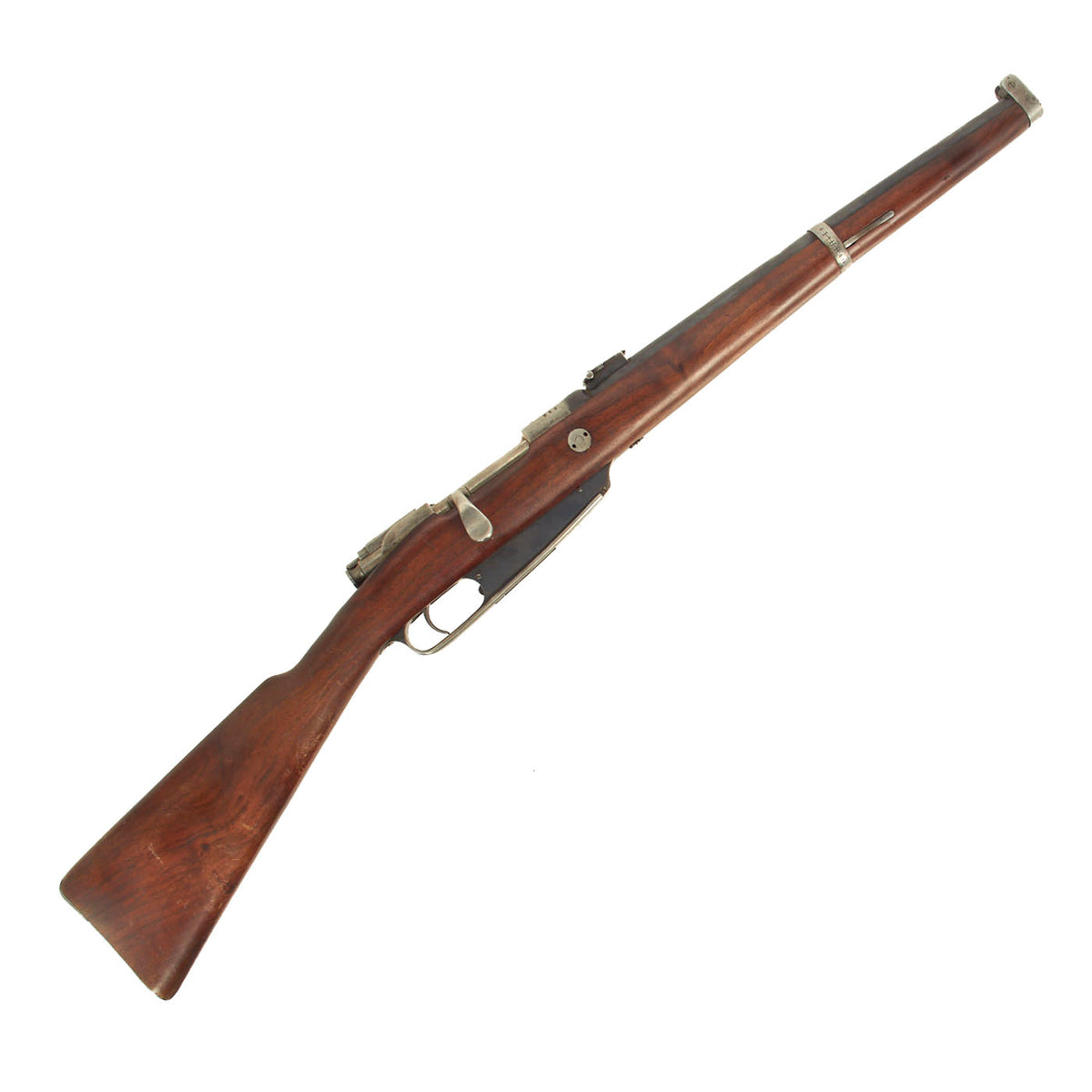
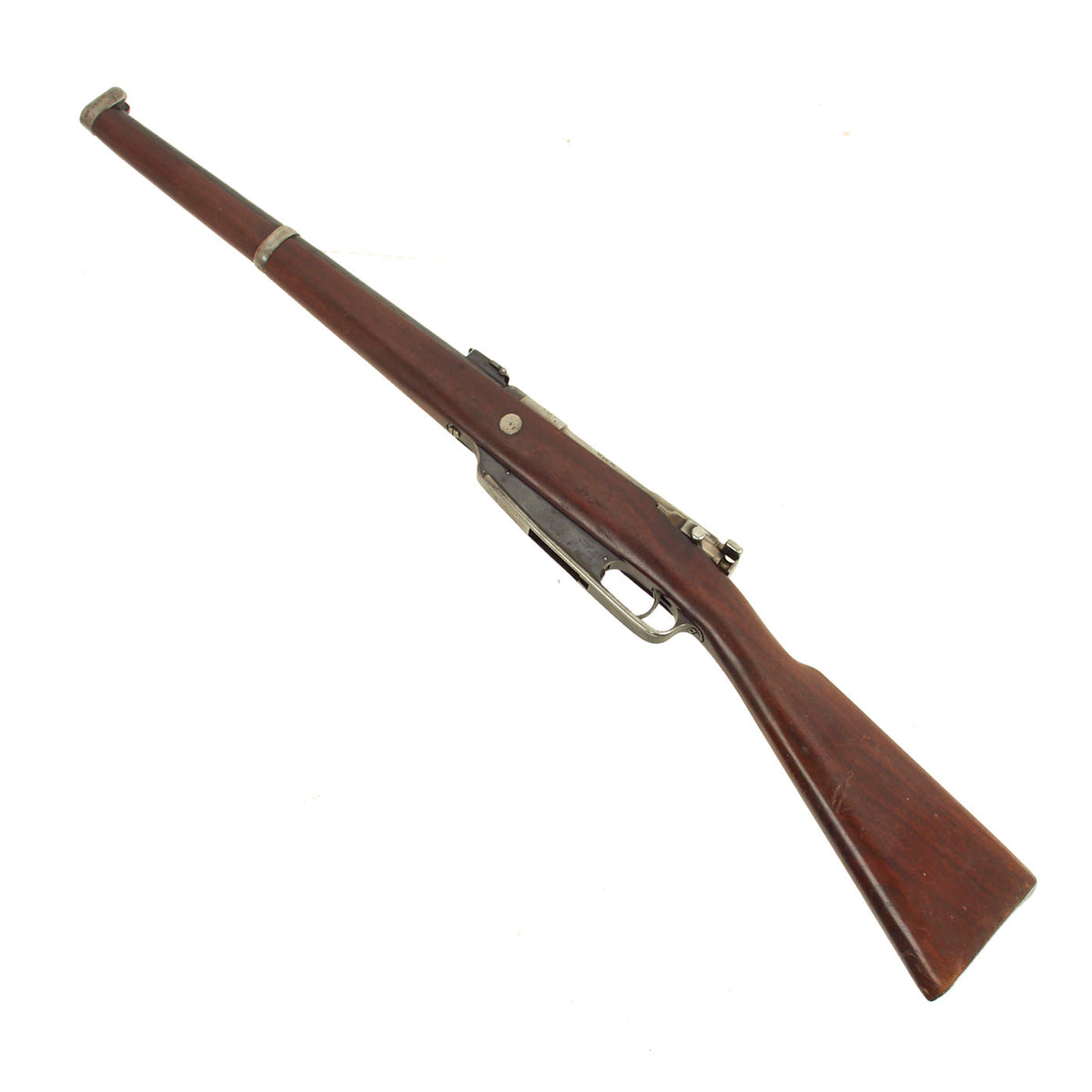
Original German Pre-WWI Karabiner 88 S Cavalry Carbine by Erfurt with Bavarian Regt. Marking – dated 1893 – Matching Serial 8293 f Original Items
$ 1.595,00 $ 398,75
Original Item: Only One Available. Adopted in 1888 the new German Infantry round in 7.92 X 57mm replaced the old 10.4mm large bore cartridge adopted in 1871. The M-1888 Rifle was referred to as the “Commission Rifle” and was manufactured as a full Infantry Rifle and a Carbine starting in 1888 and an Artillery Carbine adopted in 1891.
