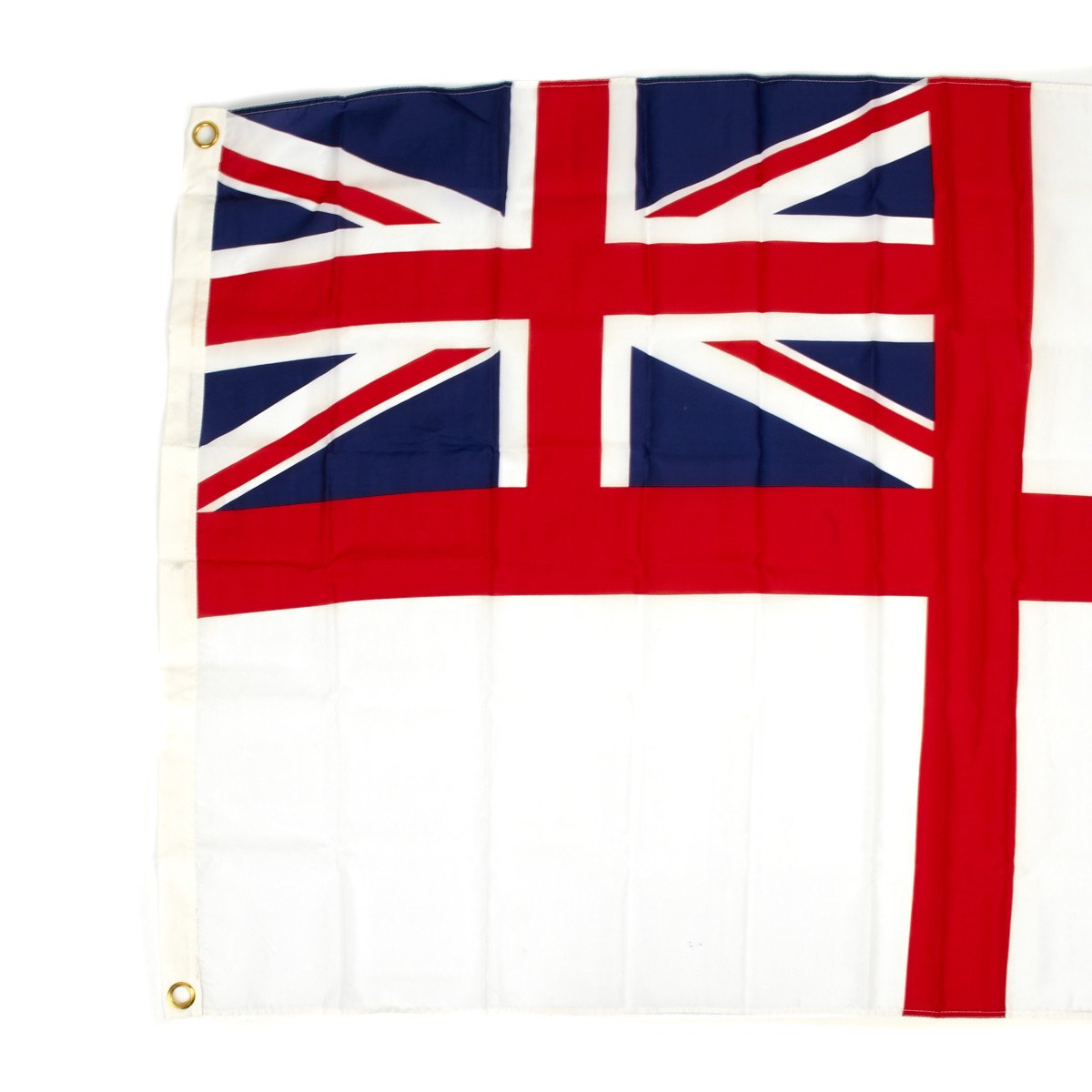
British Naval The White Ensign Flag – St George’s Ensign 3′ x 5′ New Made Items
$ 14,95 $ 8,97
New Made Item: Top quality 3′ x 5′ flag. Ready to display. Complete with 2 hang side Grommets. Constructed of Synthetic Material.
The White Ensign, at one time called the St George’s Ensign due to the simultaneous existence of a cross-less version of the flag, is an ensign flown on British Royal Navy ships and shore establishments. It consists of a red St George’s Cross on a white field with the Union Flag in the upper canton.
The White Ensign is also flown by yachts of members of the Royal Yacht Squadron and by ships of Trinity House escorting the reigning monarch.
In addition to the United Kingdom, several other nations have variants of the White Ensign with their own national flags in the canton, with the St George’s Cross sometimes being replaced by a naval badge omitting the cross altogether. Yachts of the Royal Irish Yacht Club fly a white ensign with an Irish tricolour in the first quadrant and defaced by the crowned harp from the Heraldic Badge of Ireland. The Flag of the British Antarctic Territory and the Commissioners’ flag of the Northern Lighthouse Board place the Union emblem in the first quarter of a white field, omitting the overall red St George’s Cross, but are not ensigns for use at sea.
English naval ensigns were first used during the 16th century, and were often striped in green and white (the Tudor colours), but other colours were also used to indicate different squadrons, including blue, red and tawny brown. (These striped ensigns can be seen in use on both English and Spanish warships in contemporary paintings of the 1588 Spanish Armada battles). Later, there was usually a St George’s Cross in the upper canton, or sewn across the field as on the modern White Ensign. These striped ensigns continued in use under the Stuart kings: the Naval ensign of 1623 is described as having “15 horizontal stripes alternately blue, white and yellow with a Cross of St George in the canton”. This design fell out of use after 1630, with the introduction of the Red, White and Blue ensigns. The use of stripes continued in the red and white of both the flag of the Honourable East India Company, adopted in 1600, and of the 1775 Grand Union Flag that formed the basis for the modern flag of the United States of America, and the red, white and blue striped ensign that serves as the flag of Hawaii.
The first recognisable White Ensign appears to have been in use during the 16th century, consisting of a white field with a broad St George’s cross, and a second St. George’s cross in the canton. By 1630 the white ensign consisted of simply a white field, with a small St George’s cross in the canton, which was consistent with the red and blue ensigns of the time. In 1707, the St. George’s cross was reintroduced to the flag as a whole, though not as broad as before, and the Union Flag was placed in the canton. There was also a version of this flag without the overall St George’s cross, which appears to have been for use in home waters only, though this flag appears to have fallen out of use by 1720. In 1801, after the Act of Union 1800, the flag was updated to include the new Union Flag in the canton, and so took on the form as used today. The blue field of the Union Flag was darkened at this time at the request of the Admiralty, in the hope that the new flags would not require replacing as often as the previous design, due to fading of the blue. Throughout this period, the proportions of the flags changed. In 1687, the then Secretary of the Admiralty, Samuel Pepys, instructed that flags be of the ratio 11:18 (18 inches long for each breadth, 11 inches at the time). In the early 18th century, the breadth of cloth had been reduced to 10 inches, so the flags became 5:9. In 1837, the breadth was reduced for the final time to 9 inches, giving the current ratio of 1:2.
Throughout this period in the history of the Royal Navy, the White Ensign was one of three ensigns in use, with each one being assigned to one of the three squadrons of the navy, according to its colour (red, white and blue, with red being the most senior and blue the least). Ships flew the colour of ensign corresponding to the squadron to which they were attached, which was in turn determined by the seniority of the admiral under whose command the ship sailed (a rear admiral of the red was senior to a rear admiral of the white).
In 1864 the Admiralty decided to end the ambiguity caused by the Red Ensign being both a civil ensign and a naval ensign, and the White Ensign was reserved to the Royal Navy; the relevant Order in Council retained the option to use Red or Blue Ensigns in HM Ships if desired.
Prompt Shipping and Professional Packaging
We provide a variety of shipping options due to our long-running partnerships with UPS, FedEx and DHL. Our warehouse personnel are well trained and will pack the goods according to our exact and precise specifications. Before shipping your items will be thoroughly inspected and secured. Every day, we deliver to thousands of customers in different countries. This is a sign of our determination to become the largest online retailer worldwide. Both Europe as well as the USA have warehouses and distribution centers.
Note that orders containing more than one item will be subject to a processing period that is based to the particular item.
Prior to shipping the items, our staff will carry out an exhaustive inspection of the products you ordered. Today, most orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The estimated delivery time is between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is constantly changing. It's not entirely managed by us since we are involved with multiple entities, including the factory and our storage. Therefore, the actual inventory could alter at any time. It is possible that you will not receive your order after the order has been made.
The period of time is 30 days. Unfortunately, if 30 days have passed since you purchased your product, we are unable to provide a refund or exchange.
The item must not be in use and must be in the original packaging. The item must be in the original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Angolan Rebel 1970s era 60mm Inert Display Mortar from Angolan Civil War Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Australian WWII Owen MK1 Machine Carbine SMG Custom Fabricated Replica with Sling Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized