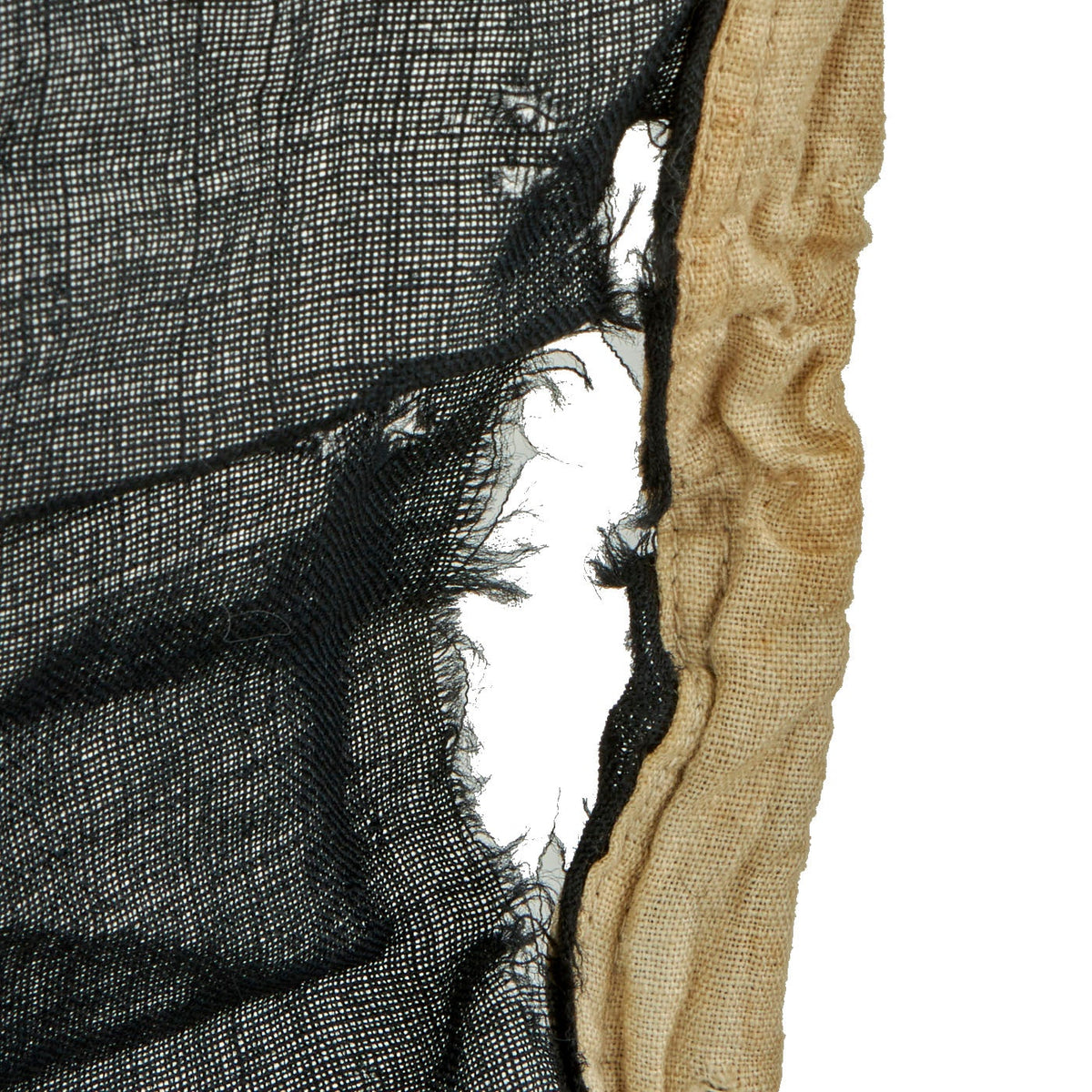
Original Belgian WWII Era Civil Ensign of Belgium Flag 69” x 33” Original Items
$ 295,00 $ 118,00
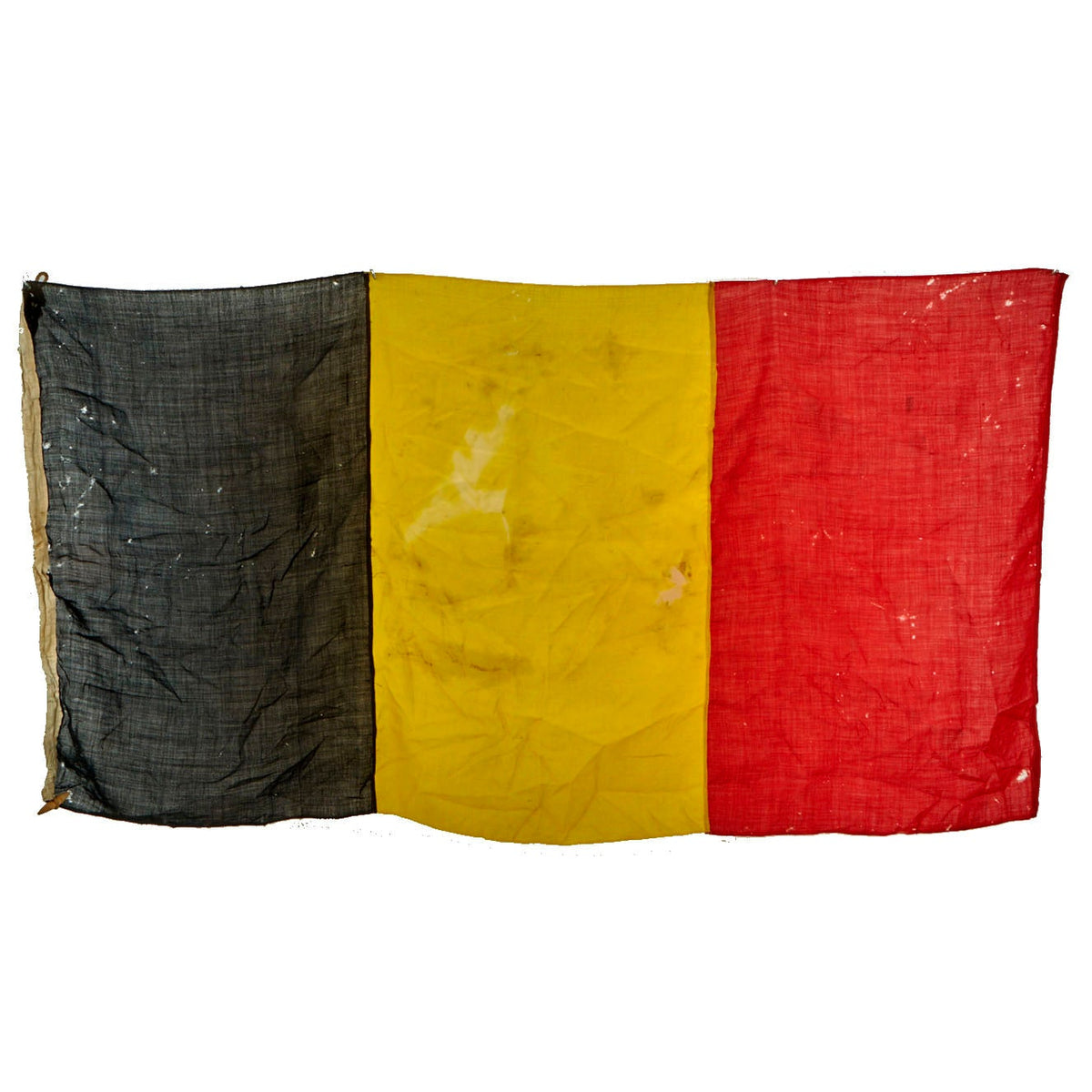
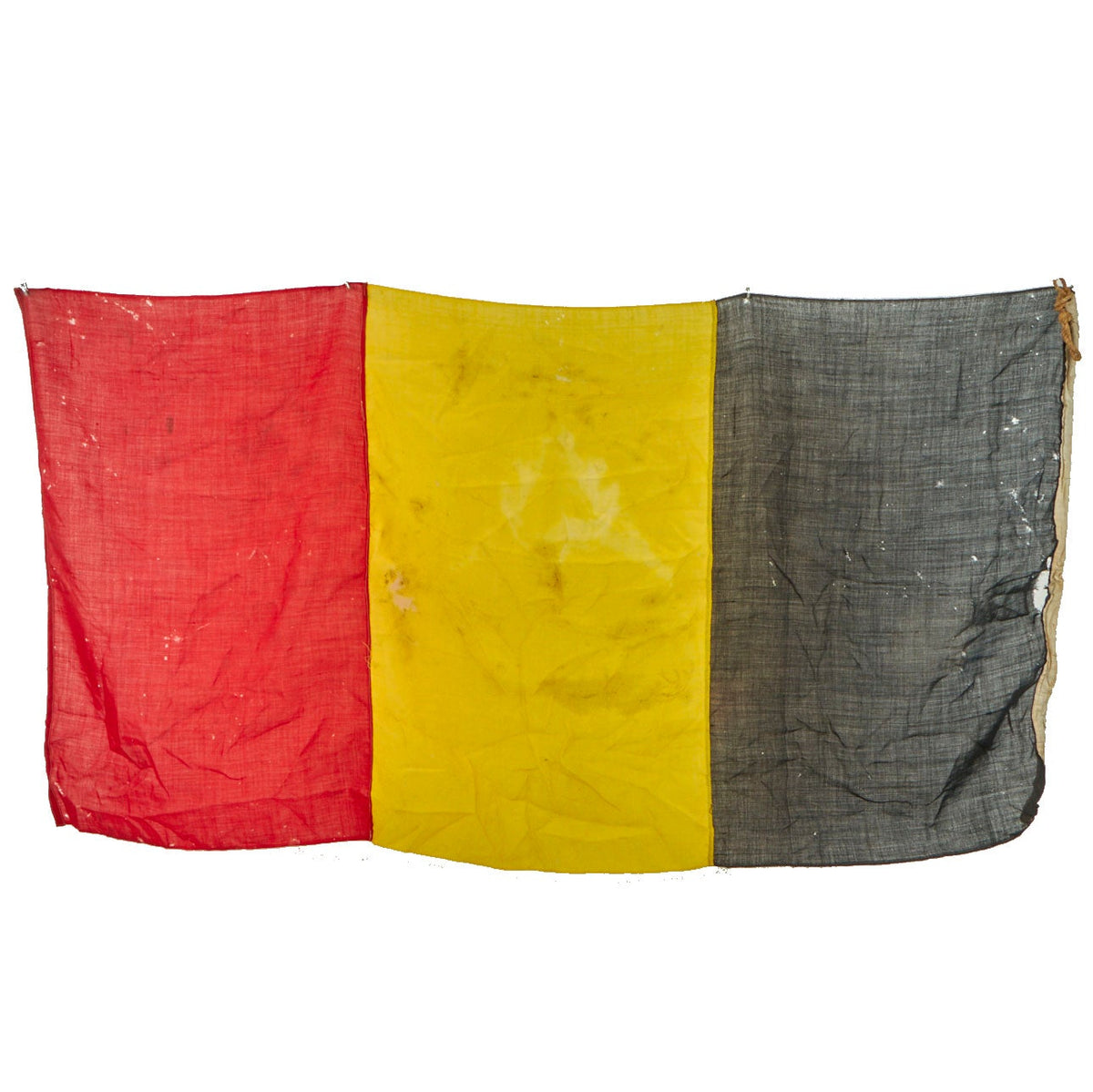
Original Item: Only One Available. The flag of Belgium is a tricolour consisting of three equal vertical bands displaying the national colours of Belgium: black, yellow, and red. The colours were taken from the coat of arms of the Duchy of Brabant, and the vertical design may be based on the flag of France. When flown, the black band is nearest the pole (at the hoist side).
In 1830 the flag, at that time non-officially, consisted of three horizontal bands, with the colors red, yellow and black. On January 23, 1831, the National Congress enshrined the tricolor in the Constitution, but did not determine the direction and order of the color bands. As a result, the “official” flag was given vertical stripes with the colors black, yellow and red.