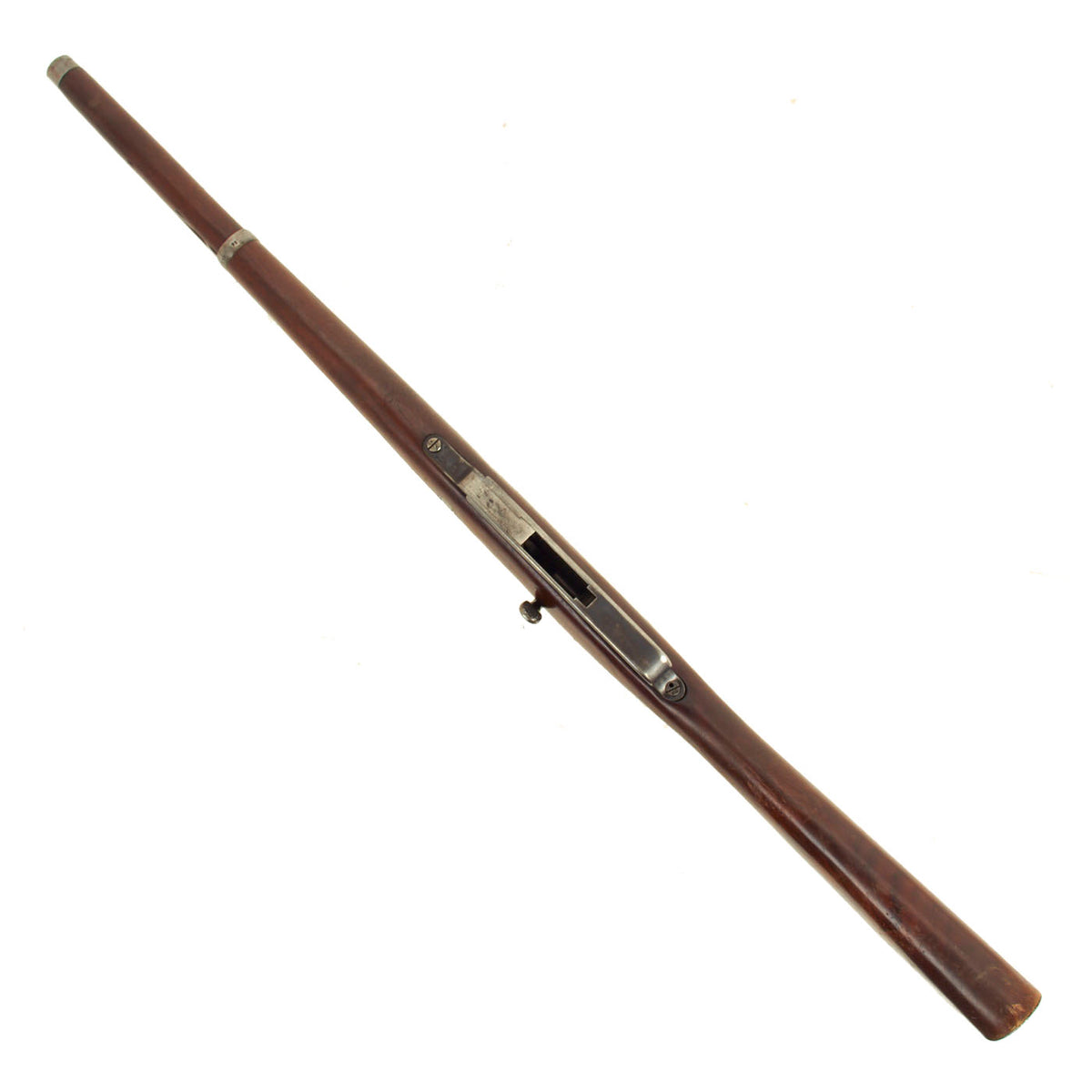
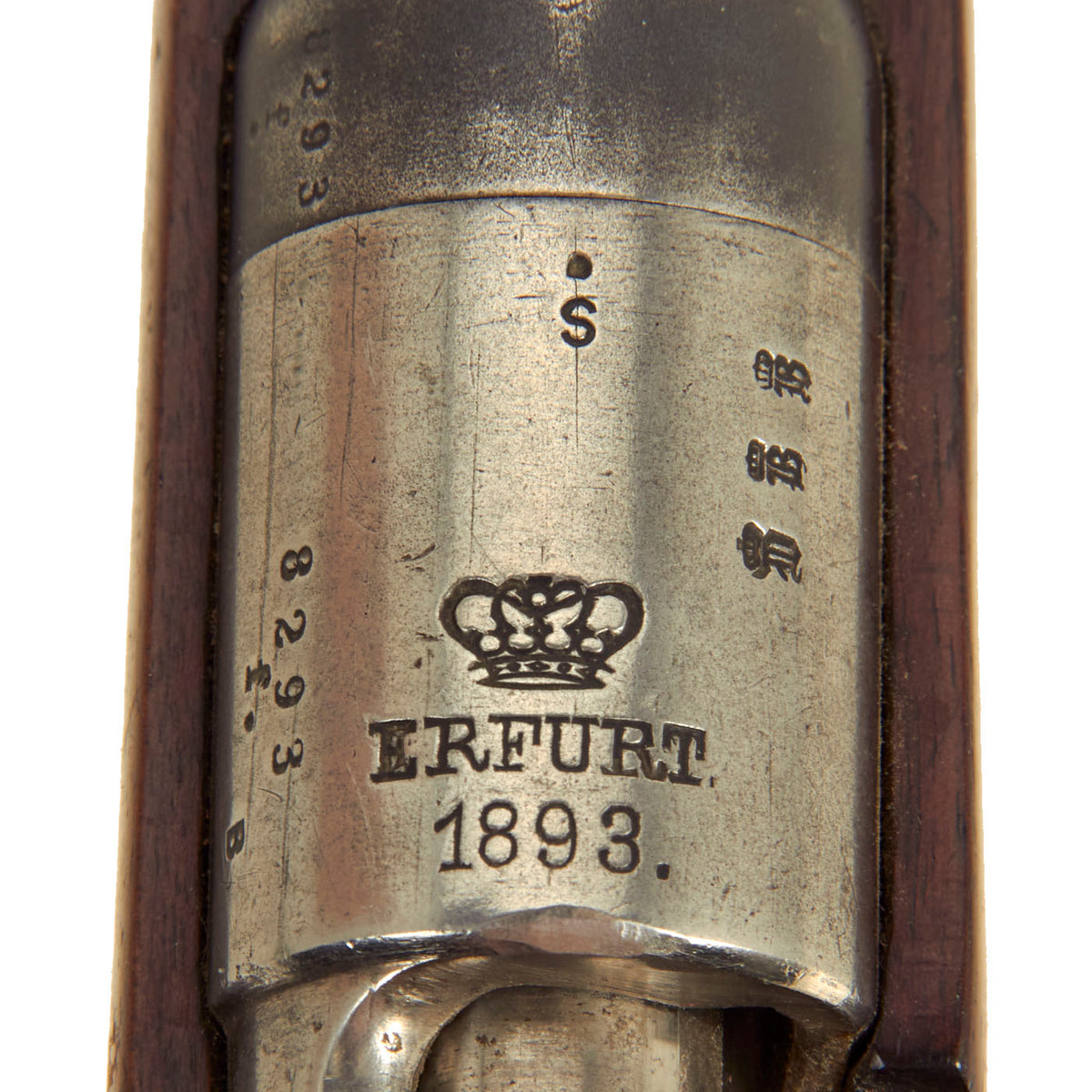
Our example is of the Cavalry Carbine is marked over the chamber with (CROWN) / ERFURT. / 1893., for 1890 manufacture at the Imperial Erfurt Arsenal, located in Thuringia. The right side of the receiver is marked with Kar. 88. / n.m. in German blackface type, and there are additional proof marks on various components of the carbine. The receiver, barrel jacket, magazine housing, bolt, and other components are marked with serial number 8293 / f, or shortened number 93. That makes this a very desirable “ALL MATCHING” example, with no parts swapped out over the years, and it’s a great one!
The stock is in excellent condition, and looks to possibly be an arsenal replacement from when the carbine was serviced, probably for use during WWI. It has a lovely color and finish, though we cannot see any traces of German proof marks. The metalwork has a lovely service used look, with much of the original bluing still present on the barrel jacket and sides of the magazine well. The receiver and bolt are still the correct bright steel, and the barrel band and nose cap have had the original finish worn away.
The carbine has an 18″ barrel which has a very good bore, showing some wear and oxidation from service. The rifling is still visible, with the lands showing a bit of wear and some fouling in the grooves. The rifle cycles and dry fire well, and the firing pin is fully intact, as is the often lost cartridge ejector on the bolt face. It bears an S marked over the chamber to indicate modification for the S-PATRONE cartridge introduced in 1903 (we do not recommend firing the S-cartridge in this carbine). This short carbine was intended for use by cavalry units.
The upper barrel band / sight guard has a great regimental marking: B. 1. U. R. 3. 10., for the 1st Royal Bavarian Uhlans Regiment “Emperor William II, King of Prussia” (Königlich Bayerisches Ulanen-Regiment „Kaiser Wilhelm II., König von Preußen“ Nr. 1), 3rd Squadron (Eskadron), Weapon (Waffen) #10. There is also a crossed out marking for a different unit of the same regiment on the lower barrel band: B. 1. U. R. 4. 12.. This was a light cavalry regiment of the Royal Bavarian Army, and later Imperial German Army. The regiment was first raised 21 December 1863 as an Uhlan unit, garrisoned in Bamberg and part of the II Royal Bavarian Corps. It fought in the Austro-Prussian War, the Franco-Prussian War and World War I. This is the exact type of unit that would have been issued this type of carbine.
In 1890 this was cutting edge technology as the Gewehr 1888 Mauser rifles and carbines were the first to use the 7.92mm cartridge that replaced the 10.4mm used in the Mauser 1871/84 tubular magazine rifles.
This little carbine used an integral 5 shot box magazine and was extremely popular. It was superseded in 1898 with the introduction of the Gew 98 rifle also in an updated version of the same caliber and many 88s were updated and then marked with a small “S” on the receiver ring to indicate it could be used with the upgraded ammunition.
Both the Kar 88 and 91 were already being slowly taken out of service before World War One, as the new Mauser 98 pattern carbines introduced in 1909 or 1910 were taking their place. This would change with the outbreak of war, of course, and every one of the 88 / 91 pattern carbines in German inventory would be re-issued during the Great War. Their size and weight made them ideal for the troops who needed a personal weapon but were unlikely to actually have to fight with it (artillery crews, cyclists, supply drivers, balloon crews, etc).
Both the Mauser Model 88 and 98 rifles and carbines saw extensive use in WWI. During the Great War cavalry was quickly becoming a thing of the past once trench warfare was introduced.
By WW2 the Germans had adopted the Mauser 98K Rifle, again in the improved 7.92mm caliber, this rifle was shorter than the Gew 98, longer than the carbine, and became the standard.
A rare 1893 dated Mauser Kar 88 Carbine, only 37 1/2″ in overall length, federally classified as an antique due to its pre-1899 manufacture date. In lovely condition and ready to display!
Specifications-
Year of Manufacture: 1890
Caliber: 7.92×57mm Mauser S Patrone
Cartridge Type: Centerfire Cartridge
Barrel Length: 18 Inches
Overall Length: 37 1/2 Inches
Action type: Bolt-Action
Feed System: 5 round internal magazine
History of the Gewehr 88
In 1886, the French Army unveiled the Modelle 1886 “Lebel” rifle. There was an immediate reaction in German military circles bordering on hysteria. Why? Because the Lebel was the world’s first small bore military rifle using an efficient smokeless powder cartridge. Now, the Lebel, which used a tubular magazine located under the barrel was not a particularly noteworthy design, but the power and flat trajectory of the new French 8mm round far outclassed the 11mm Reichspatrone black powder round used in the contemporary German infantry rifle, the Mauser 71/84.
In this rather charged atmosphere, the German Gewehr Prfungs Kommission (GPK – Rifle Testing Commission) went to work. Initially, the idea was to revise the Mauser Gewehr 71/84 to use a small caliber smokeless powder round based on the old 11mm black powder Reichspatrone. To this extent, production machinery was ordered from the Ludwig Loewe Company of Berlin-Charlottenburg in December, 1887. As things progressed, the GPK became disillusioned with this technical approach, and so a rather strange hybrid of ideas took shape.
The bolt design was highly revised by a Spandau Arsenal technician named Louis Schlegelmilch and features a separate bolt head. The ensuing rifle had a Schlegelmilch/Mauser action, a five shot clip loaded Mannlicher style magazine (note: while the clip falls out as with the Mannlicher clips, this one was markedly improved in that it could be loaded with either end down as opposed to only one end on the true Mannlicher), and a full length barrel jacket designed by Armand Mieg. The pitch and profile of the rifling were copied directly from that of the Lebel. The cartridge chosen was a modified Swiss style rimless design based on the ideas of Eduard Rubin. By March 23, 1888, the Bavarian military observer in Berlin, General von Xylander reported that the development was virtually complete.
Field trials for the new rifle were completed in November, 1888, and the GPK recommended that it be adopted immediately. The adoption orders were signed by Kaiser Wilhelm II on November 12, 1888. Issue of the Gewehr 88 as the new rife was designated, were first made in the spring of 1889 to the XV and XVI Armeekorps stationed in Elsass-Lothringen. Issue to the Bavarian military units began in October 1889, and by August 1890, all Prussian, Saxon, and Wurttemberger line units had been re-equipped.
The Gewehr 88 was made by the three primary Prussian arsenals at Danzig, Erfurt, and Spandau, a smaller Bavarian establishment at Amberg, as well as several private contractors, including the Ludwig Loewe Company, Osterreichische Waffenfabrik Gesellschaft (Steyr), and Haenel. Production figures up to the time production ceased in 1897 are as follows:
Prussian Government Arsenals: 750,000
Amberg: 425,000
Loewe: 425,000
Steyr: 300,000
Haenel: 100,000
Total: 1,675,000
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Angolan Rebel 1970s era 60mm Inert Display Mortar from Angolan Civil War Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Australian WWII Owen MK1 Machine Carbine SMG Custom Fabricated Replica with Sling Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized