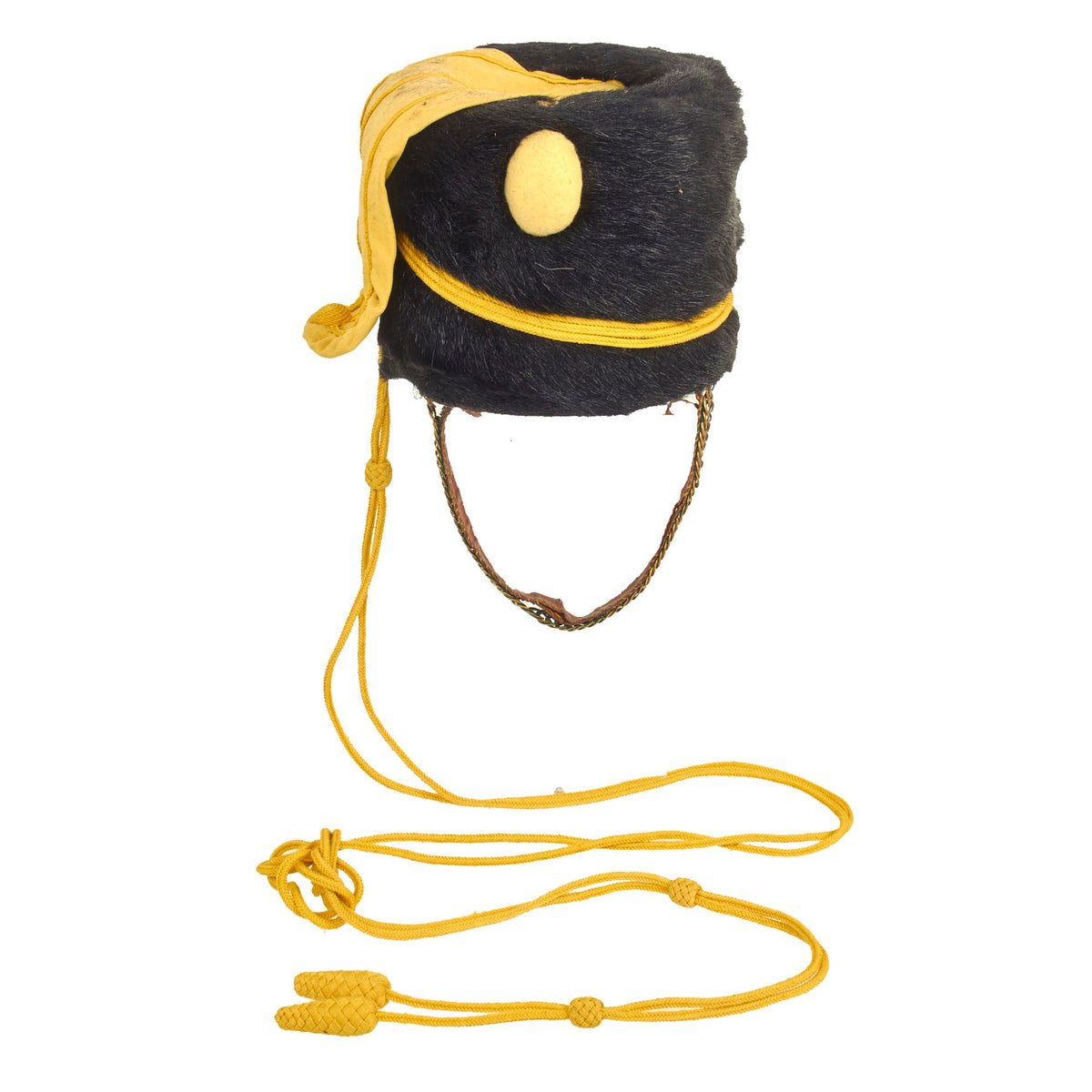
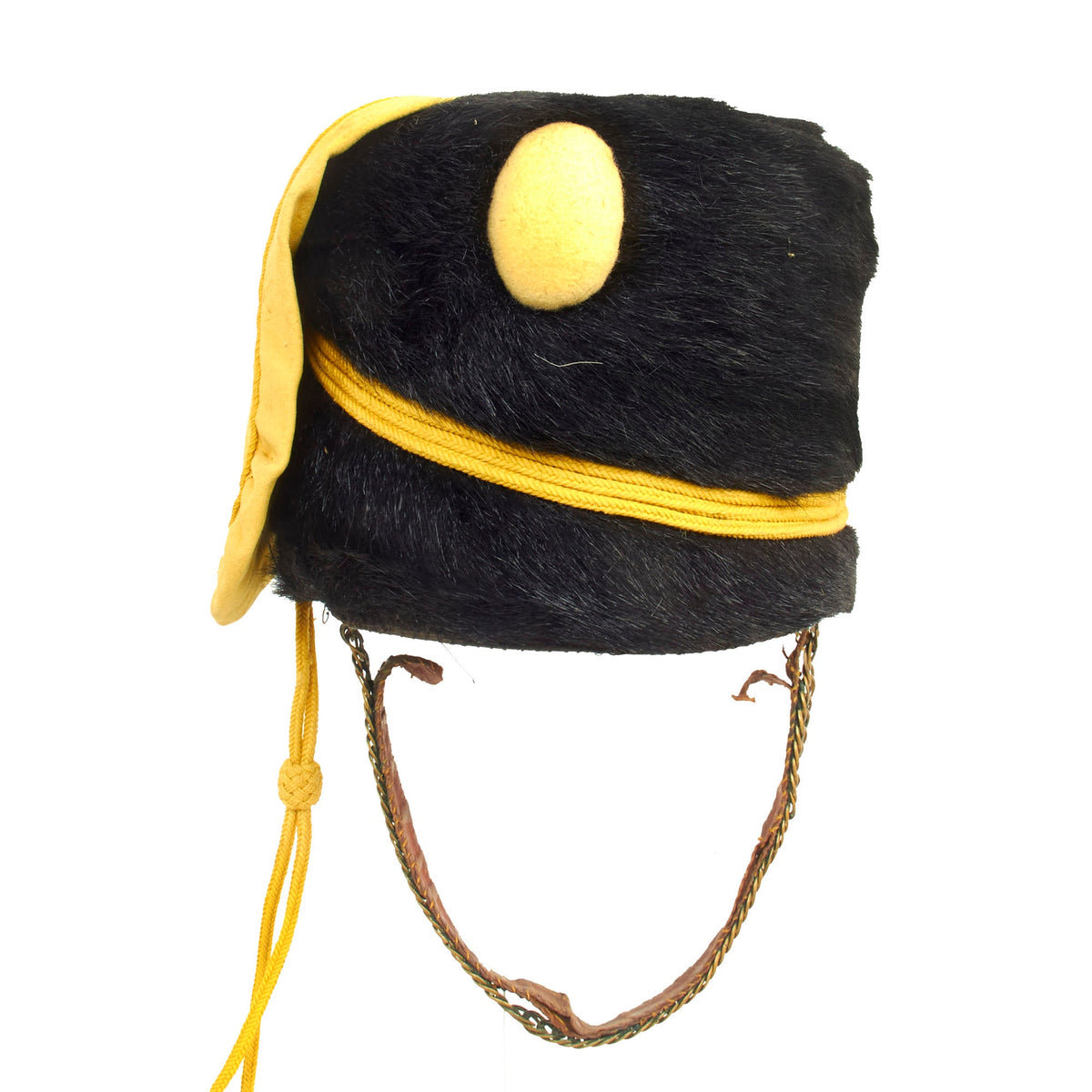
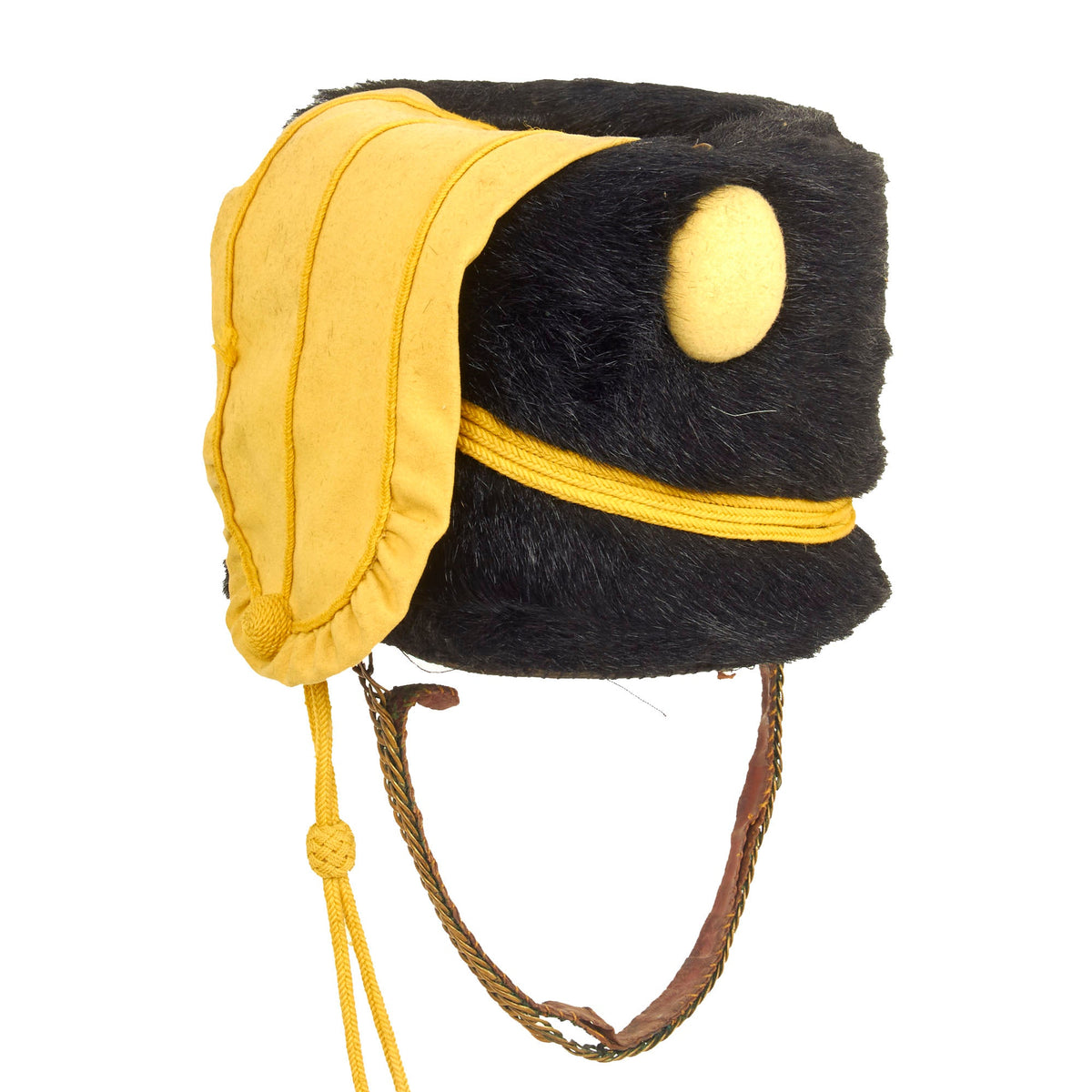
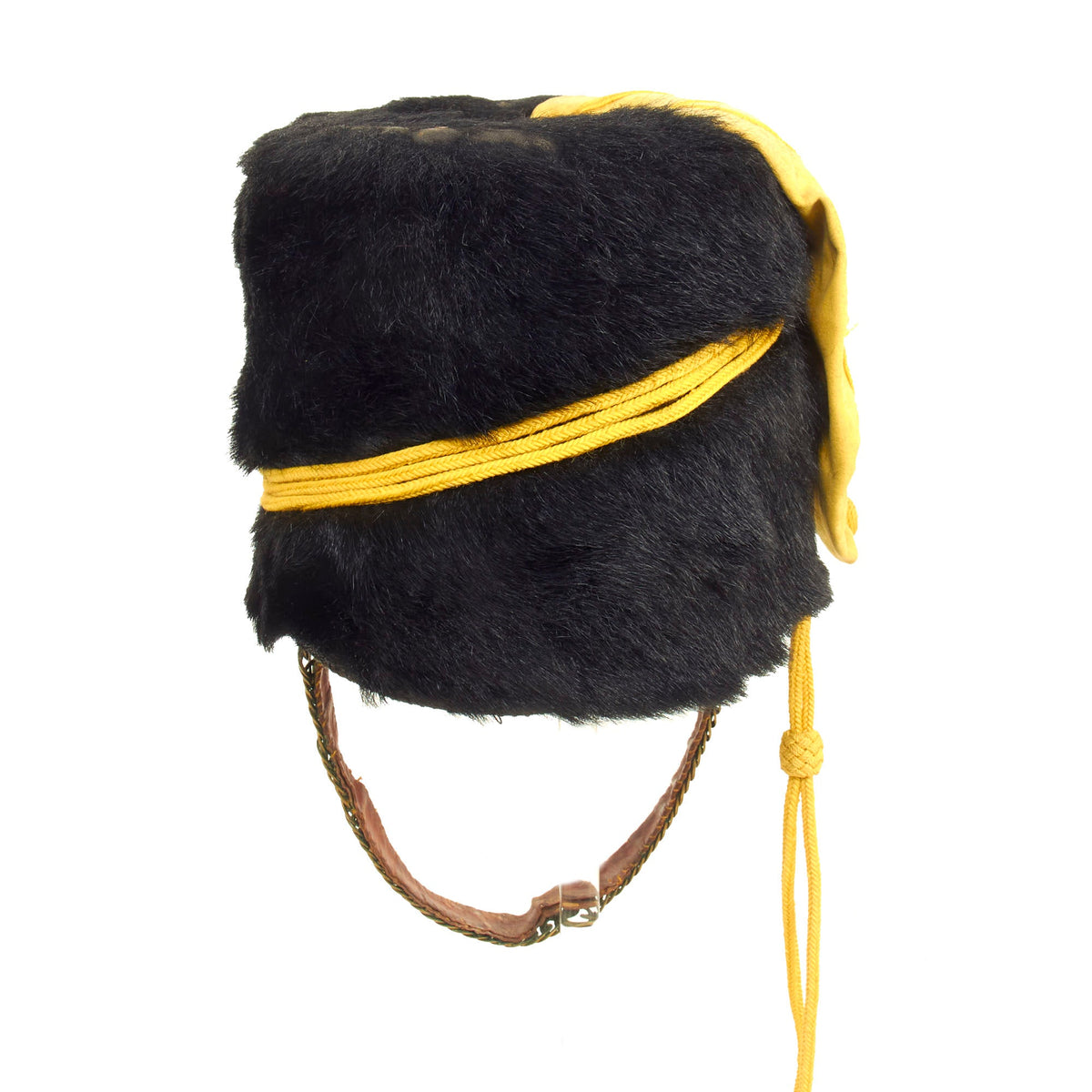
Original British Second Boer War Era 4th Queen’s Own Hussars Enlisted Busby – Dated 1901 Original Items
$ 595,00 $ 178,50
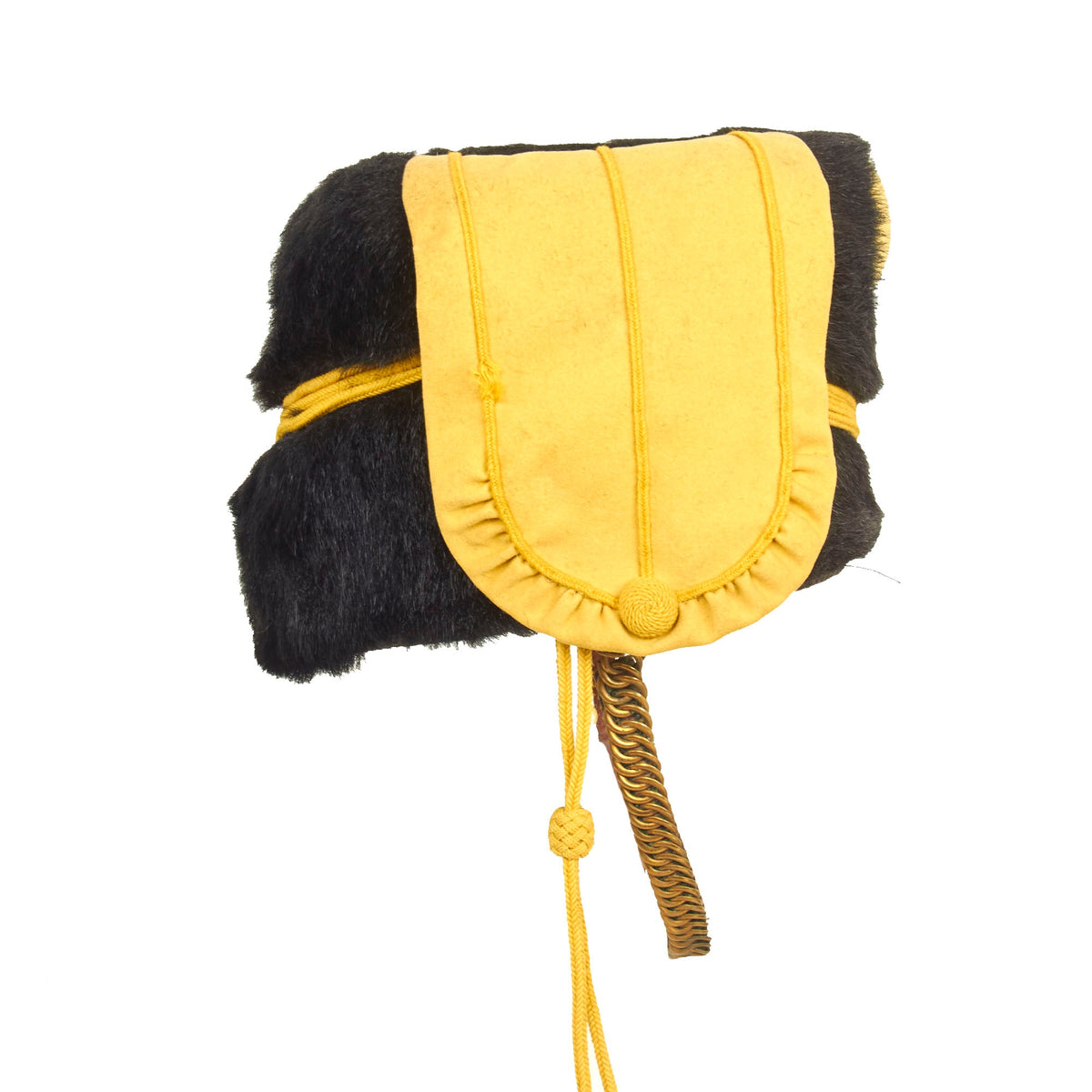
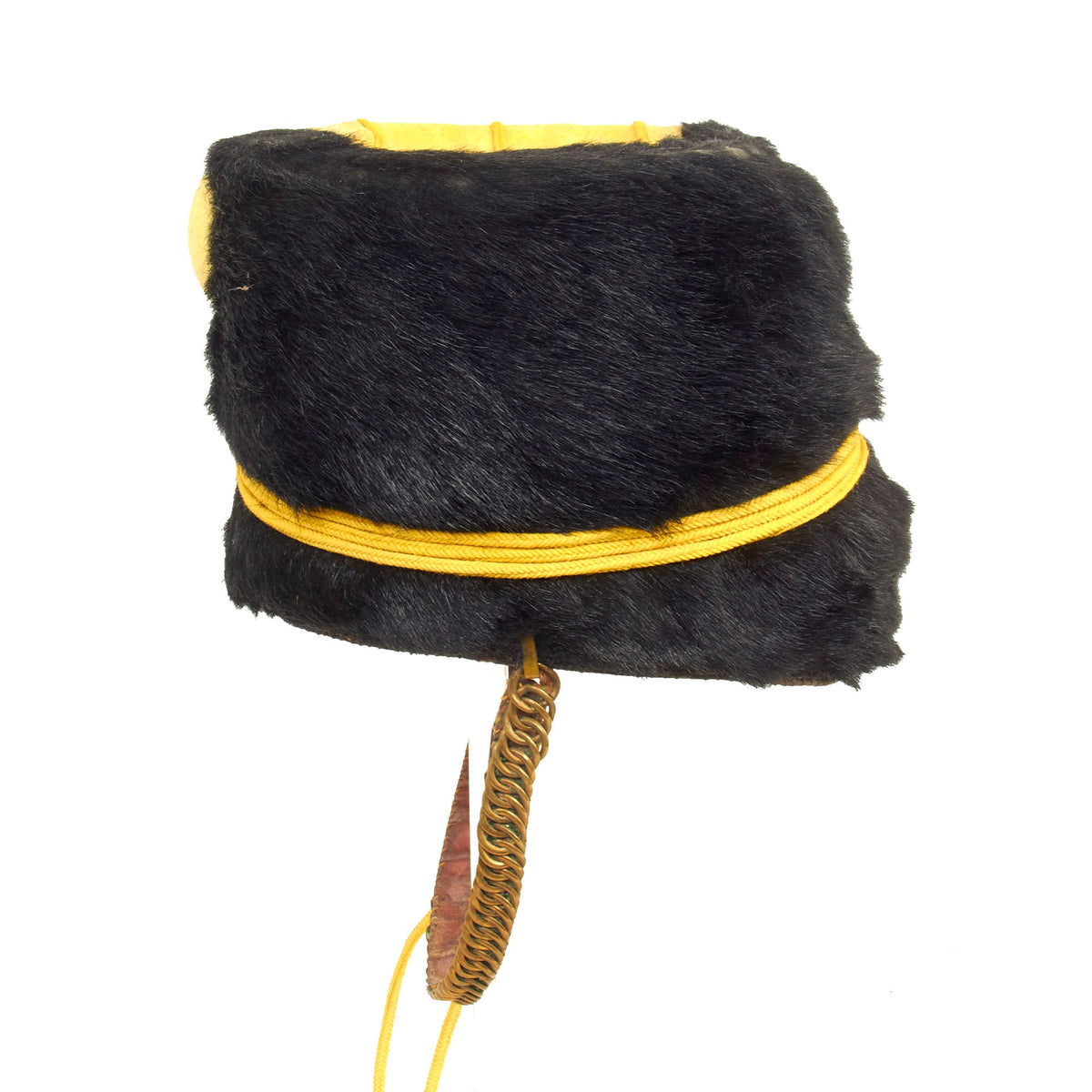
Original Item: Only One Available. This is a very beautiful genuine fur bearskin Busby used by the 4th Hussars, and has