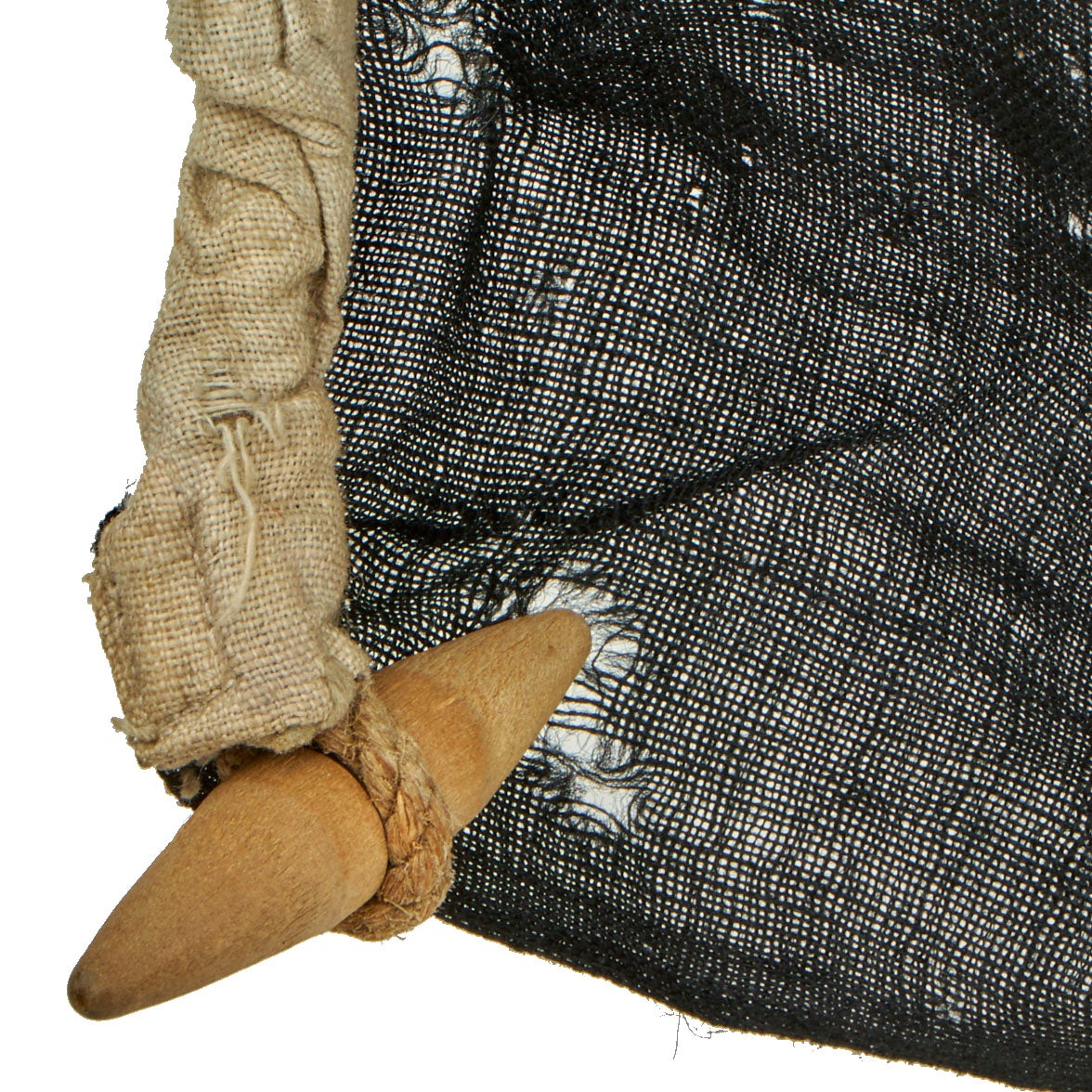
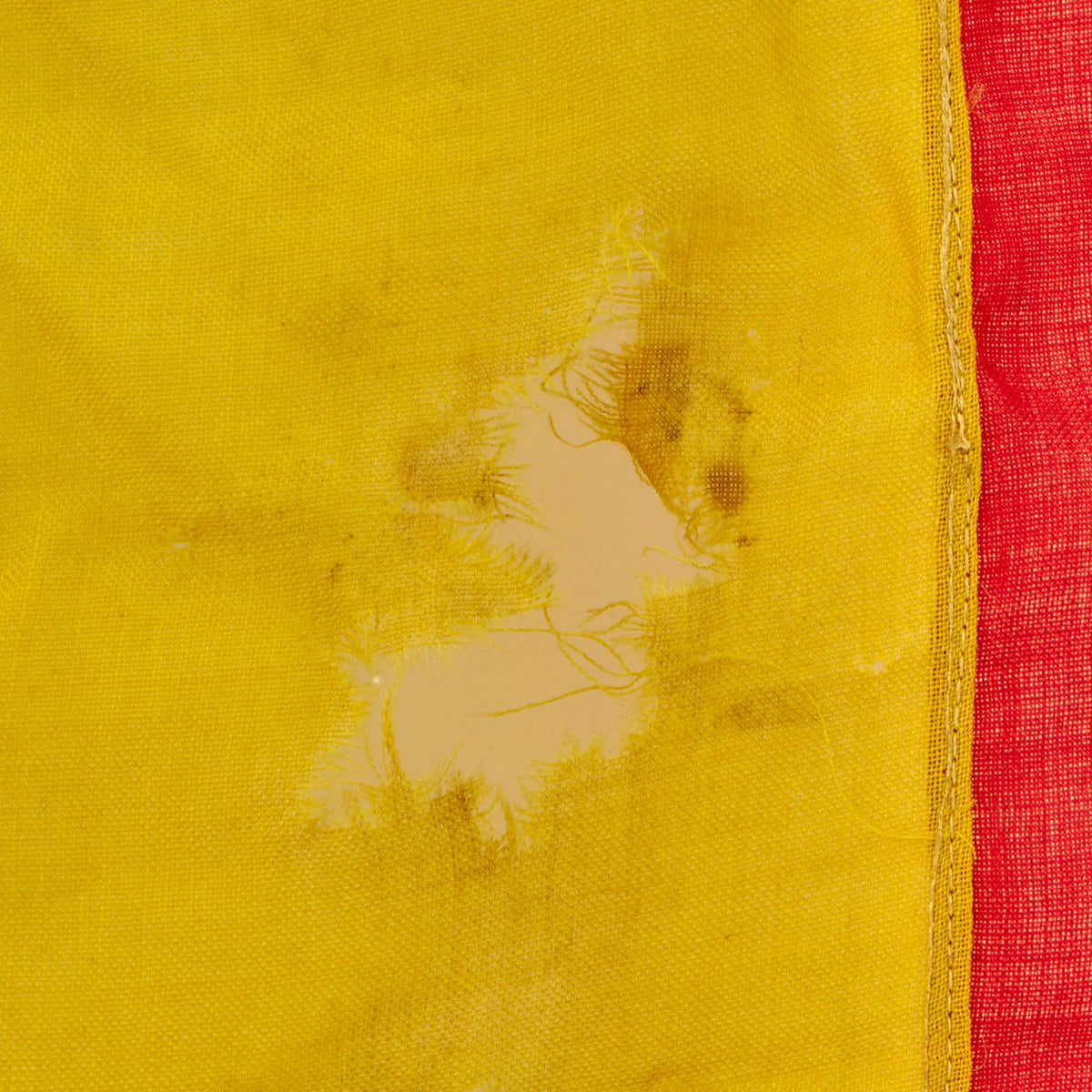
This example measures approximately 69” x 33” and shows signs of heavy use. The flag material is thinning and can be easily seen through. There are some holes throughout the flag, indication it was flown with pride for many years. The hoist side still has the original rope and wooden toggle on the top, in good condition. There is some ghosting of a stamp on the white hoist side edge, but it can no longer be read.
This is a wonderful and proudly used example of a WWII Era Belgian Flag! Comes ready to display in your collections.
Despite being neutral at the start of World War II, Belgium and its colonial possessions found themselves at war after the country was invaded by German forces on 10 May 1940. After 18 days of fighting in which Belgian forces were pushed back into a small pocket in the north-west of the country, the Belgian military surrendered to the Germans, beginning an occupation that would endure until 1944. The surrender of 28 May was ordered by King Leopold III without the consultation of his government and sparked a political crisis after the war. Despite the capitulation, many Belgians managed to escape to the United Kingdom where they formed a government and army-in-exile on the Allied side.
The Belgian Congo remained loyal to the Belgian government in London and contributed significant material and human resources to the Allied cause. Many Belgians were involved in both armed and passive resistance to German forces, although some chose to collaborate with the German forces. Support from far right political factions and sections of the Belgian population allowed the German army to recruit two divisions of the Waffen-SS from Belgium and also facilitated the NSDAP persecution of Belgian Jews in which nearly 25,000 were killed.
Most of the country was liberated by the Allies between September and October 1944, though areas in the far east of the country remained occupied until early 1945. In total, approximately 88,000 Belgians died during the conflict, a figure representing 1.05 percent of the country’s pre-war population, and around 8 percent of the country’s GDP was destroyed.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Australian WWII Owen MK1 Machine Carbine SMG Custom Fabricated Replica with Sling Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Angolan Rebel 1970s era 60mm Inert Display Mortar from Angolan Civil War Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Band of Brothers ORIGINAL GERMAN WWII Le. F.H. 18 10.5cm ARTILLERY PIECE Original Items
Uncategorized
Armored Burgonet Helmet & Polearm from Scottish Castle Leith Hall Circa 1700 Original Items
Uncategorized