Original Australian WWI KIA Death Penny Soldier Memorial For Pte John F. Thompson, 57th Battalion, Australian Imperial Force – Killed at Battle of St. Quentin Canal Original Items
$ 295,00 $ 118,00
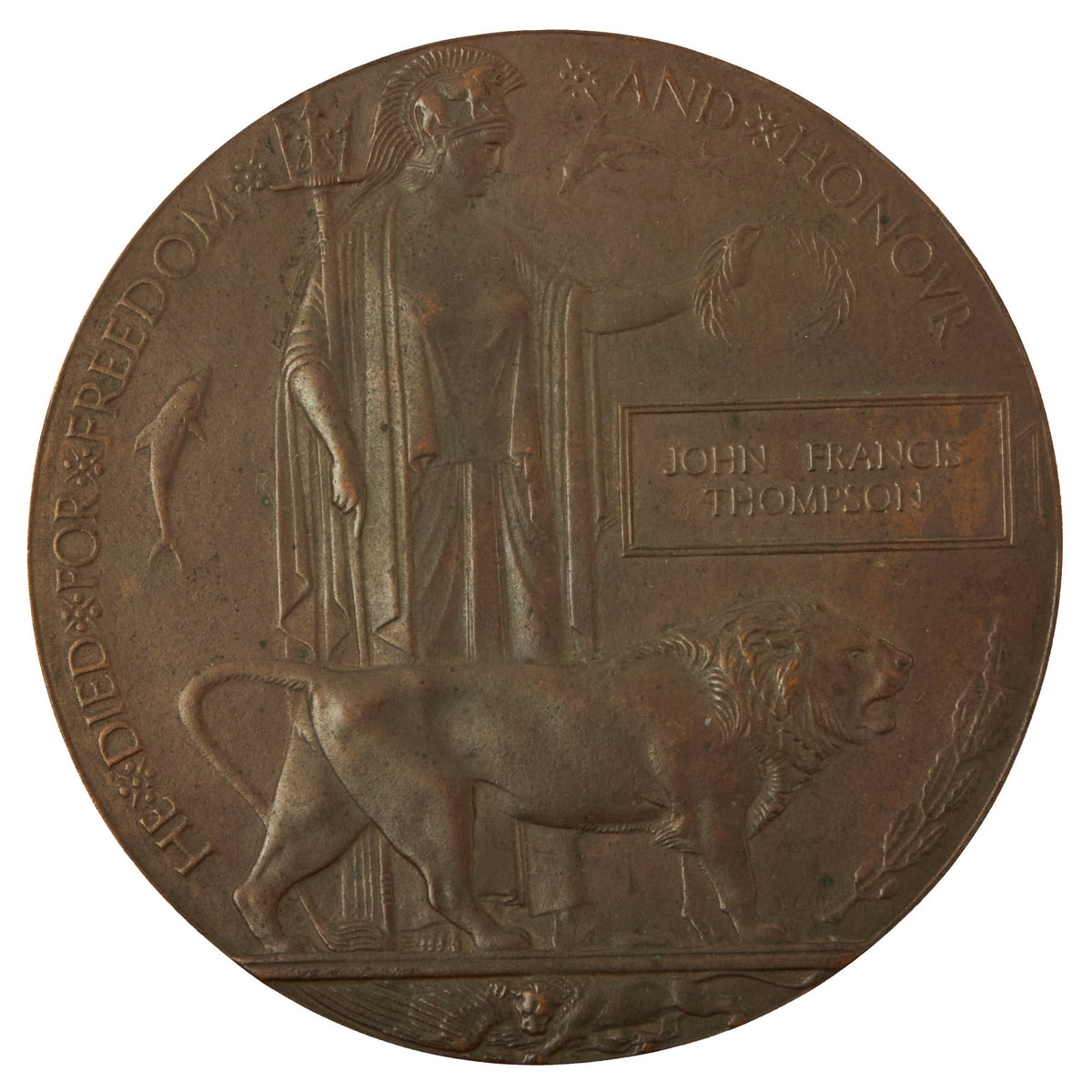
Original Item: Only One Available. Original WWI Memorial Plaque commemorating Australian Soldier John Francis Thompson. Thompson served with the 57th Battalion of the Australian Imperial Force (AIF).
Service Number: 3802
Rank: Private
Unit: 57th Australian Infantry Battalion
Service: Australian Imperial Force
Date of Death: 01 October 1918
Place of Death: France
Age at Death: 19
Unfortunately Private John Francis Thompson has no known grave and is listed as “Known Unto God”. Thompson is just one of the 6 Million soldiers that went missing and ultimately presumed dead. His death date is listed as October 1, 1918 which is around the time that the 57th Battalion took part at the Battle of St. Quenton.
The Battle of St Quentin Canal was a pivotal battle of World War I that began on 29 September 1918 and involved British, Australian and American forces operating as part of the British Fourth Army under the overall command of General Sir Henry Rawlinson. Further north, part of the British Third Army also supported the attack. South of the Fourth Army’s 19 km (12 mi) front, the French First Army launched a coordinated attack on a 9.5 km (6 mi) front. The objective was to break through one of the most heavily defended stretches of the German Siegfriedstellung (Hindenburg Line), which in this sector used the St Quentin Canal as part of its defences. The assault achieved its objectives (though not according to the planned timetable), resulting in the first full breach of the Hindenburg Line, in the face of heavy German resistance. In concert with other attacks of the Grand Offensive along the length of the line, Allied success convinced the German high command that there was little hope of an ultimate German victory.
Thomspon is listed at the Australian War Memorial, Hall of Memory and his name will be projected on the outside of the Hall of Memory.
Roll of Honour name projection
John Francis Thompson’s name will be projected onto the exterior of the Hall of Memory on:
Tue 30 January 2024 at 10:19pm
Sat 13 April 2024 at 2:50am
These dates and times are estimates. Please note that previous advised times on this site have recently been changed to ensure that early evening projections are clearly visible and not affected by twilight. The actual time of projection could also change as a result of weather and other factors, so it is advisable to check closer to the date. In the rare event of a temporary loss of electrical power, the names scheduled for display in that period will not appear until the next time listed.
More information can be found at the Australian War Memorial website.
Comes more than ready for further research and display.
The Memorial Plaque was issued after the First World War to the next-of-kin of all British Empire service personnel who were killed as a result of the war.
The plaques (which could be described as large plaquettes) about 4.72 inches (120 mm) in diameter, were cast in bronze, and came to be known as the “Dead Man’s Penny”, or “Death Penny”, because of the similarity in appearance to the much smaller penny coin which itself had a diameter of only 1.215 inches (30.9 mm). 1,355,000 plaques were issued, which used a total of 450 tons of bronze, and continued to be issued into the 1930s to commemorate people who died as a consequence of the war.
It was decided that the design of the plaque was to be chosen from submissions made in a public competition. Over 800 designs were submitted, and the competition was won by the sculptor and medallist Edward Carter Preston using the pseudonym Pyramus, receiving two first place prizes of £250 for his winning and also an alternative design. The name Pyramus comes from the story of Pyramus and Thisbē which is part of Ovid’s Metamorphoses, a Roman tragedy narrative poem.
Carter Preston’s winning design includes an image of Britannia holding a trident and standing with a lion. The designer’s initials, E.CR.P., appear above the front paw. In her outstretched left hand Britannia holds an olive wreath above the ansate tablet bearing the deceased’s name cast in raised letters. Below the name tablet, to the right of the lion, is an oak spray with acorns. The name does not include the rank since there was to be no distinction between sacrifices made by different individuals. Two dolphins swim around Britannia, symbolizing Britain’s sea power, and at the bottom a second lion is tearing apart the German eagle. The reverse is blank, making it a plaquette rather than a table medal.
Around the picture the legend reads (in capitals) “He died for freedom and honour”, or for the 1500 plaques issued to commemorate women, “She died for freedom and honour”.
They were initially made at the Memorial Plaque Factory, 54/56 Church Road, Acton, W3, London from 1919. Early Acton-made plaques did not have a number stamped on them but later ones have a number stamped behind the lion’s back leg.
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Thanks to our longstanding association with UPS FedEx DHL, and other major international carriers, we are able to provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is expertly trained and will wrap your products according to our exact and precise specifications. Prior to shipping, your goods will be thoroughly examined and securely secured. We ship to thousands clients each day across multiple countries. This shows how we're dedicated to be the largest retailer on the internet. Warehouses and distribution centres can be located throughout Europe as well as the USA.
Note: Orders with more than one item will be assigned a processing date depending on the item.
Before shipping before shipping, we'll conduct a thorough inspection of the items you have ordered. Today, the majority of orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The delivery time will be between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we cannot completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may alter at any time. It's possible that you may not receive your order once the order has been made.
Our policy is valid for a period of 30 days. If you don't receive the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
You can only return an item if it is unused and in the same state as the day you received it. You must have the item in its original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Armoured Fighting Vehicles of the World: AFVs of World War One (Hardcover Book) New Made Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Australian WWII Owen MK1 Machine Carbine SMG Custom Fabricated Replica with Sling Original Items