been ever since the infamous “Charge of the Light Brigade” in the 1850s. The helmet is complete with the symbolic right side “Yellow Bag” and yellow/gold cord surrounding, without chin scales and yellow cockade. Size is approximately a US 7 1/4.
The regiment was designated a light dragoons in 1818, becoming the 4th (The Queen’s Own) Regiment of (Light) Dragoons and went to fight at the Battle of Ghazni in July 1839 during the First Anglo-Afghan War.
The regiment next saw action, as part of the light brigade under the command of Major General the Earl of Cardigan, at the Battle of Alma in September 1854. The regiment was in the second line of cavalry on the right flank during the Charge of the Light Brigade at the Battle of Balaclava in October 1854. The brigade drove through the Russian artillery before smashing straight into the Russian cavalry and pushing them back; it was unable to consolidate its position, however, having insufficient forces and had to withdraw to its starting position, coming under further attack as it did so. The regiment lost four officers and 55 men in the debacle. Private Samuel Parkes was awarded the Victoria Cross during the charge for saving the life of a Trumpeter, Hugh Crawford.
The regiment became the 4th (Queen’s Own) Hussars in 1861. Winston Churchill was commissioned as a cornet in the 4th Hussars in February 1895.
Makes a wonderful display item!
The Second Boer War, also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South African Republic and the Orange Free State) over the Empire’s influence in Southern Africa from 1899 to 1902.
Following the discovery of gold deposits in the Boer republics, there was a large influx of “foreigners”, mostly British from the Cape Colony. They were not permitted to have a vote, and were regarded as “unwelcome visitors”, invaders, and they protested to the British authorities in the Cape. Negotiations failed and, in the opening stages of the war, the Boers launched successful attacks against British outposts before being pushed back by imperial reinforcements. Though the British swiftly occupied the Boer republics, numerous Boers refused to accept defeat and engaged in guerrilla warfare. Eventually, British scorched earth policies, and the poor conditions suffered in concentration camps by Boer women and children who had been displaced by these policies, brought the remaining Boer guerrillas to the negotiating table, ending the war.
The conflict broke out in 1899 after the failure of the Bloemfontein Conference when Boer irregulars and militia attacked colonial settlements in nearby British colonies. Starting in October 1899, the Boers placed Ladysmith, Kimberley, and Mafeking under siege, and won a string of victories at Colenso, Magersfontein and Stormberg. In response to these developments, increased numbers of British Army soldiers were brought to Southern Africa, and mounted largely unsuccessful attacks against the Boers. However, British military fortunes changed when their commanding officer, General Redvers Buller was replaced by Lord Roberts and Lord Kitchener, who relieved the three besieged cities and invaded the two Boer Republics in early 1900 at the head of a 180,000-strong expeditionary force. The Boers, aware they were unable to resist such a large force, chose to refrain from fighting pitched battles, allowing the British to occupy both republics and their capitals, Pretoria and Bloemfontein.
Boer politicians, including President of the South African Republic Paul Kruger either fled the region or went into hiding; the British Empire officially annexed the two republics in 1900. In Britain, the Conservative ministry led by Lord Salisbury attempted to capitalize on British military successes by calling an early general election, which was dubbed by contemporary observers a “khaki election”. However, numerous Boer fighters took to the hills and launched a guerrilla campaign against the British occupational forces, becoming known as bittereinders. Led by prominent generals such as Louis Botha, Jan Smuts, Christiaan de Wet, and Koos de la Rey, Boer guerrillas launched a campaign of hit-and-run attacks and ambushes against the British, which would continue for two years.
The Boer guerrilla campaign proved difficult for the British to defeat, due in part to British unfamiliarity with guerrilla tactics and extensive support for the guerrillas among the civilian population in the Boer Republics. In response to continued failures to defeat the Boer guerillas, British high command ordered several scorched earth policies to be implemented as part of a large scale and multi-pronged counterinsurgency campaign; a complex network of nets, blockhouses, strongpoints and barbed wire fences was constructed, virtually partitioning the occupied republics. British troops committed several war crimes and were ordered to destroy farms and slaughter livestock to deny them to Boer guerillas. Over a hundred thousand Boer civilians (mostly women and children) were forcibly relocated into concentration camps, where 26,000 died of various causes, mostly starvation and disease. Black Africans in the same areas were also interned in concentration camps as well to prevent them from supplying the Boers; 20,000 died in the camps as well, largely due to the same causes as in the case of their Boer counterparts.
In addition to these scorched earth policies, British mounted infantry units were deployed to track down and engage individual Boer guerilla units; by this stage of the war, all battles being fought were small-scale skirmishes. Few combatants on either side were killed in action, with most casualties coming via disease. Lord Kitchener began to offer generous terms of surrender to remaining Boer leaders in an effort to bring an end to the conflict. Eager to ensure their fellow Boers were released from the concentration camps, the majority of Boer commanders accepted the British terms in the Treaty of Vereeniging, formally surrendering in May 1902. The former republics were transformed into the British colonies of the Transvaal and Orange River, and in 1910 were merged with the Natal and Cape Colonies to form the Union of South Africa, a self-governing dominion within the British Empire.
British expeditionary efforts were aided significantly by colonial forces from the Cape Colony, the Natal, Rhodesia, as well as large numbers of volunteers from the British Empire worldwide, particularly Australia, Canada, India and New Zealand. Later in the war, Black African recruits contributed increasingly to the British war effort. International public opinion was generally sympathetic to the Boers and hostile to the British. Even within the United Kingdom, there existed significant opposition to the war. As a result, the Boer cause attracted thousands of volunteers from neutral countries all over the world, including the German Empire, United States, Russia and even some parts of the British Empire such as Australia and Ireland. Many consider the Boer War as marking the beginning of the questioning of the British Empire’s veneer of impenetrable global dominance; this is due to the war’s surprisingly long duration and the unforeseen, discouraging losses suffered by the British fighting the “cobbled-together army” of Boers.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Australian WWII Owen MK1 Machine Carbine SMG Custom Fabricated Replica with Sling Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized