Original German WWII HJ / DAF Kreis Level National Trade Competition Badge by G. Brehmer of Markneukirchen – Kreissieger Original Items
$ 250,00 $ 100,00
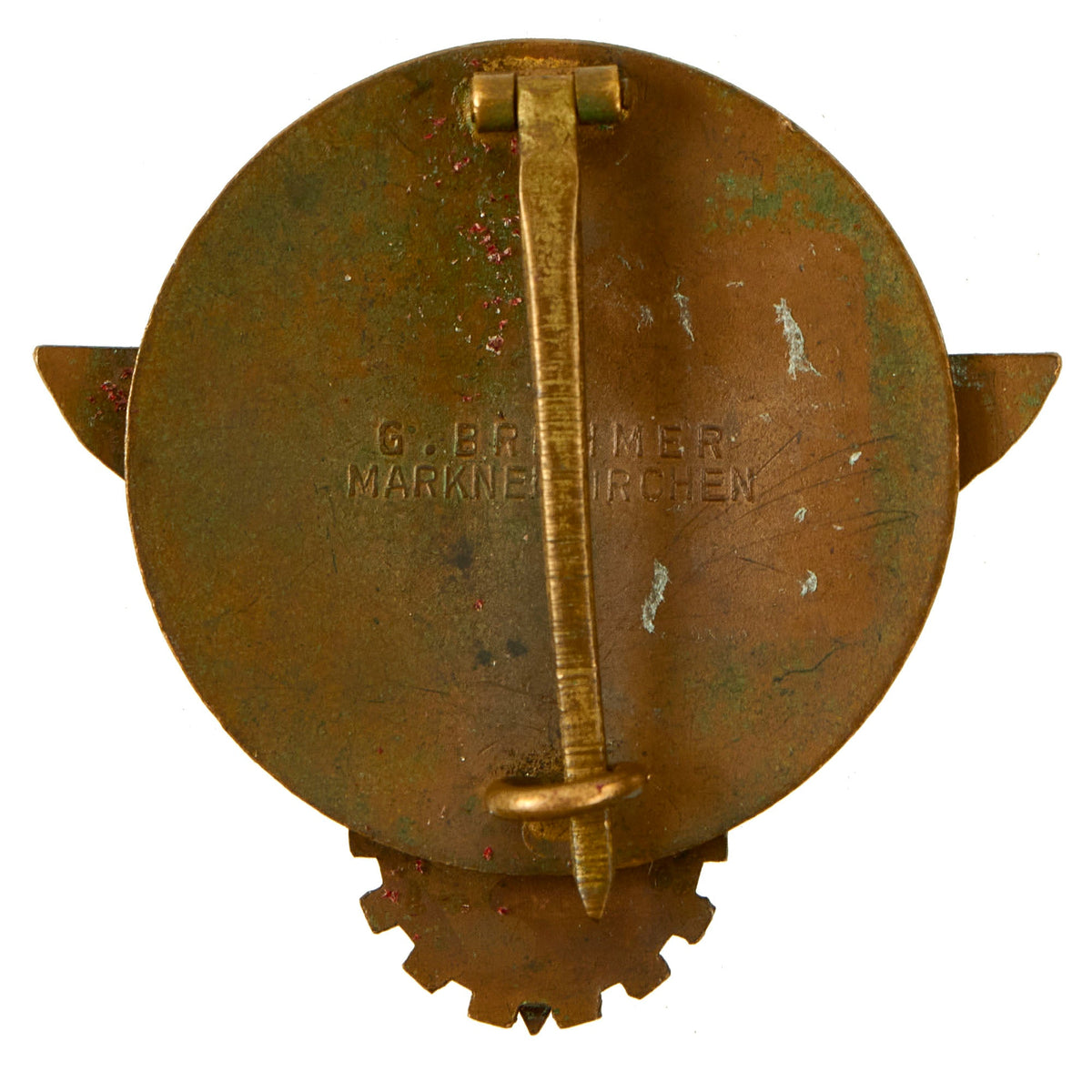
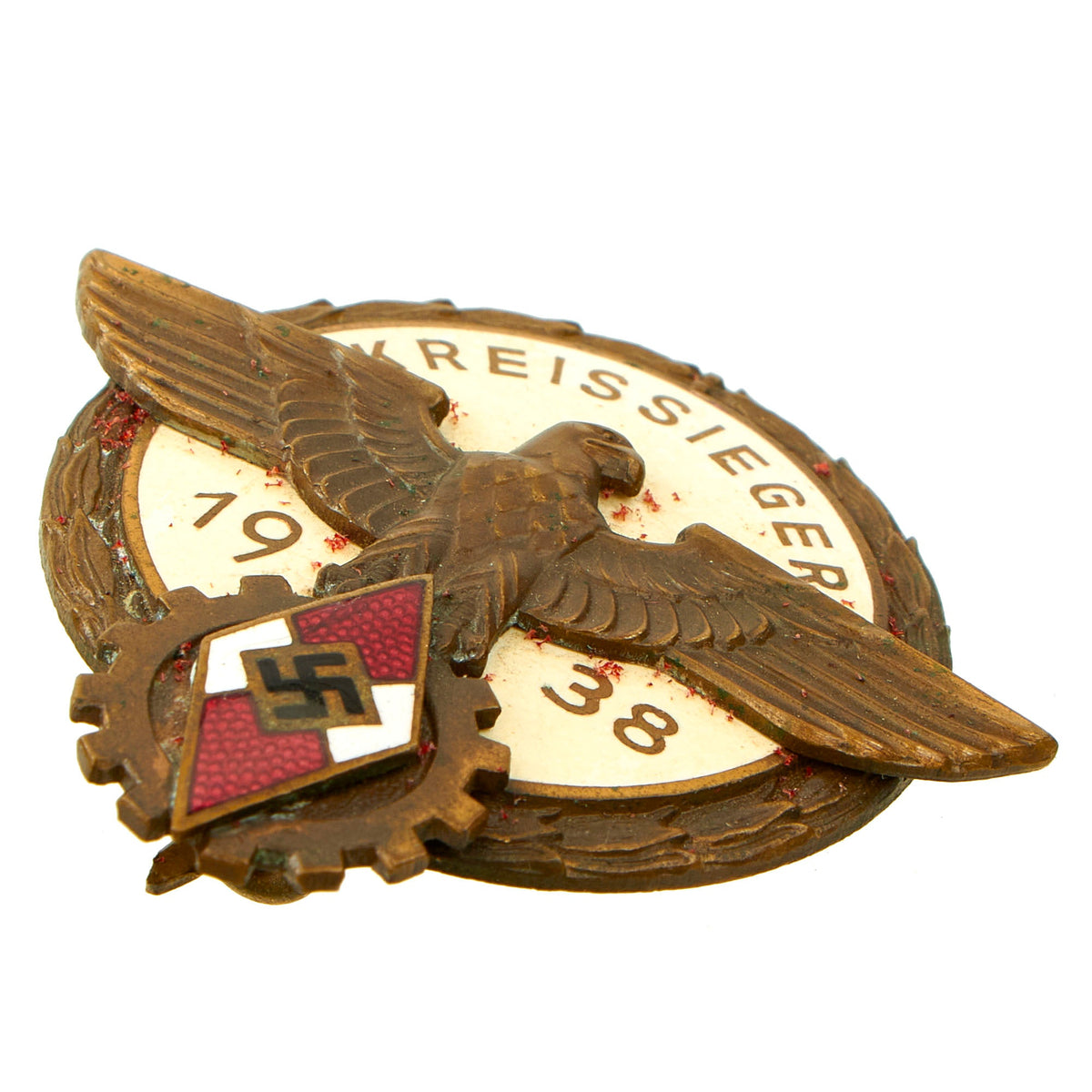
Original Item: Only One Available. This is a very nice German WWII Kreissieger Abzeichen im Reichsberufswettkampf (District Winner Badge in the National Trade Competition), one of the many awards given to members of the HJ National Youth Association. The badge is made from bronze-plated tombak alloy, and features multi-colored enamel work. The badge shows a central “spread wing” eagle perched on a DAF “Gear” insignia, which is surmounted by a HJ Diamond insignia. The background is a large white circle with a laurel leaf wreath surrounding it, which is marked with KREISSIEGER 1938 (District Winner 1938).
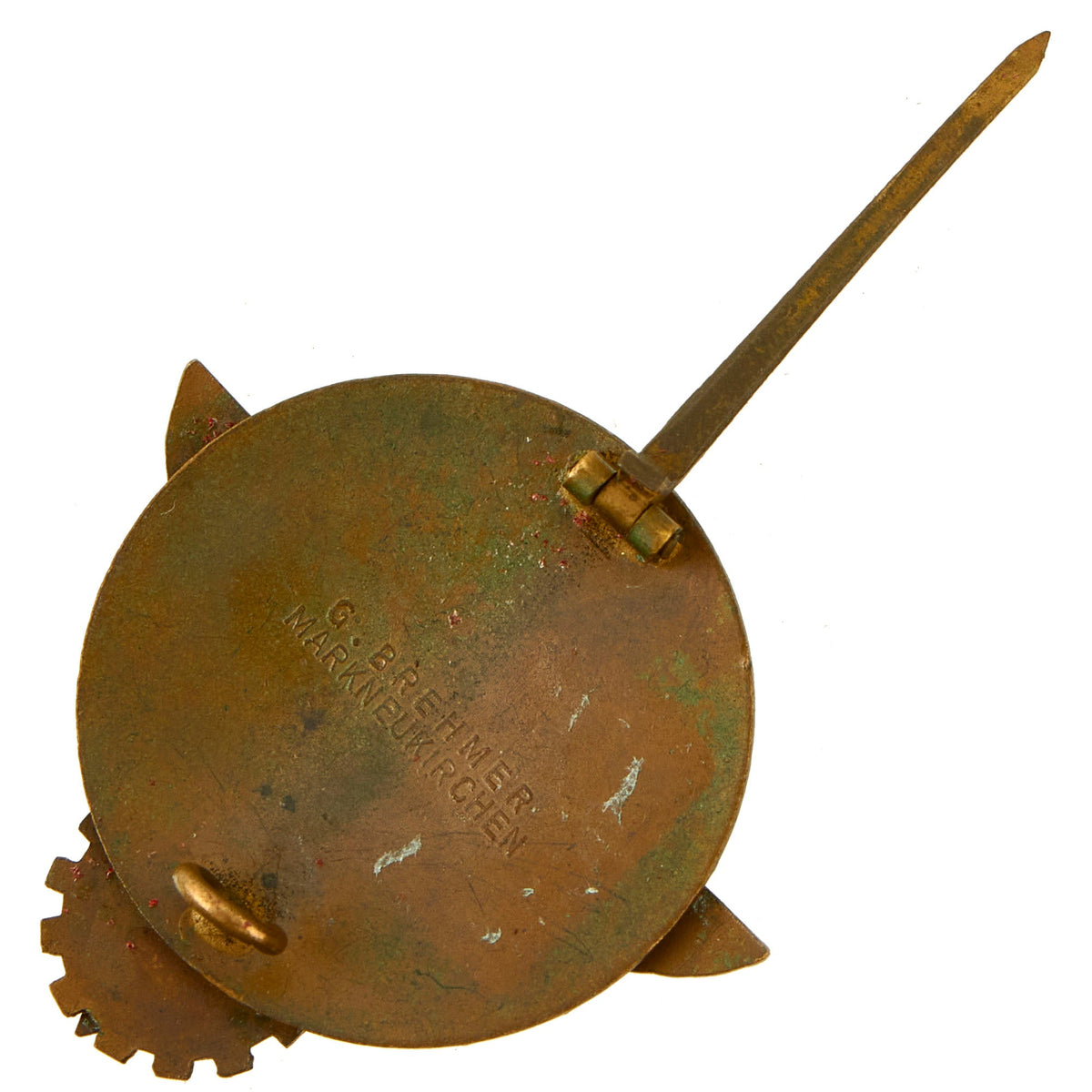
The rear of the badge features a vertical pinback, which is fully functional, and has a clear maker marking of G. BREHMER / MARKNEUKIRCHEN. Condition overall is very good, with the original plating partly retained, and all metal surfaces showing a lovely oxidized patina. The enamel is retained at nearly 100%, showing just a bit of light wear. There is a bit of red residue from an old foam rubber case, which can easily be removed.
A lovely example of a hard to find badge! Ready to display!
In February 1934, National Youth Leader Baldur von Schirach and Dr. Robert Ley, head of the German Labor Front collaborated in a joint effort to institute a National Trade Competition to encourage German youth to develop proficient skills in manual, technical or professional trades. The competitions consisted of twenty main categories with over seven hundred assorted trades being represented. All participants were required to belong to the HJ, DAF, or another NSDAP organization, and only those under 21 years old were eligible to compete. Participants were required to demonstrate their particular skills and successfully complete appropriate written tests. The competitions were held at the three different political levels with the winners advancing to the next level. Local, (Kreis), level competitions were held in February followed by the State, (Gau), level competitions in March and the National, (Reichs), level competitions held in April, with the National winners being bestowed their awards by Adolf H personally on May 1ST, the Day of National Labor. Although all competitors were issued a participants badge and certificate, originally only the National winners were bestowed an actual award with corresponding certificate. In 1938 a new award was instituted in three grades with the colored finish determining the grade of the award as follows, gold finish for the Reichs level award, a silver finish for the Gau level award and a bronze finish for the Kreis level award. Of Note: In 1938 eligibility to compete in the National Trade Competitions was extended to include those over 21 years old and participants were no longer required to belong to an NSDAP organization. After the outbreak of the war the competition was renamed, Kreigsberufswettkampf, (War Trade Competition), with the last event held in 1944.
With the dissolution of all Free Trade Unions in Germany in May 1933 the Deutsche Arbeitsfront, (German Labor Front), was established to replace the unions and to educate the workers in industry and commerce for smooth and efficient operation of all labor in the Third Reich. In October 1934 the DAF was given official status as a sub-section of the NSDAP and in March 1936 it was recognized as an independent NSDAP affiliated association and granted control of its own monetary budget. In 1934 the first pattern of DAF uniform was introduced for DAF Werkscharen, (Work Squads), and a belt buckle was introduced in late 1935 for wear by all ranks.
AH believed German youth to be the future of his 3rd Reich. The H Jugend (or HJ) National Youth Organization was formed officially in 1935, and with the exception of NSDAP ideology indoctrination was very similar to the Boy Scouts. Beginning at about the age of ten years, both boys (AH Jugend) and girls (Bund Deutscher Mädel) were enlisted in the Party-run organization. The The Deutsches Jungvolk (DJ) was the junior branch of the HJ, for boys aged 10 to 14.
History of the HJ National Youth Organization:
In 1922, the Munich-based NSDAP established its official youth organization called Jugendbund der NSDAP. It was announced on 8 March 1922 in the Völkischer Beobachter, and its inaugural meeting took place on 13 May the same year. Another youth group was established in 1922 as the Jungsturm Adolf “AH”. Based in Munich, Bavaria, it served to train and recruit future members of the Sturmabteilung (SA), the main paramilitary wing of the NSDAP Party at that time.
One reason the HJ so easily developed was that regimented organizations, often focused on politics, for young people and particularly adolescent boys were a familiar concept to German society in the Weimar Republic. Numerous youth movements existed across Germany prior to and especially after World War I. They were created for various purposes. Some were religious and others were ideological, but the more prominent ones were formed for political reasons, like the Young Conservatives and the Young Protestants. Once AH came onto the revolutionary scene, the transition from seemingly innocuous youth movements to political entities focused on AH was swift.
Following the abortive Beer Hall Putsch (in November 1923), NSDAP youth groups ostensibly disbanded, but many elements simply went underground, operating clandestinely in small units under assumed names. In April 1924, the Jugendbund der NSDAP was renamed Grossdeutsche Jugendbewegung (Greater German Youth Movement). On 4 July 1926, the Grossdeutsche Jugendbewegung was officially renamed HJ Bund der deutschen Arbeiterjugend (HJ League of German Worker Youth). This event took place a year after the NSDAP Party was reorganised. The architect of the re-organization was Kurt Gruber, a law student from Plauen in Saxony.
After a short power struggle with a rival organization—Gerhard Roßbach’s Schilljugend—Gruber prevailed and his “Greater German Youth Movement” became the NSDAP Party’s official youth organisation. In July 1926, it was renamed H -Jugend, Bund deutscher Arbeiterjugend (“H” Youth, League of German Worker Youth”) and, for the first time, it officially became an integral part of the SA. The name H -Jugend was taken up on the suggestion of Hans Severus Ziegler. By 1930, the Hjugend (HJ) had enlisted over 25,000 boys aged 14 and upward. They also set up a junior branch, the Deutsches Jungvolk (DJ), for boys aged 10 to 14. Girls from 10 to 18 were given their own parallel organization, the League of German Girls (BDM).
In April 1932, Chancellor Heinrich Brüning banned the H Youth movement in an attempt to stop widespread political violence. However, in June, Brüning’s successor as Chancellor, Franz von Papen, lifted the ban as a way of appeasing “AH”, the rapidly ascending political star. A further significant expansion drive started in 1933, after Baldur von Schirach was appointed by H as the first Reichsjugendführer (Reich Youth Leader). All youth organizations were brought under Schirach’s control.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Armoured Fighting Vehicles of the World: AFVs of World War One (Hardcover Book) New Made Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Angolan Rebel 1970s era 60mm Inert Display Mortar from Angolan Civil War Original Items
Uncategorized