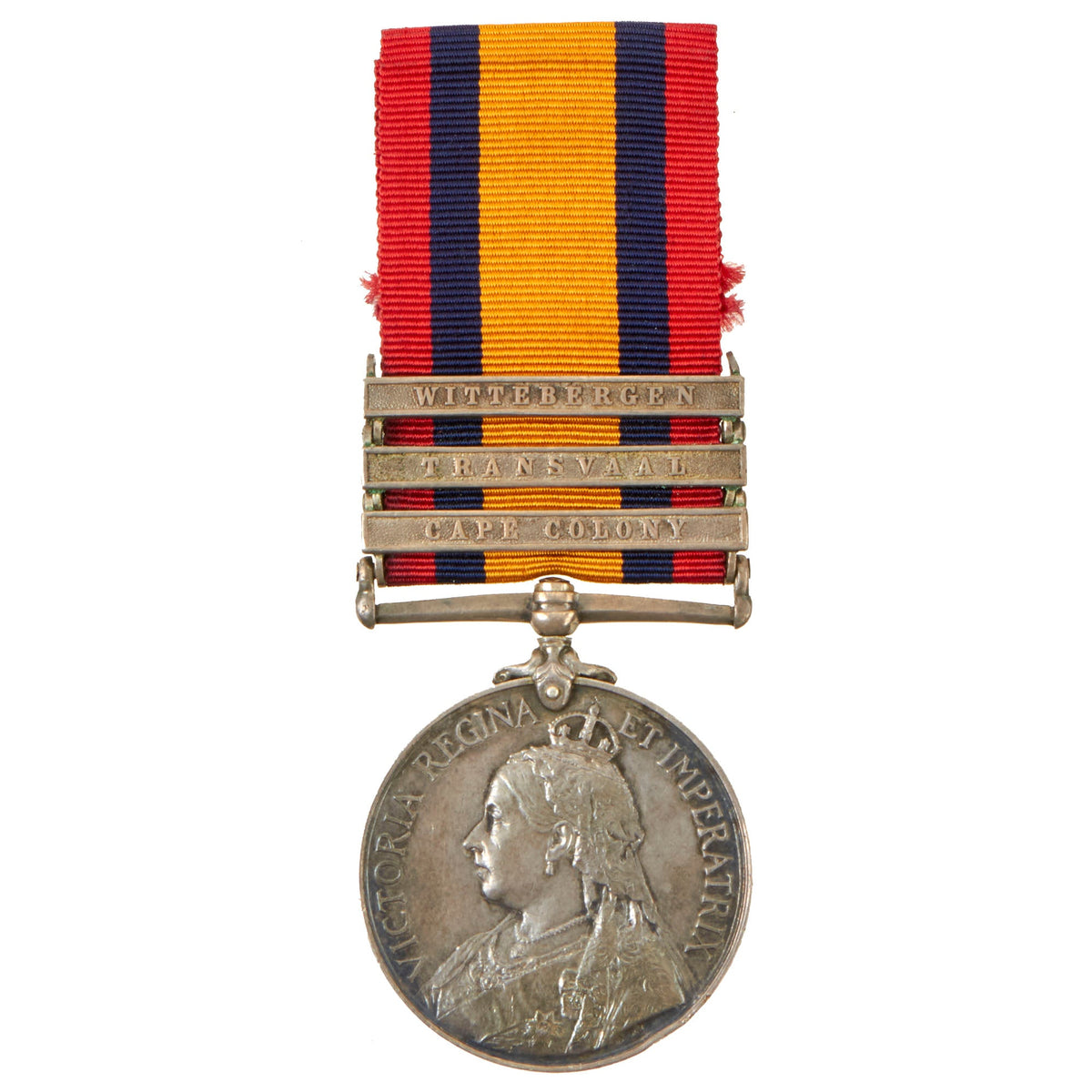
Original British Second Boer War Named Version Three Queen’s South Africa Medal With 5 Clasps – Sergeant James Price (4380), Prince of Wales’s Leinster Regiment (Royal Canadians) Original Items
$ 295,00 $ 118,00
Original Item: Only One Available. The Queen’s South Africa Medal is a British campaign medal awarded to British and Colonial military personnel, and to civilians employed in an official capacity, who served in the Second Boer War in South Africa. Altogether twenty-six clasps were awarded, to indicate participation in particular actions and campaigns.
Poor logistics and disease, combined with having to fight against a disciplined and capable enemy of excellent horsemen and marksmen who perfected guerrilla warfare, made this a hard-won medal. In addition to men often having to go without basics such as food and water, enteric fever killed several thousand and was a constant drain on manpower. The published casualty rolls run to over 50,000 names, while studies of contemporary publications and reports put the actual figure for all casualties, including caused by disease, at 97,000.
The Queen’s South Africa Medal is a silver disc, 38 millimeters (1.5 inches) in diameter. The bronze medal was awarded to non-combatant Indian troops and other non-combatant men of whatever nationality who drew military pay, although some silver medals were awarded to native troops. The suspender is attached to the medal with a claw mount and a pin through the upper edge of the medal.
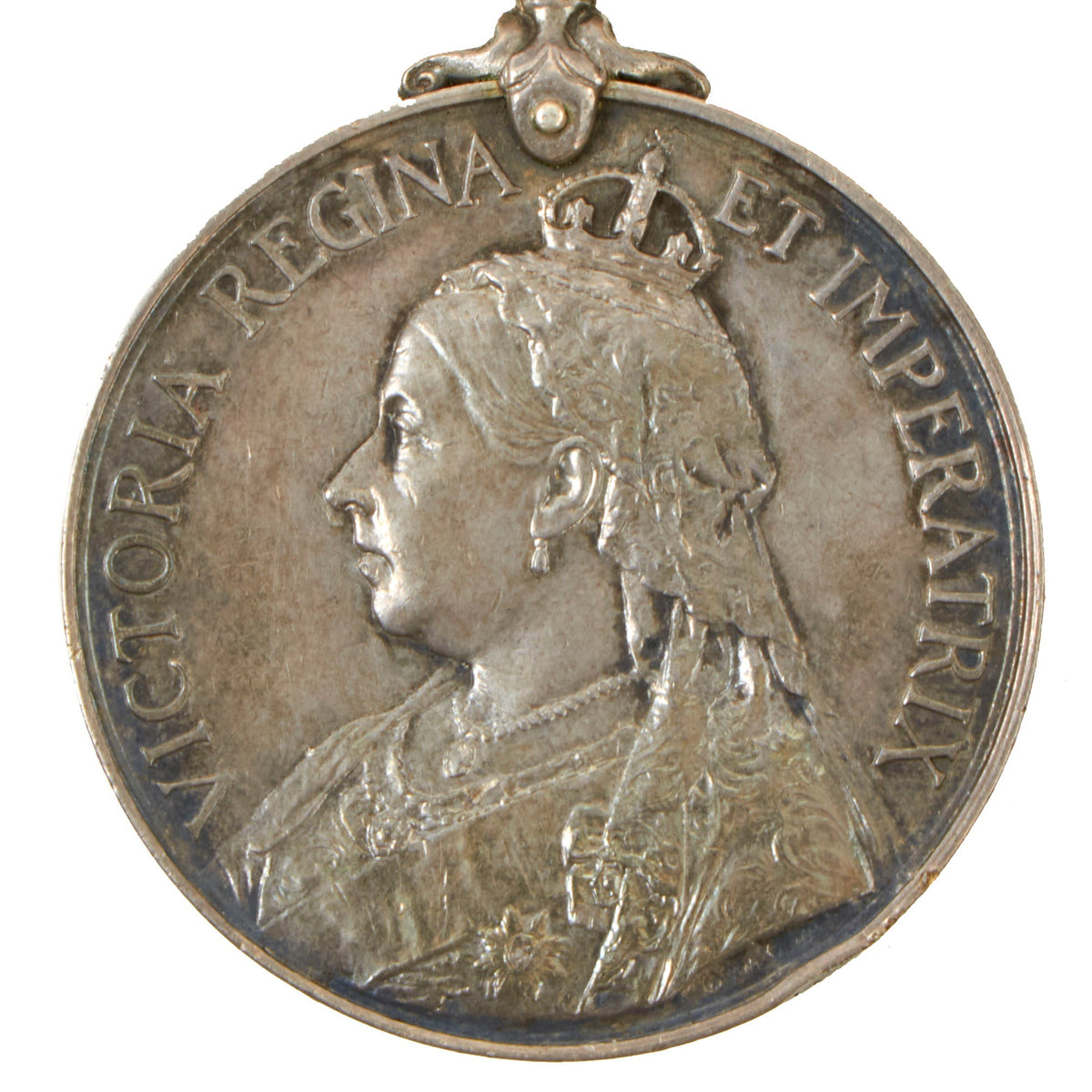
Obverse
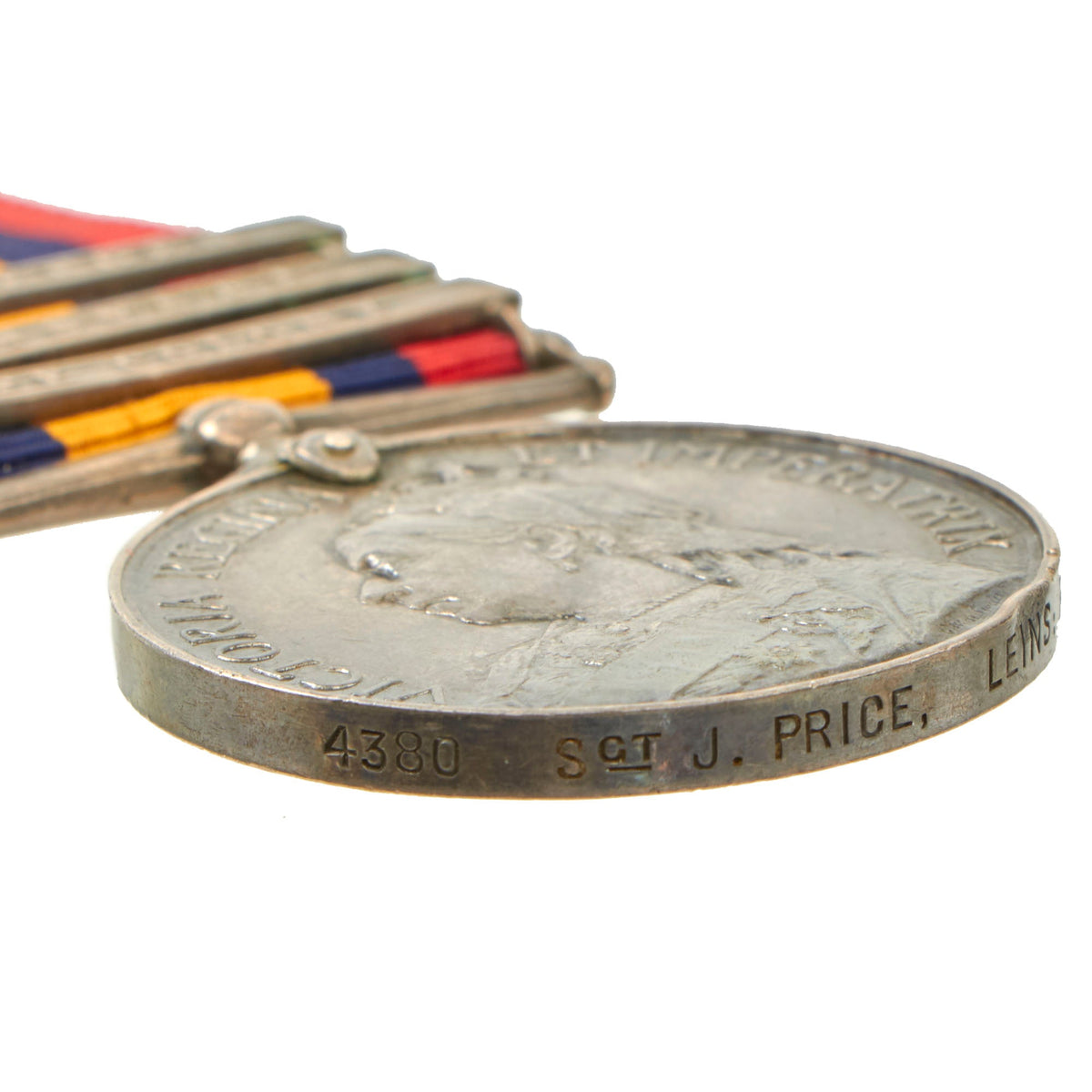
The obverse shows a crowned and veiled effigy of Queen Victoria, facing left, with the legend “VICTORIA REGINA ET IMPERATRIX” around the upper perimeter.
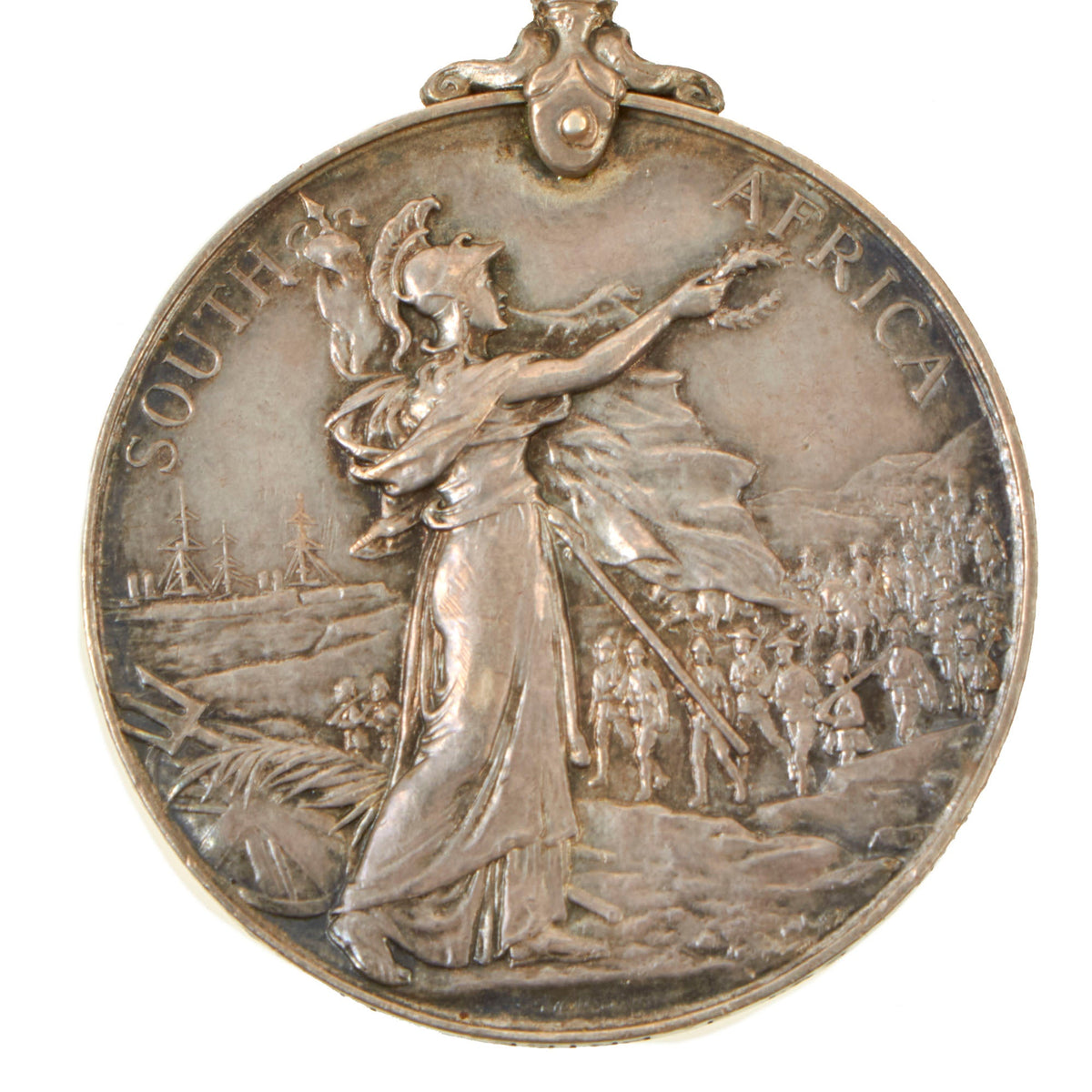
Reverse
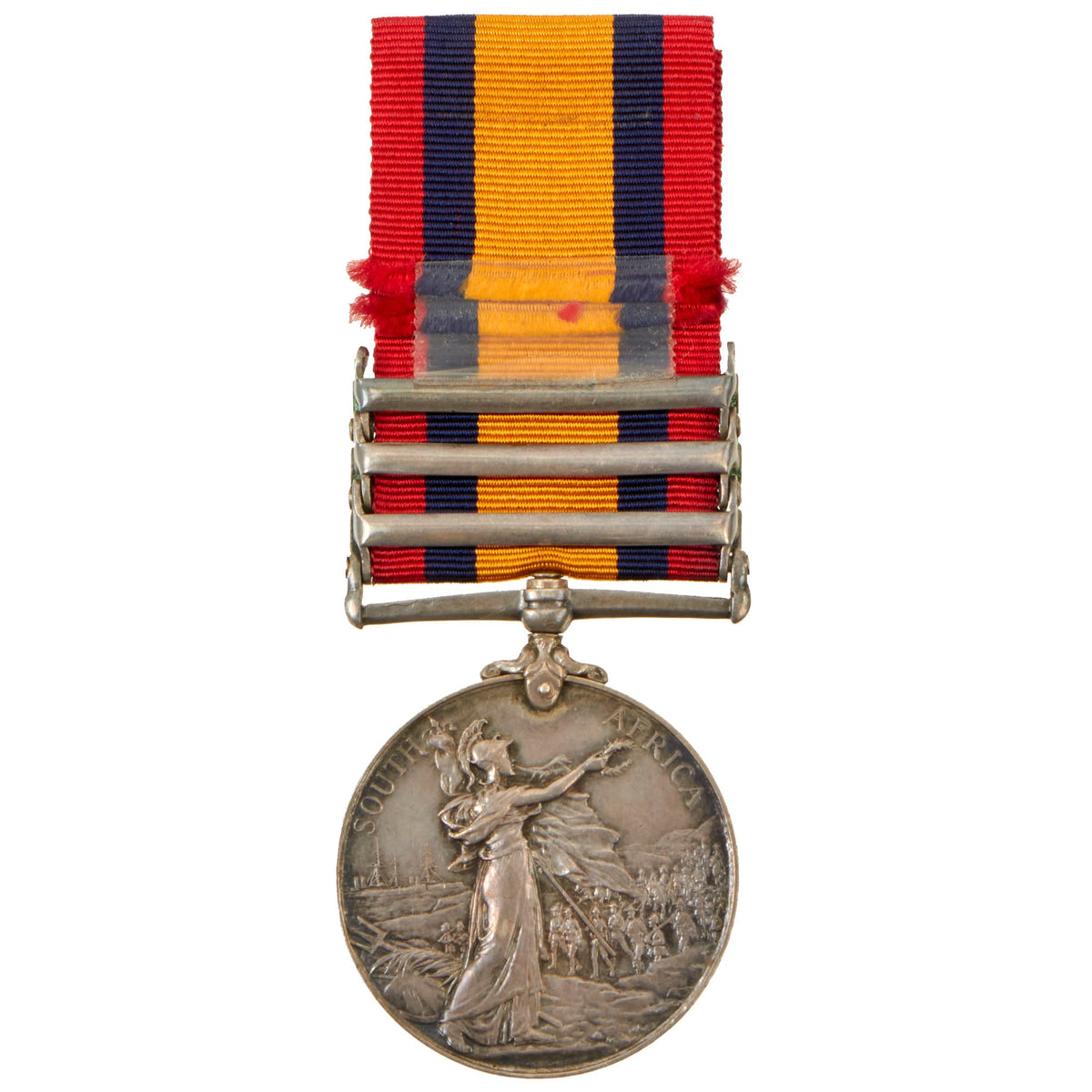
The reverse, designed by G. W. de Saulles, shows Britannia holding the Union Flag in her left hand and a laurel wreath in her right hand. In the right background are troops marching inland from the coast. In the left background are two men-of-war, with Neptune’s Trident and Britannia’s shield on the ground in the foreground. Around the top perimeter are the words “SOUTH AFRICA“. Three types of reverse exist.
The first medals were awarded to Lord Strathcona’s Horse and bore the years “1899” and “1900” below Britannia’s wreath, with the wreath almost touching the “R” of “AFRICA”. Approximately fifty of these medals were awarded. This example is the third version that was struck with a new die with Africa in a lower position.
Clasps
The clasps were attached to the suspender and to each other in roller chain fashion with rivets. Clasps were often issued after the medal, in particular those for South Africa 1901 and 1902, with the result that they were sometimes attached with unofficial rivets, or worn loose on the ribbon.
The clasps on this example:
– WITTEBERGEN (1–29 July 1900): Awarded to those who were inside a line drawn from Harrismith to Bethlehem, thence to Senekal and Clocolan in the Orange Free State along the Basutoland border, and back to Harrismith.
– SOUTH AFRICA 1901 (1 January – 31 December 1901): Awarded to those who served in South Africa during 1901 and who were not eligible for the King’s South Africa Medal.
– TRANSVAAL (24 May 1900 – 31 May 1902): For service in the South African Republic where no clasp for a specific action in the South African Republic had been received.
– CAPE COLONY (11 October 1899 – 31 May 1902): For service in the Cape of Good Hope where no clasp for a specific action in the Cape had been received.
Naming
The recipient’s name and details were impressed on the rim of the medal, with some officer’s medals engraved.
About 1,500 medals were presented unnamed to members of Australian and New Zealand forces during the 1901 tour of those countries by the future King George V. Many were later named locally, either officially at public expense, or privately.
This example is named as:
4380 SGT. J. PRICE, LEINS:REGI
Ribbon
The ribbon is 32 millimeters wide, with a 7 millimeters wide red band and a 4 millimeters wide dark blue band, repeated in reverse order and separated by a 10 millimeters wide orange band.
The overall condition is quite nice with the only “real defect” is the silver now has a lovely blue tinted tarnishing present in small areas. The tarnish that is present does not subtract from the beauty of the medal.
Comes more than ready for further research and display.
The Prince of Wales’s Leinster Regiment (Royal Canadians) was an infantry regiment of the line in the British Army, formed in 1881 by the amalgamation of the 100th (Prince of Wales’s Royal Canadian) Regiment of Foot and the 109th Regiment of Foot (Bombay Infantry). The 100th Foot was first raised in 1858 and the 109th was first raised in 1853. Between the time of its formation and Irish independence, it was one of eight Irish regiments raised largely in Ireland, with its Birr Barracks home depot in Birr. It was disbanded with the Partition of Ireland following establishment of the independent Irish Free State in 1922 when the five regiments that had their traditional recruiting grounds in the counties of the new state were disbanded.
Both regular battalions were deployed to South Africa for the Second Boer War. The 1st Battalion saw action around Bethlehem in April 1902 when 14 men were wounded while the 2nd Battalion held the Heilbron branch line in February 1902 when they had 10 casualties. The 1st battalion stayed until the end of the war, following which 370 officers and men left Cape Town on the SS Englishman in late September 1902, and arrived at Southampton in late October, when they were posted to Fermoy. A 3rd Militia Battalion, formed from the former King′s County Militia, was embodied in early 1900 for service in South Africa. 520 officers and men embarked from Southampton on the SS Kildonan Castle in early March 1900, returning to Ireland after more than two years in late May 1902.
In 1908, the Volunteers and Militia were reorganised nationally, with the former becoming the Territorial Force and the latter the Special Reserve; the regiment now had three Reserve but no Territorial battalions.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Band of Brothers ORIGINAL GERMAN WWII Le. F.H. 18 10.5cm ARTILLERY PIECE Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Armored Burgonet Helmet & Polearm from Scottish Castle Leith Hall Circa 1700 Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized