British Enfield Pattern 1853 Rifle Musket Replacement Hardwood Wood Stock New Made Items
$ 295,00 $ 118,00
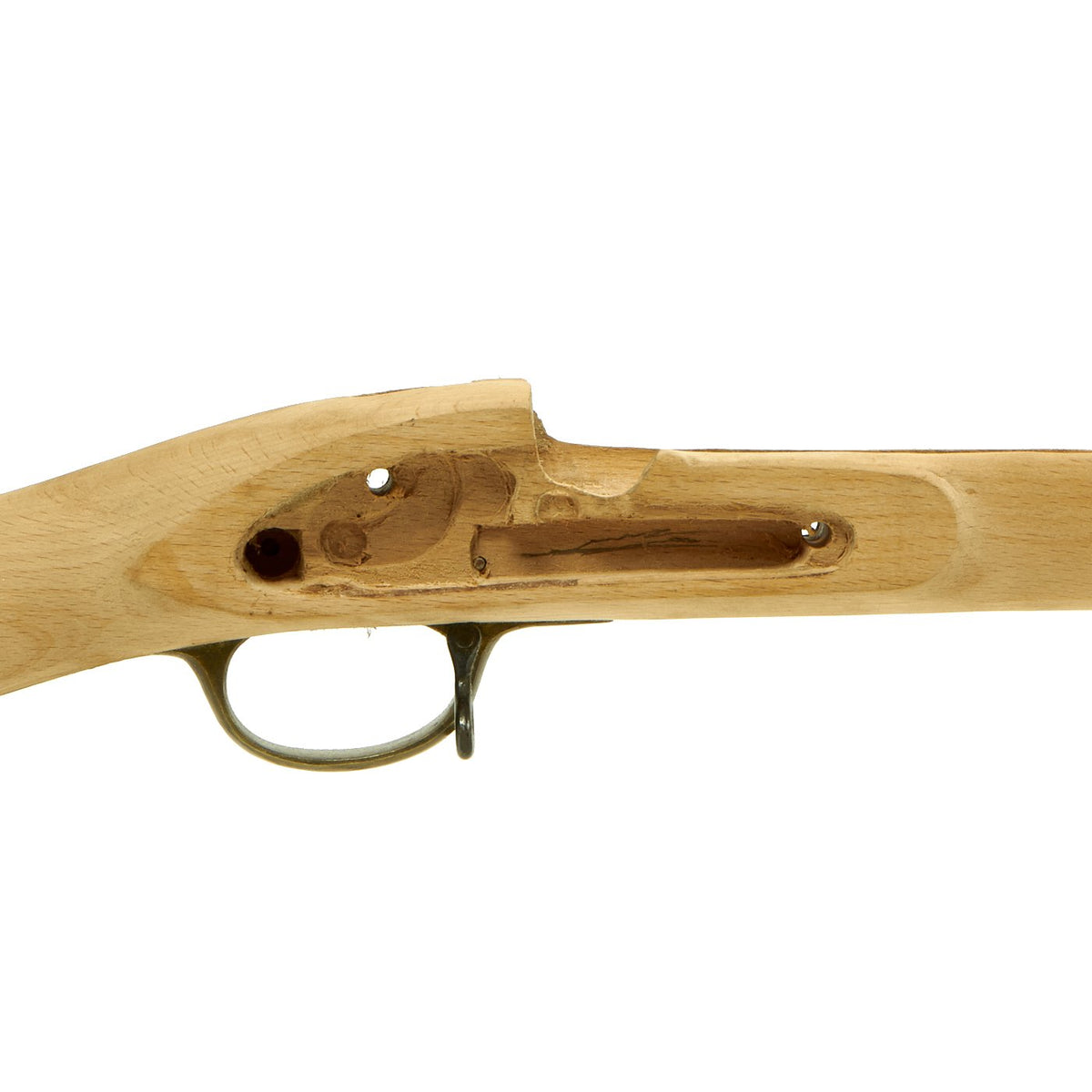
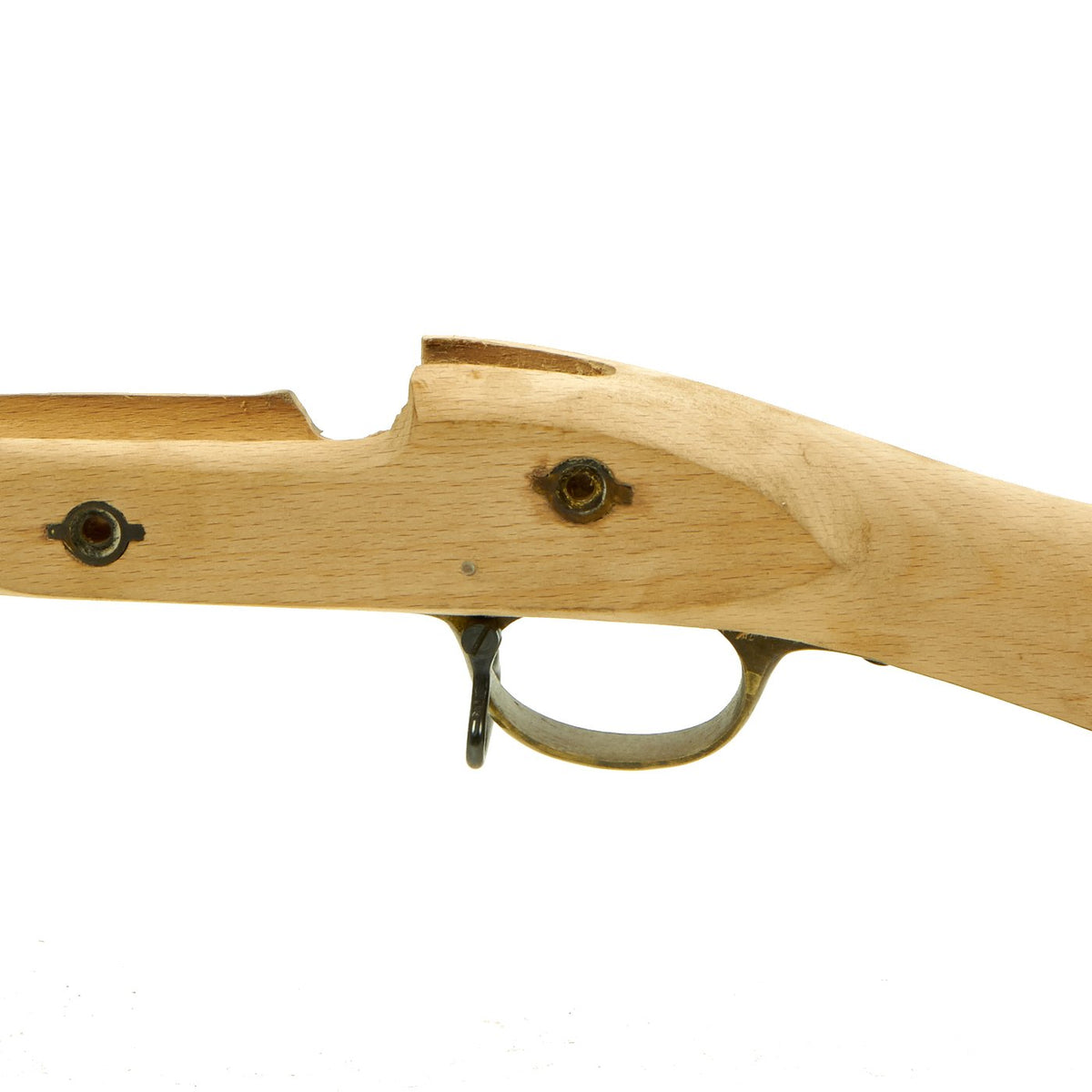
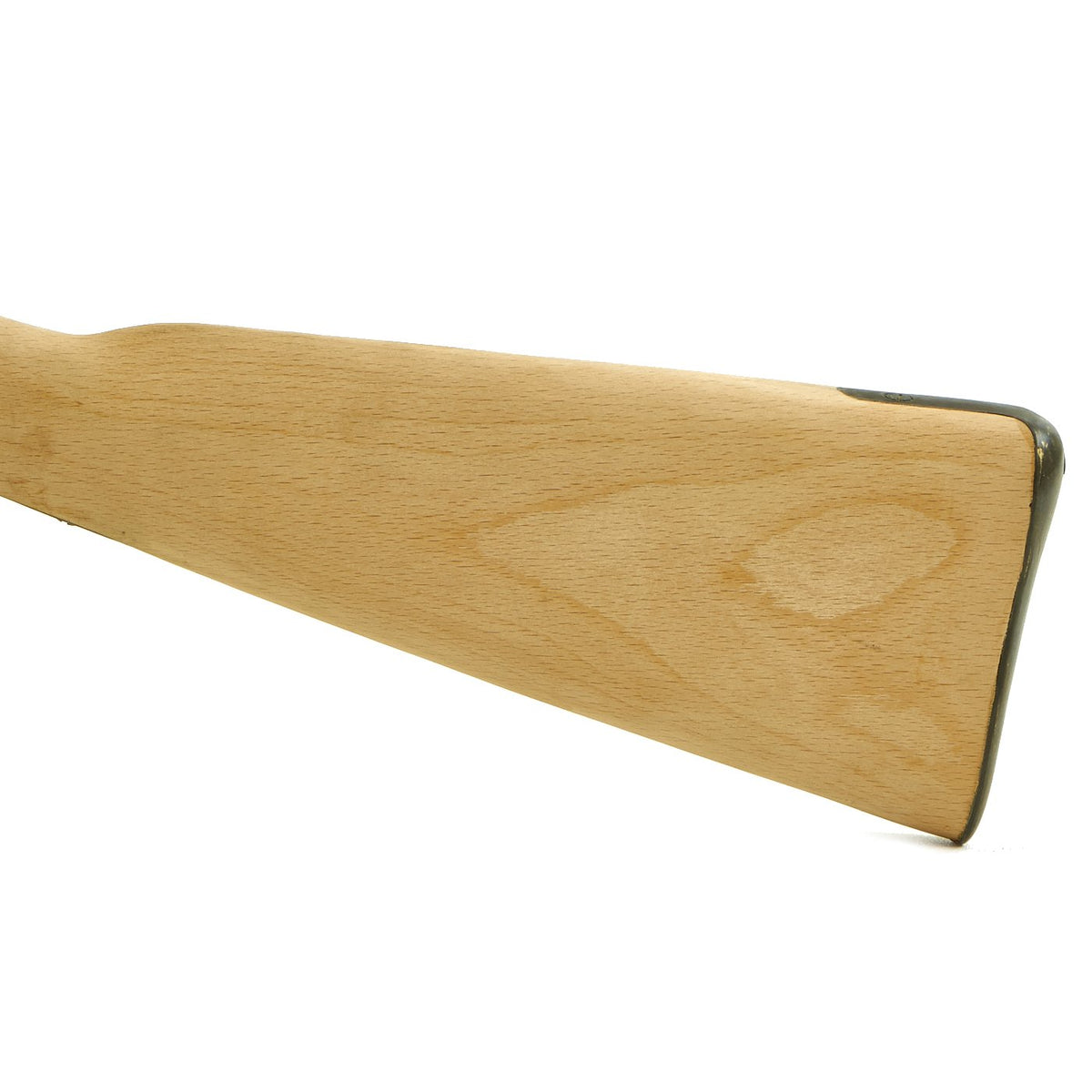
New Made Item: High quality reproduction British Enfield Pattern 1853 Rifle Musket Replacement Hardwood Wood Stock. The stock is fully inleted and comes complete with brass trigger guard, brass butt plate, brass left side lock screw escutcheons, brass nose cap, blued steel ram rod and trigger assembly. The inlets are cut to approximate size so custom fitting of your specific parts will be required. Wood is sanded but untreated for you to stain and finish. (With some skill this stock can be converted to be an Pattern 1864 Snider rifle stock). Approximate overall length is 50″.
The Enfield Pattern 1853 rifle-musket (also known as the Pattern 1853 Enfield, P53 Enfield, and Enfield rifle-musket) was a .577 calibre Minié-type muzzle-loading rifled musket, used by the British Empire from 1853 to 1867; after which many were replaced in service by the cartridge-loaded Snider–Enfield rifle.
The Enfield P53 was introduced to Indian troops under British rule in 1856.[7] The Enfield rifle-musket was a contributing cause of the Indian rebellion of 1857. Sepoys in the British East India Company’s armies in India were issued with the new rifle in 1857, and rumours were spread that the cartridges (referring here to paper-wrapped powder and projectile, not to metallic cartridges) were greased with beef tallow, pig fat, or a combination of the two – a situation abhorrent to Hindu and Muslim soldiers based on religious beliefs.
British military drills of the time required soldiers to tear open by biting open the prepared cartridge, pour the gunpowder contained within down the barrel, snap off the greased end of the cartridge containing the bullet at the muzzle, ram it home, bring up the rifle to the hip, replace the percussion cap, ready the rifle by setting the sights and moving it to full cock, then to present the rifle, marking the target and squeezing the trigger. The musketry books also recommended that, “Whenever the grease around the bullet appears to be melted away, or otherwise removed from the cartridge, the sides of the bullet should be made wet in the mouth before putting it into the barrel; the saliva will serve the purpose of grease for the time being”.
The idea of having anything which might be tainted with pig or beef fat in their mouths was unacceptable to the Indian soldiers, and when they objected it was suggested that they were more than welcome to make up their own batches of cartridges, using a religiously acceptable greasing agent such as ghee or vegetable oil. This seemed to prove that the issued cartridges were, in fact, greased with pig and/or beef fat. A further suggestion that the Sepoys tear the cartridges open with their hands (instead of biting them open) was rejected as impractical – many of the Sepoys had been undertaking musket drill daily for years, and the practice of biting the cartridge open was second nature to them. Incidentally, after the Mutiny, manuals amended the method of opening the cartridge to, “Bring the cartridge to the forefinger and thumb of the left hand, and with the arm close to the body, carefully tear off the end without spilling the powder.”
As a consequence of British fears, the Indian infantry’s long arms were modified to be less accurate by reaming out the rifling of the Pattern 1853 making it a smooth bore[citation needed] and the spherical / ball shot does not require greasing, just a patch. This greatly reduced the gun’s potency and effectiveness, as did replacing the variable distance rear sight to a fixed sight. This became the Pattern 1858. However, due to the now thinner walls, the barrel would bulge and bursting was not an unknown problem. Furthermore, with the bayonet fitted excessive flexing became an issue. To remedy this, an urgent order was placed in England for around 12,000 new barrels made specifying with a thicker barrel wall. This became the very scarce Enfield Pattern 1859 which in good to very good condition attracts a premium.
The Enfield 1853 rifle-musket was also used by both the North and the South in the American Civil War, and was the second most widely used infantry weapon in the war, surpassed only by the Springfield Model 1861 Rifled Musket. The Confederates imported more Enfields during the course of the war than any other small arm, buying from private contractors and gun runners. It has been estimated that over 900,000 P53 Enfields were imported into America and saw service in every major engagement from the Battle of Shiloh (April, 1862) and the Siege of Vicksburg (May 1863), to the final battles of 1865. The gun was highly sought after in the Confederate ranks. According to a survey taken by British officials during the early stages of war on the arms of the Western Confederate Forces, nearly 70% were armed with smoothbore arms, such as the Model 1842 Springfield. Later in the war the same survey was taken, they found that more than 75% had acquired a rifle, mainly the Pattern 1853 Enfield.
The P53 Enfields capabilities were largely lost by the lack of marksmanship training by both the Union and Confederacy. Most soldiers were not trained to estimate ranges or to properly adjust their sights to account for the “rainbow-like” trajectory of the large calibre conical projectile. Unlike their British counterparts who attended extensive musketry training, new Civil War soldiers seldom fired a single cartridge until their first engagement. After the end of the war, hundreds of formerly Confederate Enfield 1853 muskets were sold from the American arms market to the Tokugawa shogunate, as well as some prominent Japanese domains including Aizu and Satsuma. These units were later used in the Boshin War, and some remaining in Satsuma were also used by rebelling former samurai in the Satsuma Rebellion about a decade later.
Prompt Shipping and Professional Packaging
We provide a variety of shipping options due to our long-running partnerships with UPS, FedEx and DHL. Our warehouse personnel are well trained and will pack the goods according to our exact and precise specifications. Before shipping your items will be thoroughly inspected and secured. Every day, we deliver to thousands of customers in different countries. This is a sign of our determination to become the largest online retailer worldwide. Both Europe as well as the USA have warehouses and distribution centers.
Note that orders containing more than one item will be subject to a processing period that is based to the particular item.
Prior to shipping the items, our staff will carry out an exhaustive inspection of the products you ordered. Today, most orders will be delivered within 48 hours. The estimated delivery time is between 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is constantly changing. It's not entirely managed by us since we are involved with multiple entities, including the factory and our storage. Therefore, the actual inventory could alter at any time. It is possible that you will not receive your order after the order has been made.
The period of time is 30 days. Unfortunately, if 30 days have passed since you purchased your product, we are unable to provide a refund or exchange.
The item must not be in use and must be in the original packaging. The item must be in the original packaging.
Related products
Uncategorized
Armored Burgonet Helmet & Polearm from Scottish Castle Leith Hall Circa 1700 Original Items
Uncategorized
Band of Brothers ORIGINAL GERMAN WWII Le. F.H. 18 10.5cm ARTILLERY PIECE Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Angolan Rebel 1970s era 60mm Inert Display Mortar from Angolan Civil War Original Items
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized