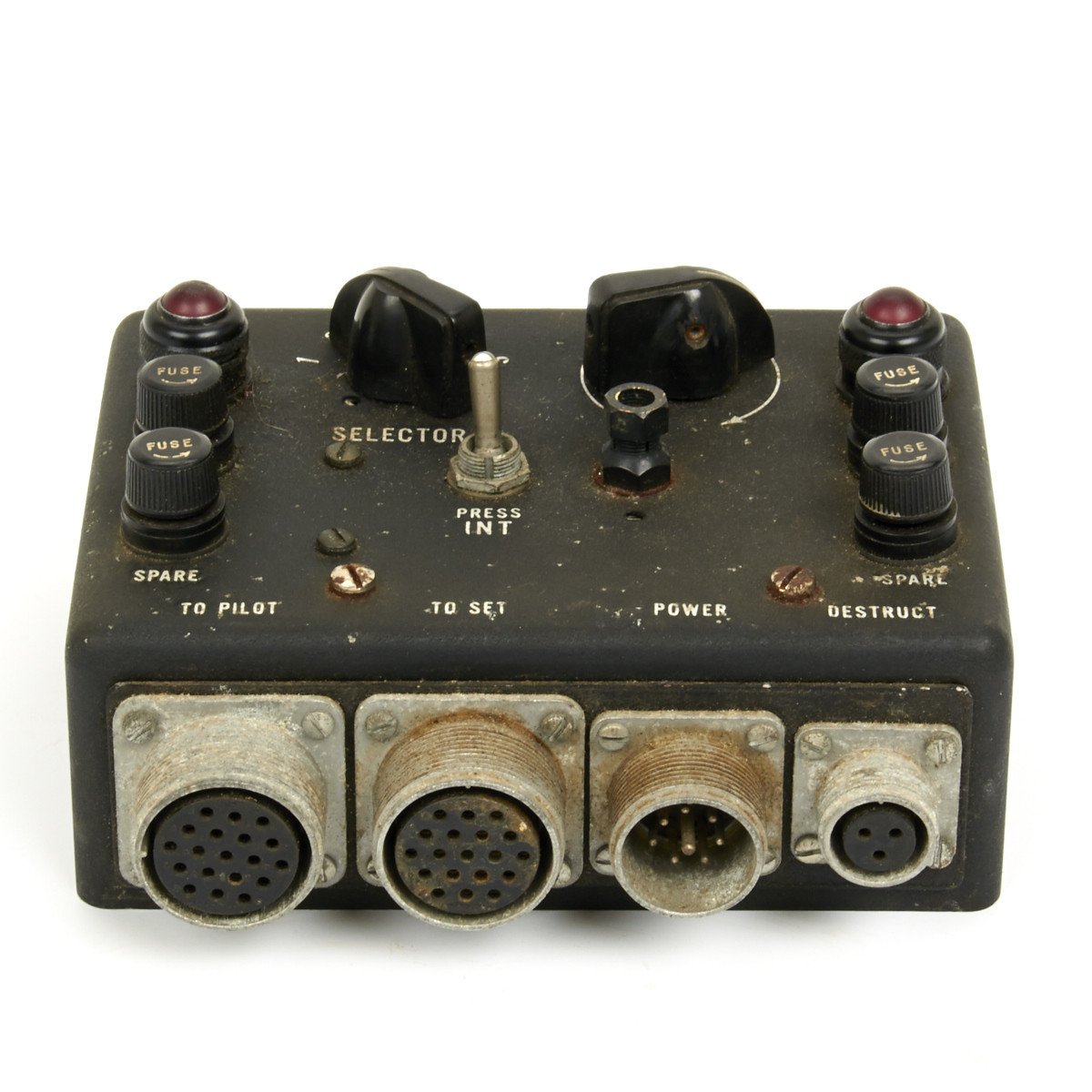
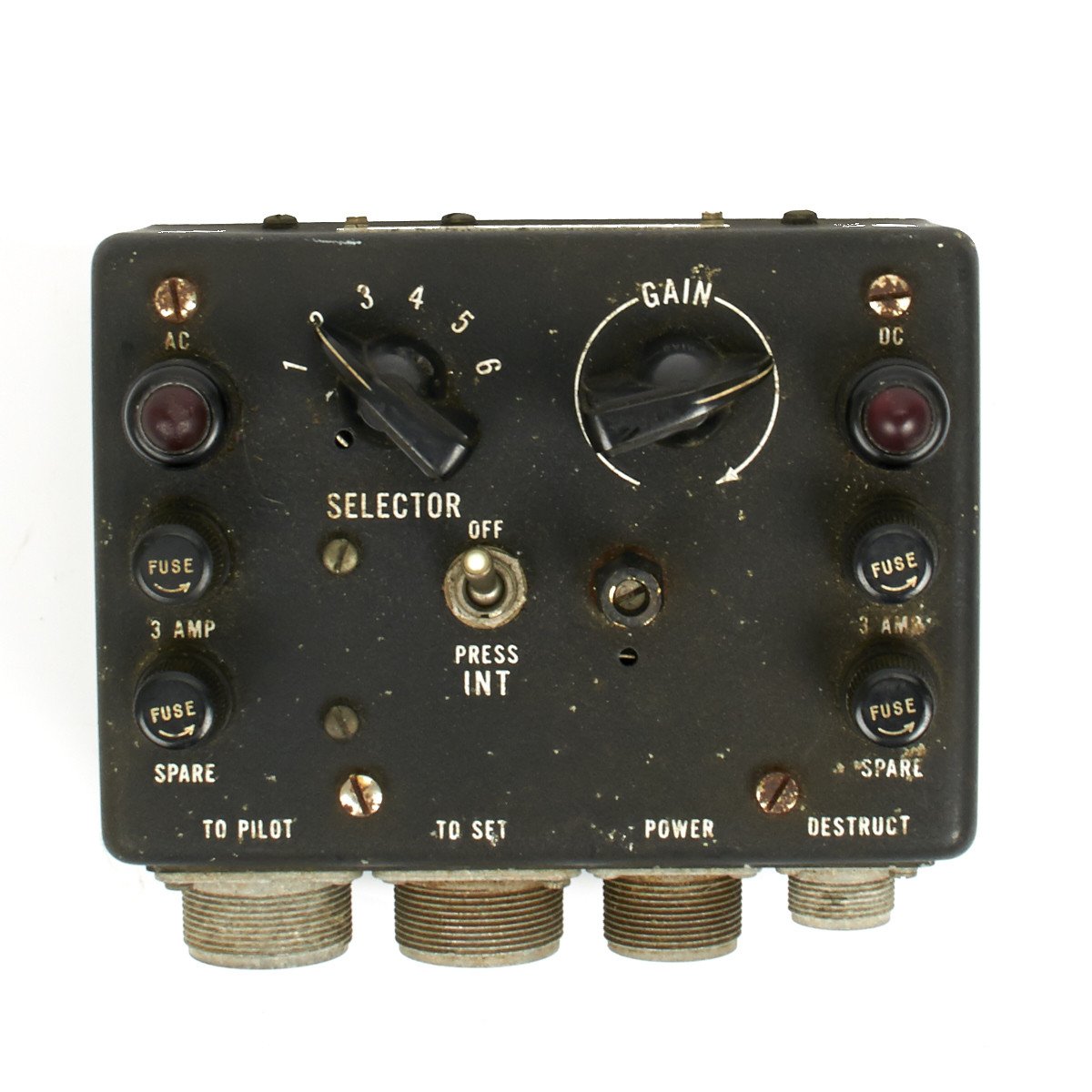
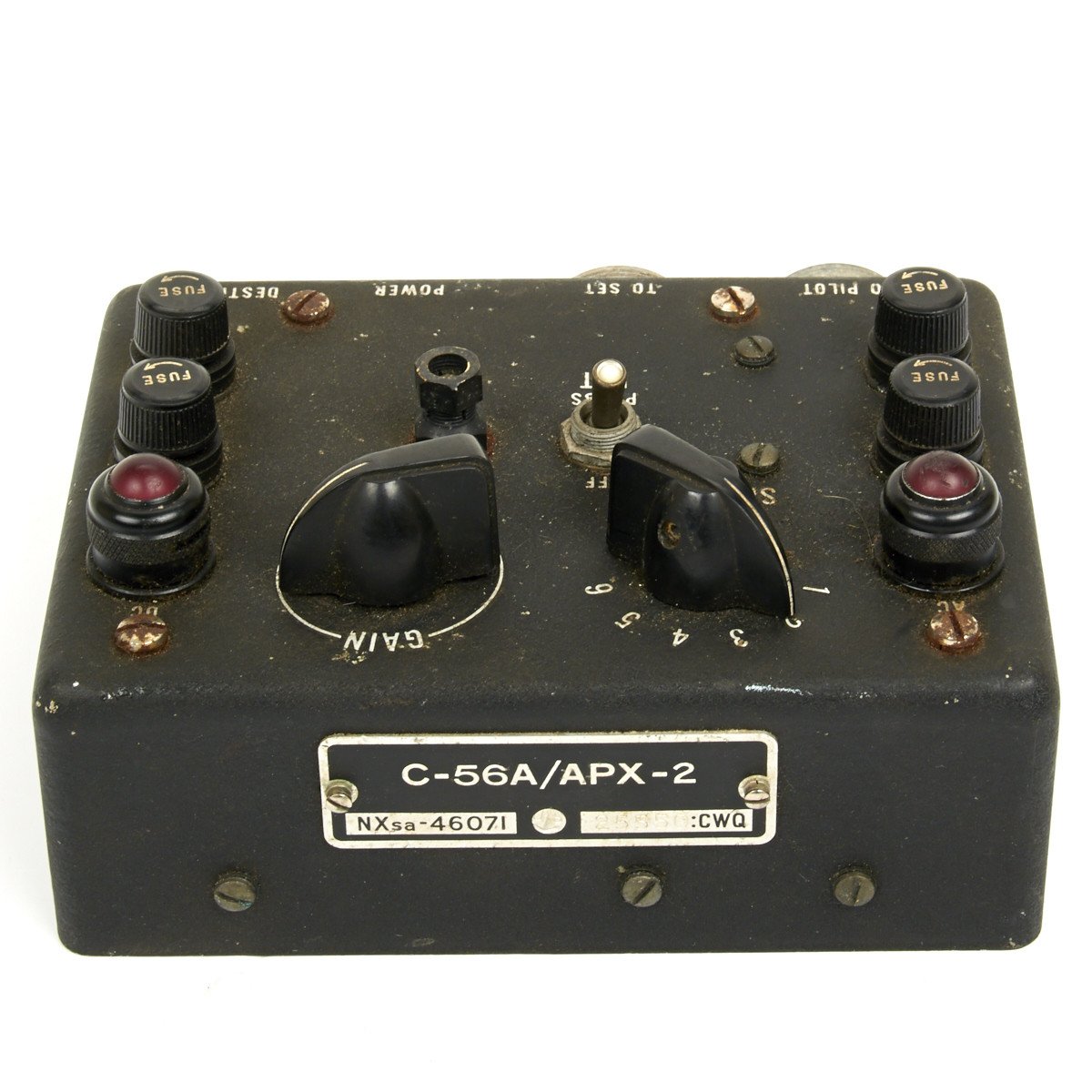
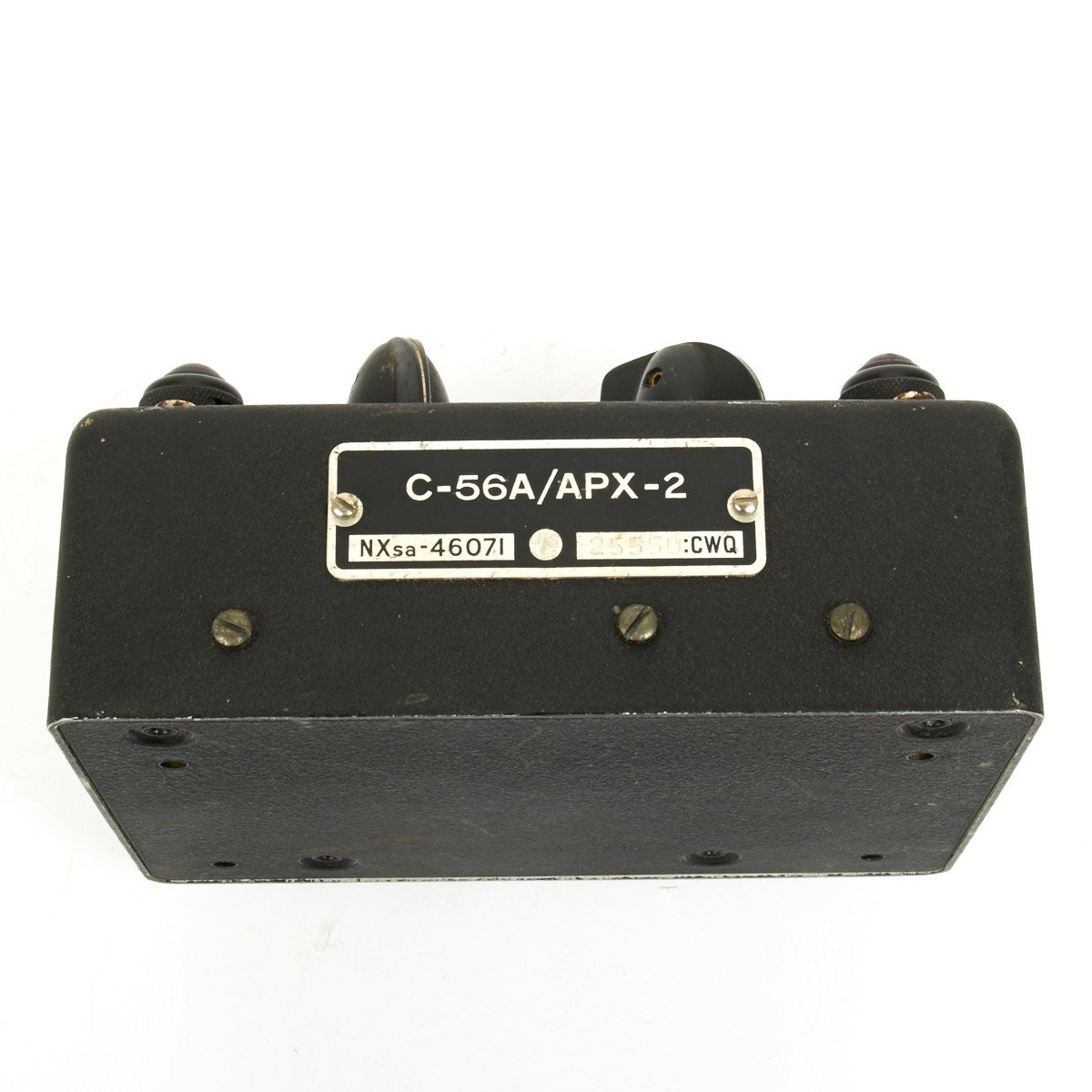
Original British WWII RAF Lockheed Hudson C-56A/APX2 IFF Radio Control Head Original Items
$ 95,00 $ 47,50
Original Item: Only One Available. The Lockheed Hudson was an American-built light bomber and coastal reconnaissance aircraft built initially for the Royal Air Force shortly before the outbreak of the Second World War and primarily operated by the RAF thereafter. The Hudson was the first significant aircraft construction contract for the Lockheed Aircraft Corporationthe initial RAF order for 200 Hudsons far surpassed any previous order the company had received. The Hudson served throughout the war, mainly with Coastal Command but also in transport and training roles as well as delivering agents into occupied France. They were also used extensively with the Royal Canadian Air Force’s anti-submarine squadrons.
By February 1939, RAF Hudsons began to be delivered, initially equipping No. 224 Squadron RAF at RAF Leuchars, Scotland in May 1939. By the start of the war in September, 78 Hudsons were in service. Due to the United States’ neutrality at that time, early series aircraft were flown to the Canadian border, landed, and then towed on their wheels over the border into Canada by tractors or horse drawn teams, before then being flown to Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) airfields where they were then dismantled and “cocooned” for transport as deck cargo, by ship to Liverpool. The Hudsons were supplied without the Boulton Paul dorsal turret, which was installed on arrival in the United Kingdom.
Although later outclassed by larger bombers, the Hudson achieved some significant feats during the first half of the war. On 8 October 1939, over Jutland, a Hudson became the first Allied aircraft operating from the British Isles to shoot down an enemy aircraft (earlier victories by a Fairey Battle on 20 September 1939 over Aachen and by Blackburn Skuas of the Fleet Air Arm on 26 September 1939 had been by aircraft based in France or on an aircraft carrier). Hudsons also provided top cover during the Battle of Dunkirk.
On 27 August 1941, a Hudson of No. 269 Squadron RAF, operating from Kaldadarnes, Iceland, attacked and damaged the U-boat U-570 causing the submarine’s crew to display a white flag and surrender the aircraft achieved the unusual distinction of capturing a naval vessel. The Germans were taken prisoner and the submarine taken under tow when Royal Navy ships subsequently arrived on the scene. A PBO-1 Hudson of the United States Navy squadron VP-82 became the first US aircraft to destroy a German submarine, when it sank U-656 southwest of Newfoundland on 1 March 1942. German U-boat U-701 was destroyed on 7 July 1942 while running on the surface off Cape Hatteras by a Hudson of the 396th Bombardment Squadron (Medium), United States Army Air Forces (USAAF). A Hudson of No. 113 Squadron RCAF became the first aircraft of the RCAF’s Eastern Air Command to sink a submarine, when Hudson 625 sank U-754 on 31 July 1942.
In 1941, the USAAF began operating the Hudson; the Twin Wasp-powered variant was designated the A-28 (82 acquired) and the Cyclone-powered variant was designated the A-29 (418 acquired). The US Navy operated 20 A-28s, redesignated the PBO-1. A further 300 were built as aircrew trainers, designated the AT-18.
Following Japanese attacks on Malaya, Hudsons from No. 1 Squadron RAAF became the first aircraft to make an attack in the Pacific War, sinking a Japanese transport ship, the Awazisan Maru, off Kota Bharu at 0118h local time, an hour before the attack on Pearl Harbor.
Skilled and experienced pilots found that the Hudson had an exceptional maneuverability for a twin-engined aircraft, especially a tight turning circle if either engine was briefly feathered.
In all 2,941 of these light bombers were manufactured between 1939 and 1943 and were used by the British and Commonwealth Air Forces, the U.S. Army Air Corp and the U.S. Navy.
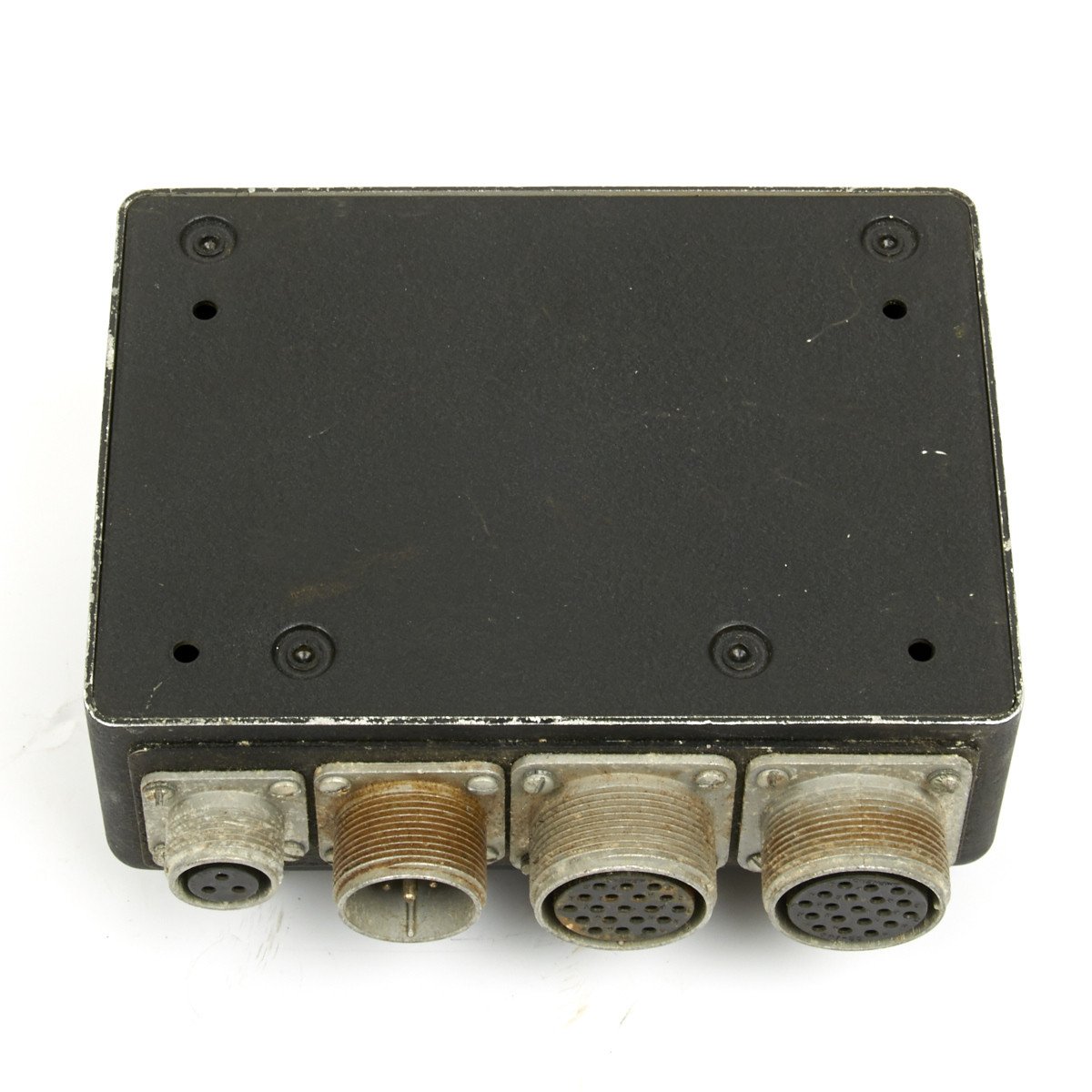
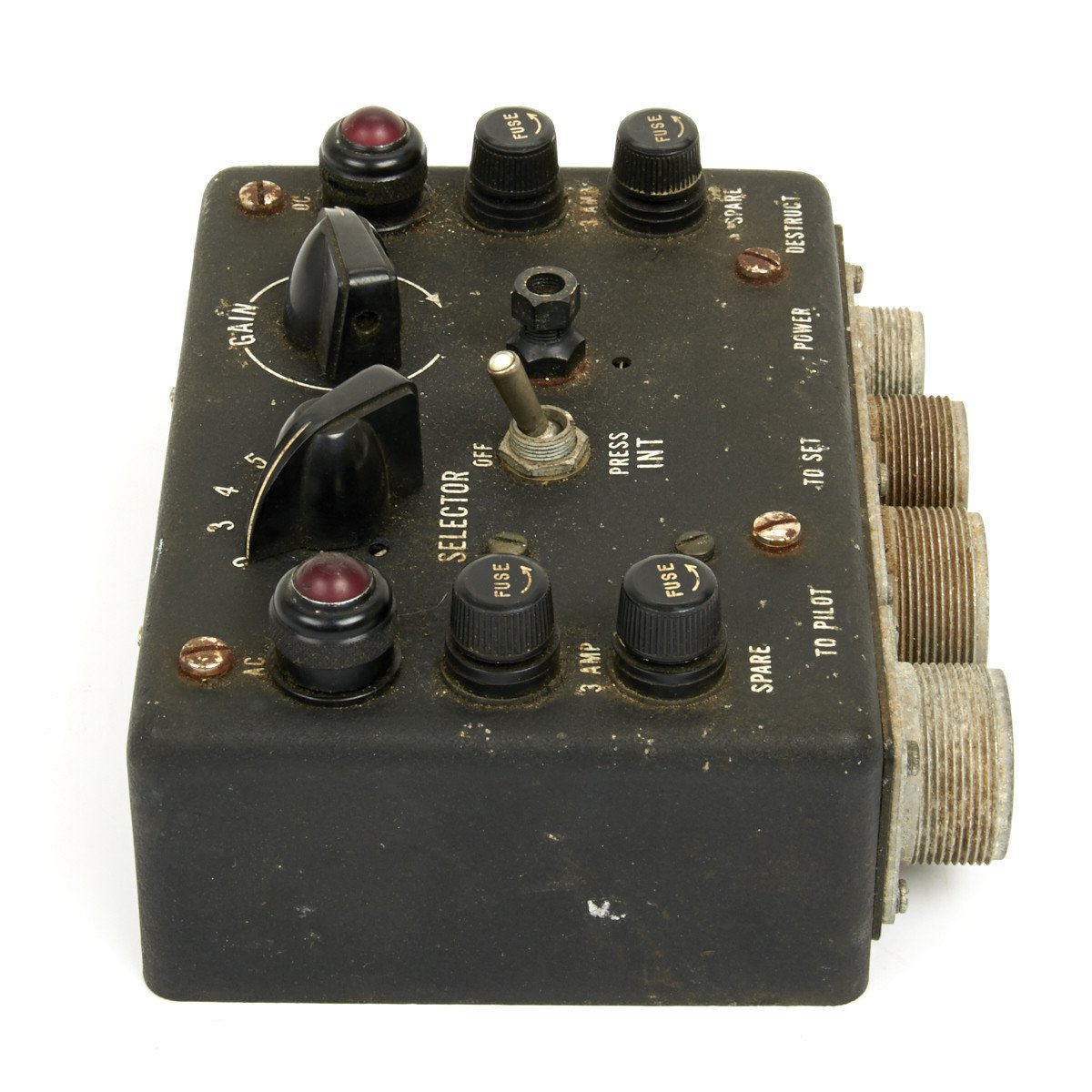
This C-56A/APX2 IFF Radio Control Head is marked with “U.S.” around an anchor denoting U.S. Navy use but then transferred to the UK for use in RAF aircraft.
Untested so we no idea if this is functioning however an interesting original WWII air war item.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Armoured Fighting Vehicles of the World: AFVs of World War One (Hardcover Book) New Made Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Australian WWII Owen MK1 Machine Carbine SMG Custom Fabricated Replica with Sling Original Items
Uncategorized
Armored Burgonet Helmet & Polearm from Scottish Castle Leith Hall Circa 1700 Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Band of Brothers ORIGINAL GERMAN WWII Le. F.H. 18 10.5cm ARTILLERY PIECE Original Items