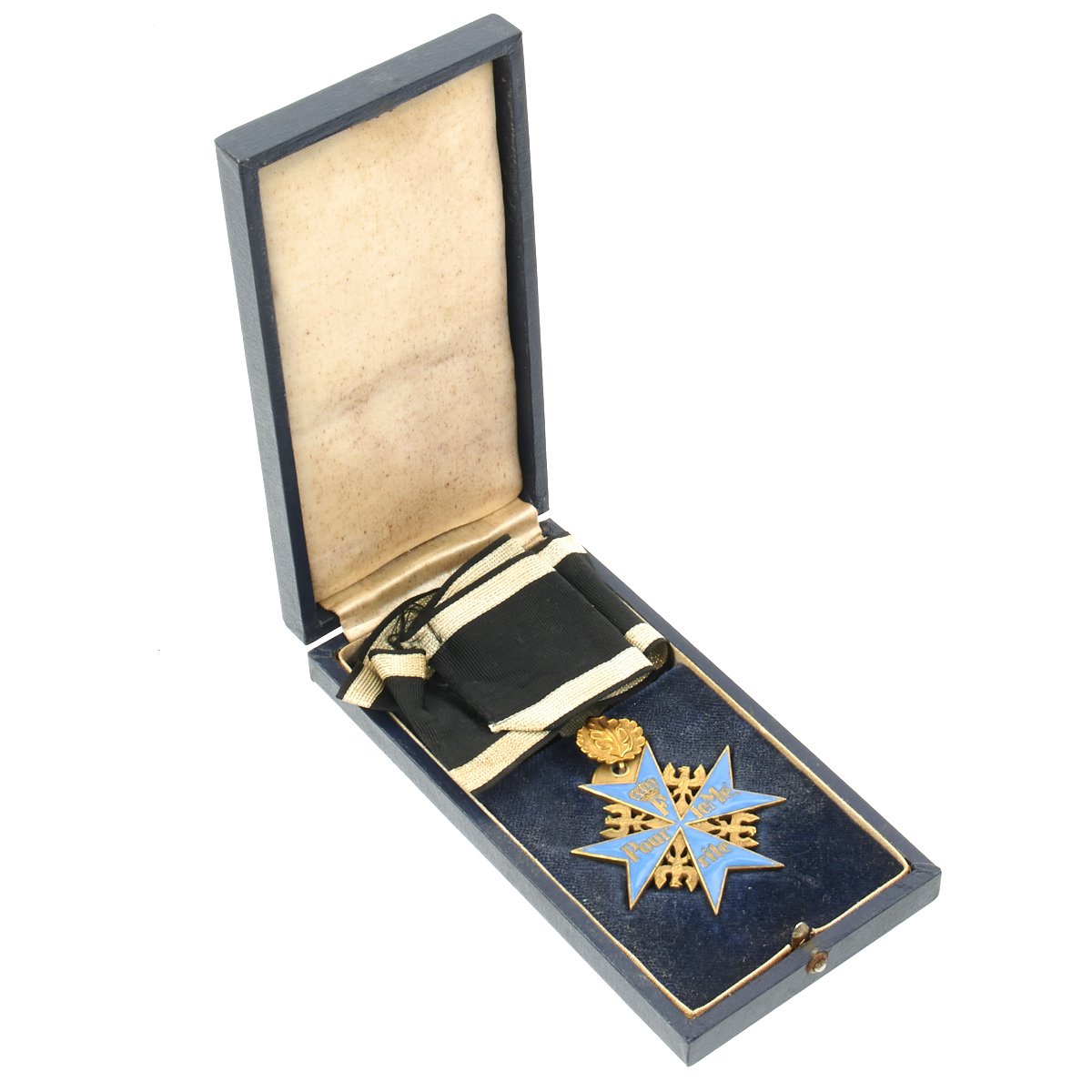
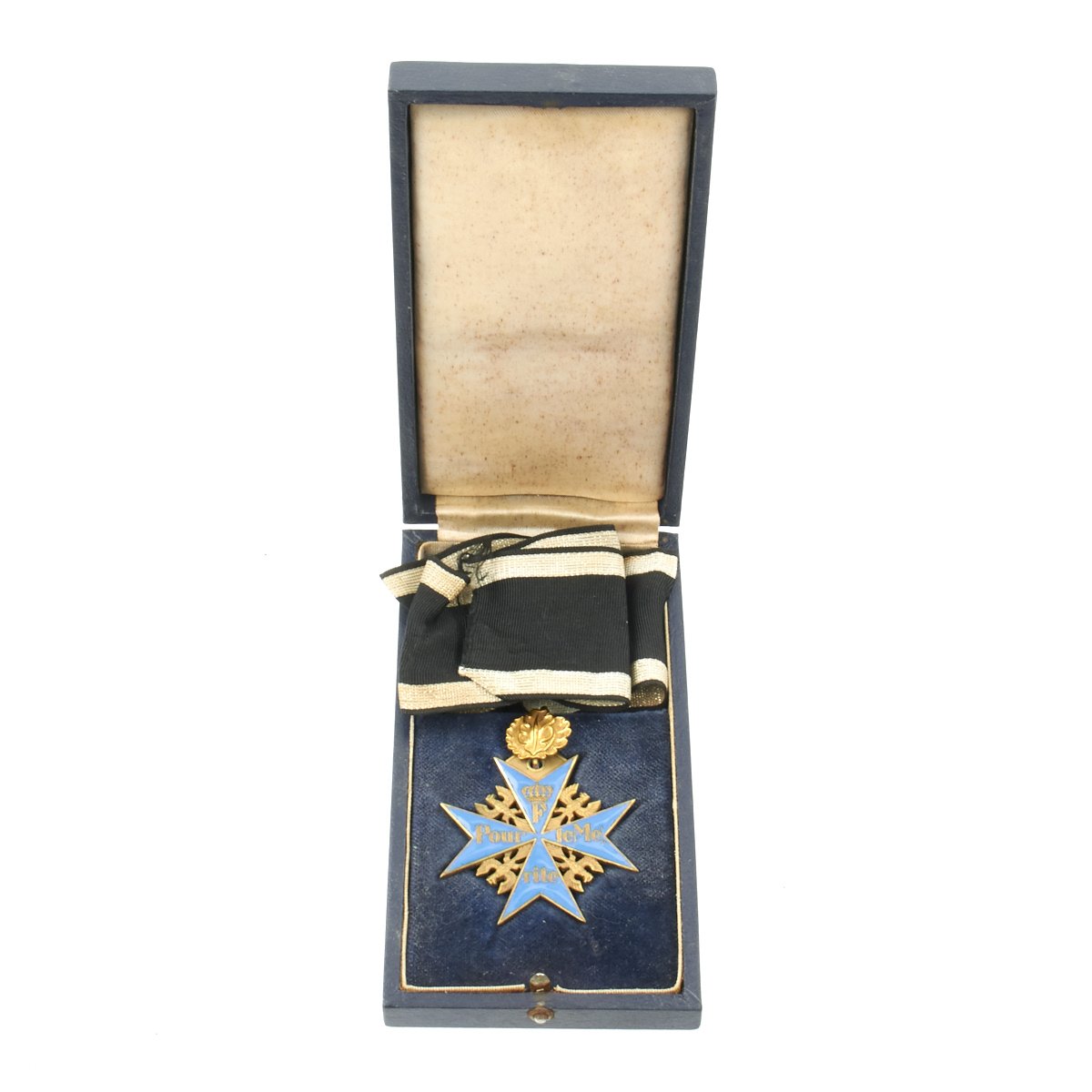
German WWI Prussian Blue Max Medal with Case – High Quality Forgery Original Items
$ 595,00 $ 178,50
Original 196s Production, this Pour le Mérite, or Prussian Blue Max Medal was manufactured to the highest quality and detail during the 1960s with a singular purpose to deceive unsuspecting collectors. It comes complete with ribbon and case which both appear to be original but its unlikely.
The Pour le Mérite ([puʁ lə me.ʁit], French, literally “For Merit”) is an order of merit (German: Verdienstorden) established in 1740 by King Frederick II of Prussia. The Pour le Mérite was awarded as both a military and civil honour and ranked, along with the Order of the Black Eagle, the Order of the Red Eagle and the House Order of Hohenzollern, among the highest orders of merit in the Kingdom of Prussia. After 1871, when the various German kingdoms, grand duchies, duchies, principalities and Hanseatic city states had come together under Prussian leadership to form the federally structured German Empire, the Prussian honours gradually assumed, at least in public perception, the status of honours of Imperial Germany, even though many honours of the various German states continued to be awarded.
The Pour le Mérite was an honour conferred both for military (1740–1918) and civil (1740–1810, after 1842 as a separate class) services. It was awarded strictly as a recognition of extraordinary personal achievement, rather than as a general marker of social status or a courtesy-honour, although certain restrictions of social class and military rank were applied. The order was secular, and membership endured for the remaining lifetime of the recipient, unless renounced or revoked.
New awards of the military class (known in First World War informally as the Blue Max, German: Blauer Max)[3] ceased with the end of the Prussian monarchy in November 1918. The civil class was revived as an independent organization in 1923 (Pour le Mérite für Wissenschaften und Künste). Instead of the King of Prussia, the President of Germany acted as head of the order. After the Second World War, the civil class was re-established in 1952. This version of the Pour le Mérite is still active today. The Pour le Mérite is still an order into which a person is admitted into membership, like the United Kingdom’s Order of the British Empire, and is not simply a medal or state decoration. German author Ernst Jünger, who died in 1998, was the last living recipient of the military class award.
Origins
The Pour le Mérite was founded in 1740 by King Frederick II of Prussia.[5] It was named in French, which was the leading international language and the favoured language at Frederick’s court[6]. The French name was retained, despite the rising tide of nationalism and increasing hostility between French and Germans during the 19th century, and ironically many of its recipients were honoured for acts performed in wars against France. The insignia of the military award was a blue-enameled Maltese Cross with golden eagles between the arms (which is based on the symbol of the Johanniter Order) and the Prussian royal cypher and the words Pour le Mérite (“For Merit” in French) written in gold letters on the body of the cross. The ribbon was black with edge stripes of silver-white. The order consisted of only one class, both civil and military, until 1810. Only a few civilians were honored: Pierre Louis Maupertuis (1747), Francesco Algarotti (1747)[9] and Voltaire (1750).
Military class
In January 1810, during the Napoleonic wars, King Frederick William III decreed that the award could be presented only to serving military officers. In March 1813, the king added an additional distinction, a spray of gilt oak leaves attached above the cross. Award of the oak leaves originally indicated extraordinary achievement in battle, and was usually reserved for high-ranking officers.
The original regulations called for the capture or successful defense of a fortification, or victory in a battle. By World War I, the oak leaves often indicated a second or higher award of the Pour le Mérite, though in most cases the recipients were still high-ranking officers (usually distinguished field commanders fitting the criteria above; the few lower ranking recipients of the oak leaves were mainly general staff officers responsible for planning a victorious battle or campaign). In early 1918, it was proposed to award the oak leaves to Germany’s top flying ace, Manfred von Richthofen, but he was deemed ineligible under a strict reading of the regulations. Instead, Prussia awarded von Richthofen a slightly less prestigious honor, the Order of the Red Eagle, 3rd Class with Crown and Swords. This was still a high honor, as the 3rd Class was normally awarded to colonels and lieutenant colonels, and von Richthofen’s award was one of only two of the 3rd Class with Crown and Swords during World War I.
In 1866, a special military Grand Cross class of the award was established. This grade of the award was given to those who, through their actions, caused the retreat or destruction of an army. There were only five awards of the Grand Cross: to King Wilhelm I in 1866, to Crown Prince Frederick William of Prussia (later Emperor Frederick III) and Prince Frederick Charles of Prussia in 1873, to Tsar Alexander II of Russia in 1878, and to Helmuth Graf von Moltke in 1879.
The Pour le Mérite gained international fame during World War I. Although it could be awarded to any military officer, its most famous recipients were the pilots of the German Army Air Service (Luftstreitkräfte), whose exploits were celebrated in wartime propaganda. In aerial warfare, a fighter pilot was initially entitled to the award upon downing eight enemy aircraft.[3] Aces Max Immelmann and Oswald Boelcke were the first airmen to receive the award, on January 12, 1916. It was awarded to Germany’s highest-scoring ace, Manfred von Richthofen, in January 1917. Although it has been reported[14] that because of Immelmann’s renown among his fellow pilots and the nation at large, the Pour le Mérite became known, due to its color and Immelmann’s first name, as the “Blue Max,” that has not been confirmed.
The number of aerial victories necessary to receive the award continued to increase during the war; by early 1917, it generally required destroying 16 enemy airplanes, and by war’s end the approximate figure was 30. However, other aviation recipients included zeppelin commanders, bomber and observation aircrews, and at least one balloon observer.
Recipients of the “Blue Max” were required to wear the award whenever in uniform. Although many of its famous recipients were junior officers, especially pilots, more than a third of all awards in World War I went to generals and admirals. Senior officer awards tended to be more for outstanding leadership in combat than for individual acts of bravery.
Junior officers (army captains and lieutenants and their navy equivalents) accounted for only about a fourth of all awards. Several famous lieutenant-ranked (Kapitänleutnant) U-boat commanders, including Lothar von Arnauld de la Perière (U-35), Walther Schwieger (U-20) Otto Hersing (U-21) and Otto Weddigen, received the Pour le Mérite. The last new member admitted to the military class of the order was flying ace Theo Osterkamp, on 2 September 1918.
The military class of the Pour le Mérite became extinct as a result of Kaiser William II’s abdication as king of Prussia and German Emperor on 9 November 1918. This marked the end of the Prussian monarchy and it was never awarded thereafter; however the honour continued to be recognized for, and worn by, previous recipients.
Prompt Shipping and Professional Packaging
We provide a variety of shipping options due to our long-running partnerships with UPS, FedEx and DHL. Our warehouse personnel are well trained and will pack the goods according to our exact and precise specifications. Before shipping your items will be thoroughly inspected and secured. Every day, we deliver to thousands of customers in different countries. This is a sign of our determination to become the largest online retailer worldwide. Both Europe as well as the USA have warehouses and distribution centers.
Note that orders containing more than one item will be subject to a processing period that is based to the particular item.
Prior to shipping the items, our staff will carry out an exhaustive inspection of the products you ordered. Today, most orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The estimated delivery time is between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is constantly changing. It's not entirely managed by us since we are involved with multiple entities, including the factory and our storage. Therefore, the actual inventory could alter at any time. It is possible that you will not receive your order after the order has been made.
The period of time is 30 days. Unfortunately, if 30 days have passed since you purchased your product, we are unable to provide a refund or exchange.
The item must not be in use and must be in the original packaging. The item must be in the original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Armoured Fighting Vehicles of the World: AFVs of World War One (Hardcover Book) New Made Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Angolan Rebel 1970s era 60mm Inert Display Mortar from Angolan Civil War Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized