Original British Pre-WWI 7th Queen’s Own Hussars Busby – Dated 1912 Original Items
$ 450,00 $ 135,00
Original Item: Only One Available. The 7th Queen’s Own Hussars was a cavalry regiment in the British Army, first formed in 1689. It saw service for three centuries, including the First World War and the Second World War. The regiment survived the immediate post-war reduction in forces, but following the 1957 Defence White Paper, it was amalgamated with the 3rd The King’s Own Hussars, forming the Queen’s Own Hussars in 1958.
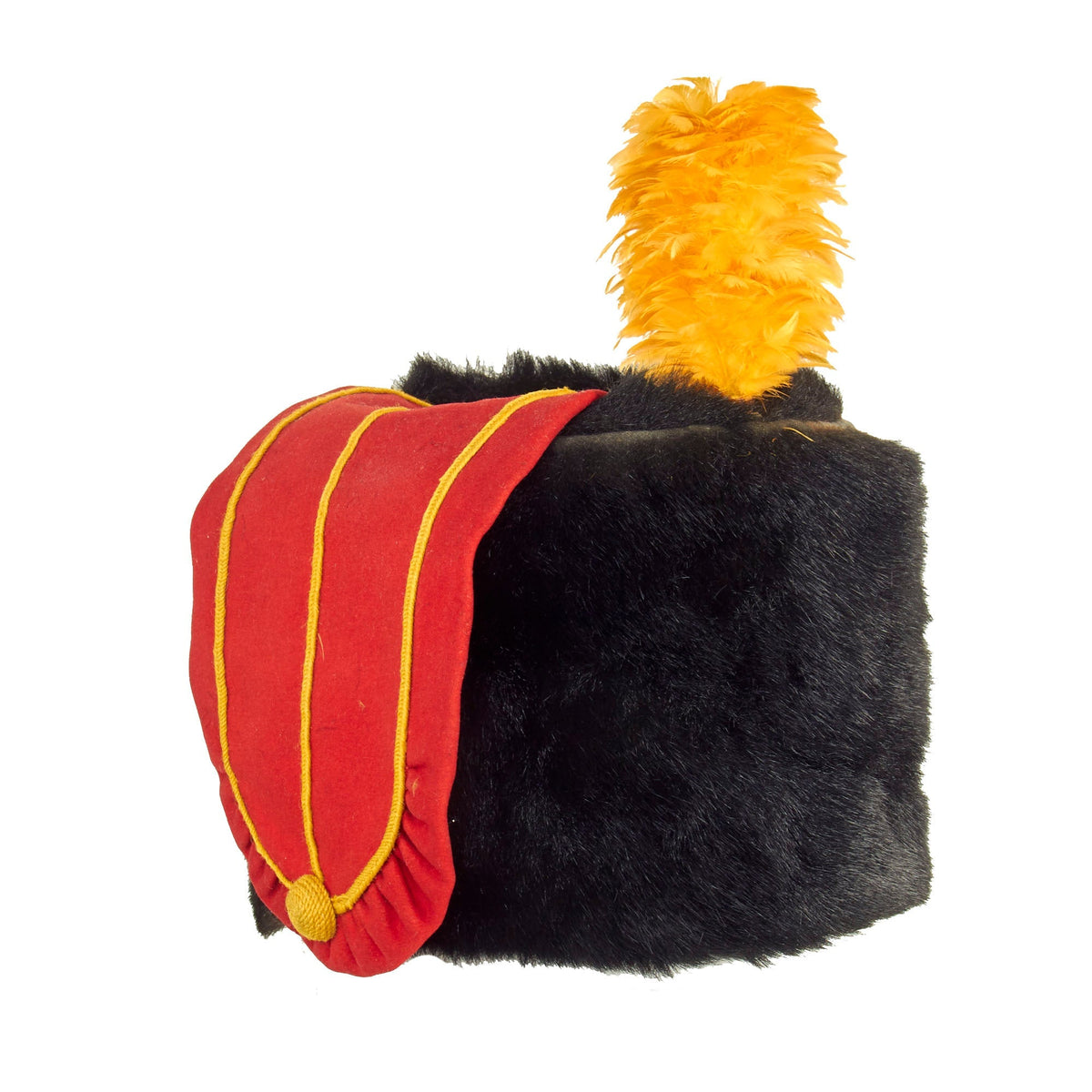
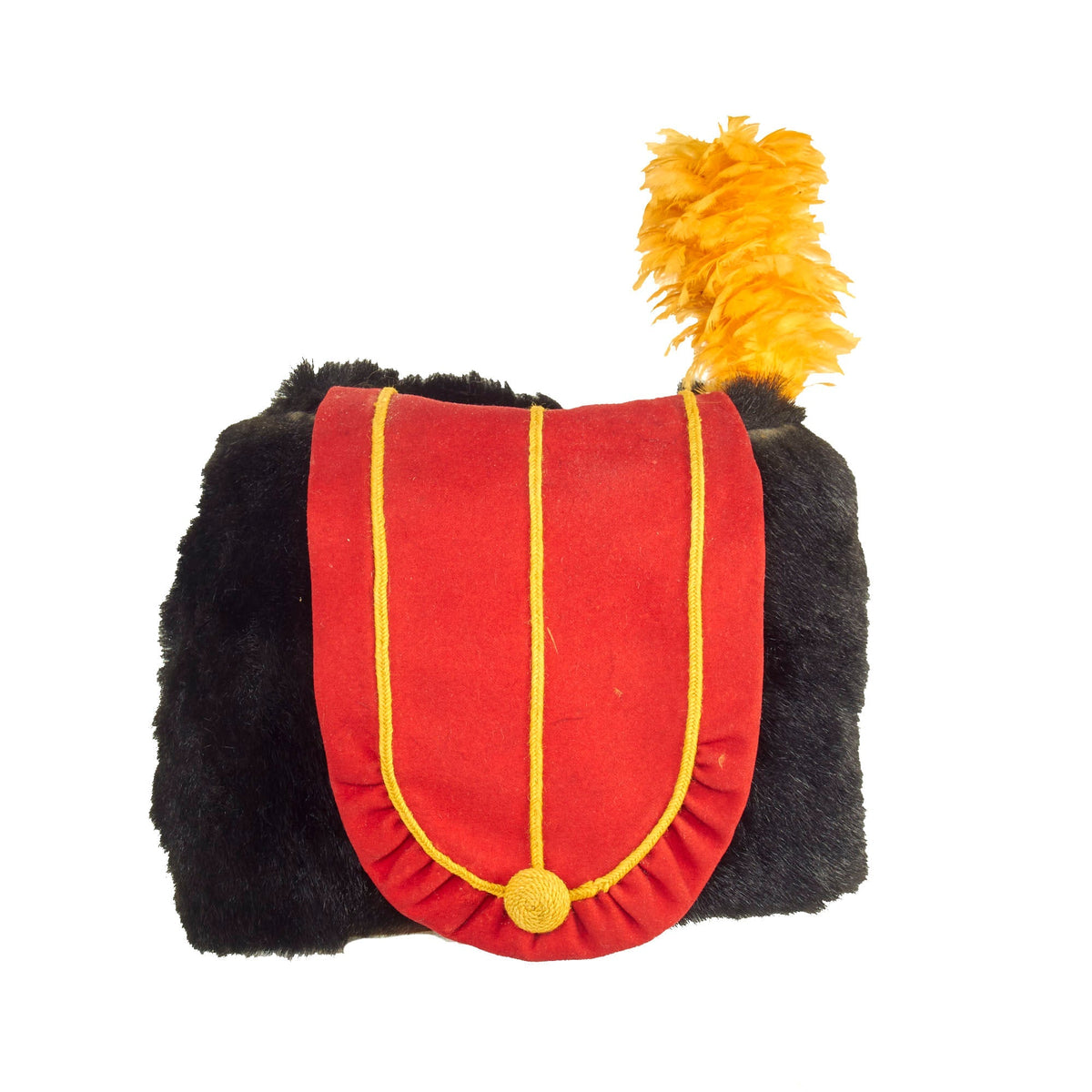
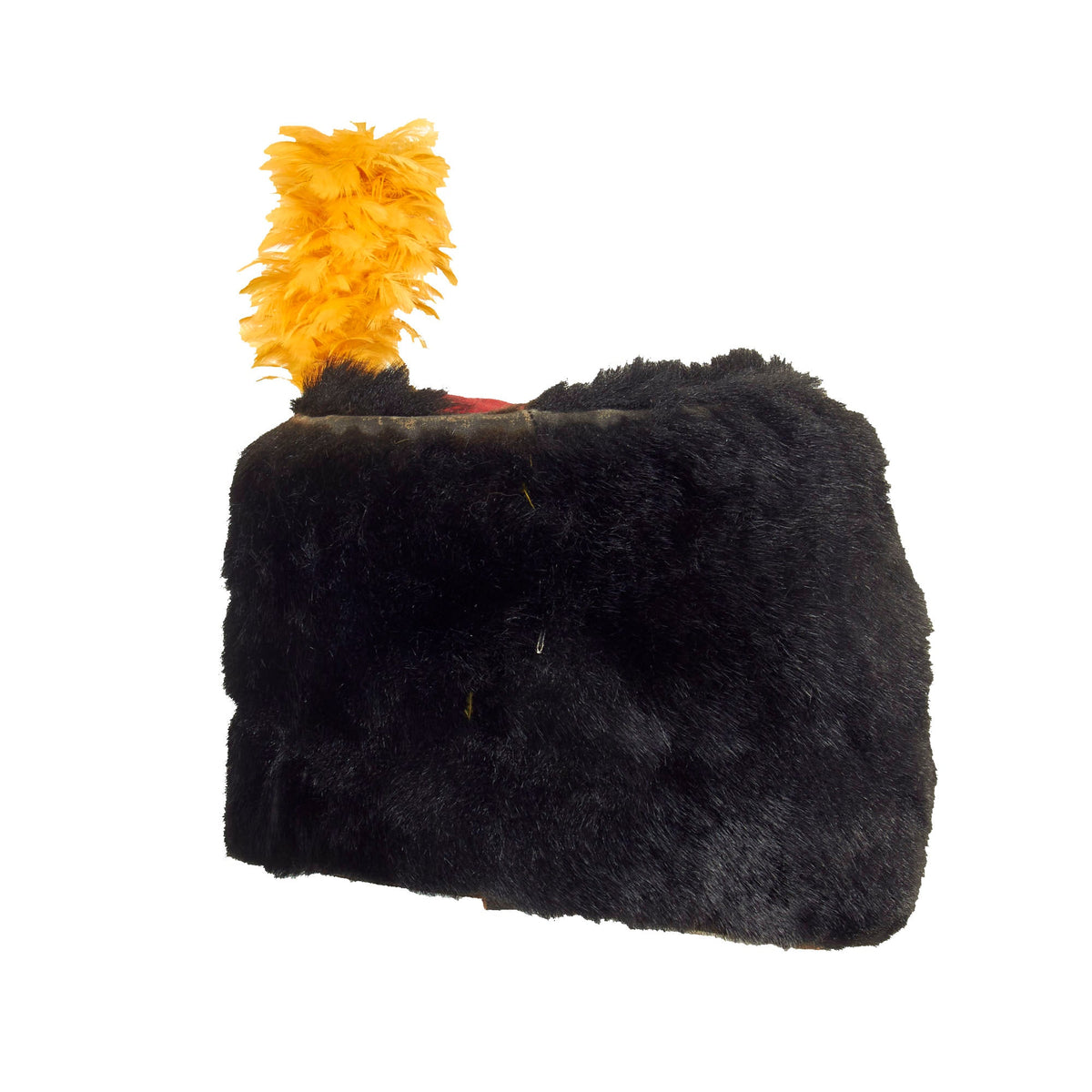
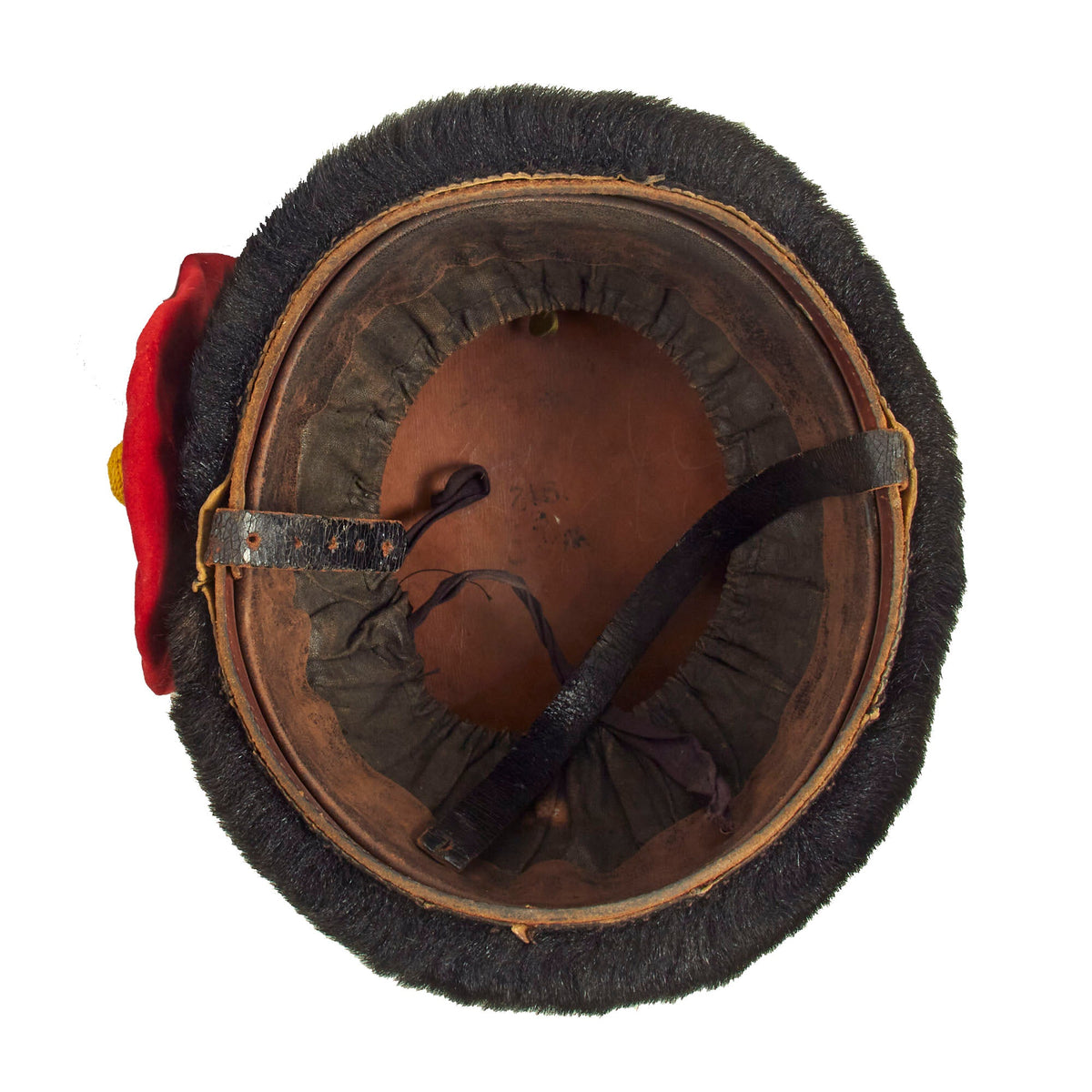
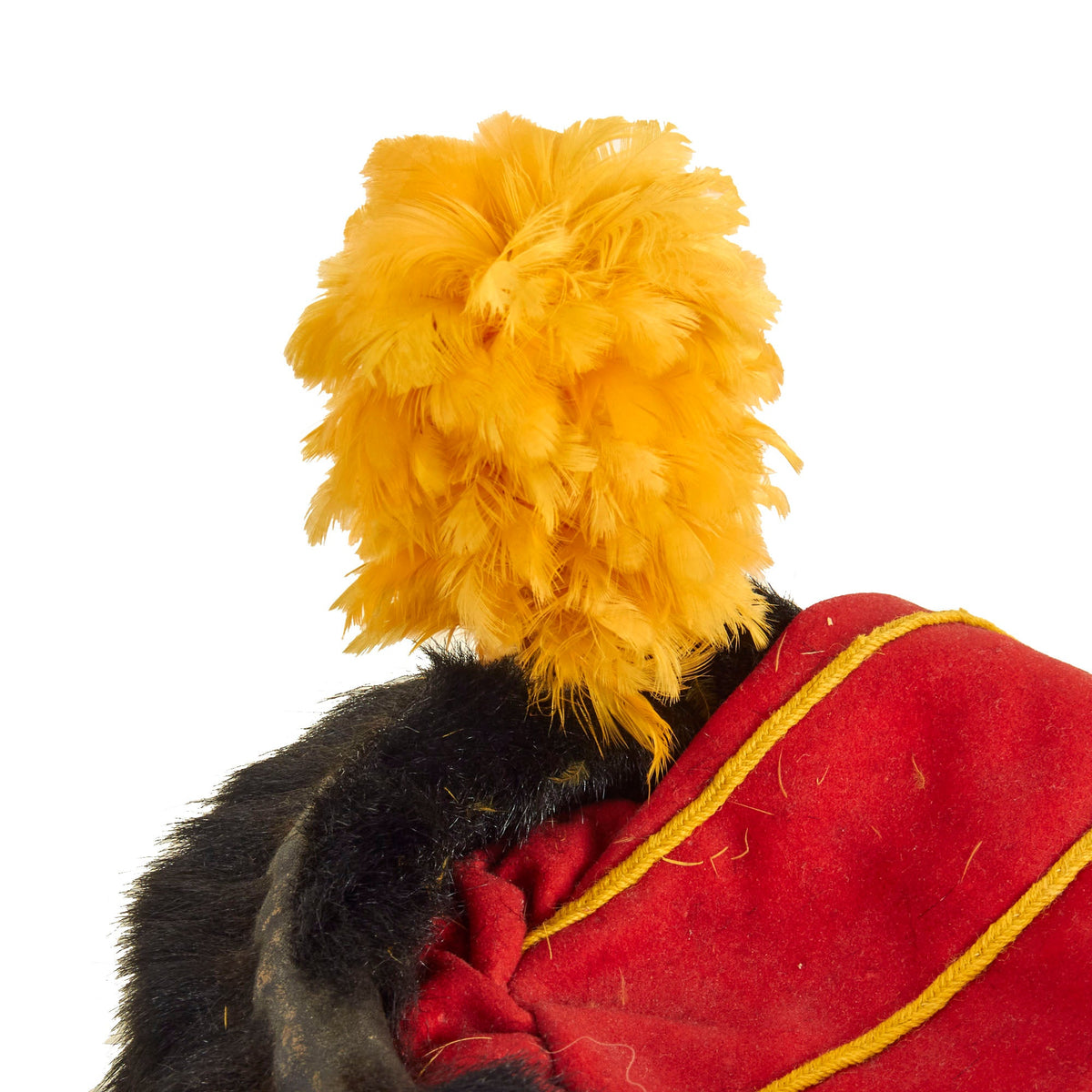
This is a very beautiful genuine fur bearskin Busby used by the 7th Hussars. The helmet is complete with the symbolic right side “Red Bag” and yellow/gold cord surrounding, with chin strap and yellow cockade. Size is approximately a US 7 1/4.
A lovely example ready for further research and display.
Busby is the English name for the Hungarian prémes csákó (“fur shako”) or kucsma, a military head-dress made of fur, originally worn by Hungarian hussars. In its original Hungarian form the busby was a cylindrical fur cap, having a bag of coloured cloth hanging from the top. The end of this bag was attached to the right shoulder as a defense against saber cuts.
In Great Britain busbies are of two kinds: (a) the hussar busby, cylindrical in shape, with a bag; this is worn by hussars and the Royal Horse Artillery; (b) the rifle busby, a folding cap of astrakhan (curly lambswool) formerly worn by rifle regiments, in shape somewhat resembling a Glengarry but taller. Both have straight plumes in the front of the headdress.
The popularity of this military headdress in its hussar form reached a height in the years immediately before World War I (1914–1918).
It was widely worn in the British (hussars, yeomanry, and horse artillery), German (hussars), Russian (hussars), Dutch (cavalry and artillery), Belgian (Guides and field artillery), Bulgarian (Life Guards), Romanian (cavalry), Austro-Hungarian (Hungarian generals), Serbian (Royal Guards), Spanish (hussars and mounted cazadores) and Italian (light cavalry) armies.
There were some variations in the materials of which cavalry busbies were made. Thus Russian Cossacks of the Imperial Guard used black sheepskin, Guard Hussars dark brown long-haired fur, and line Hussars black lambswool. All but one of the twenty Prussian Hussar regiments wore sealskin busbies dyed in black, while their officers favored dark brown otter-skin. The Brunswick Hussar Regiment No. 17 had the distinction of being issued busbies made of bearskin.
Possibly the name’s original sense of a “busby wig” came from association with Richard Busby, headmaster of Westminster School in the late seventeenth century; the later phrase buzz wig may have been derived from busby. An alternative explanation is that the British hussar cap of the early 19th century was named after the hatter who supplied the officer’s version—W. Busby of the Strand London. The modern British busby is worn with full dress by the Waterloo Band of The Rifles, the Royal Horse Artillery and ceremonial detachments at regimental expense. In its hussar version it is now made of black nylon fur, although Bandmasters still retain the original animal fur.
The busby should not be mistaken for the much taller bearskin cap, worn most notably by the five regiments of Foot Guards of the Household Division (Grenadier, Coldstream, Scots, Irish and Welsh Guards). Around 1900 the word “busby” was used colloquially to denote the tall bear and raccoon skin “caps” worn by foot guards and fusiliers and the feather bonnets of Highland infantry. This usage is now obsolete.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Armored Burgonet Helmet & Polearm from Scottish Castle Leith Hall Circa 1700 Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Australian WWII Owen MK1 Machine Carbine SMG Custom Fabricated Replica with Sling Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Band of Brothers ORIGINAL GERMAN WWII Le. F.H. 18 10.5cm ARTILLERY PIECE Original Items
Uncategorized
Angolan Rebel 1970s era 60mm Inert Display Mortar from Angolan Civil War Original Items